|
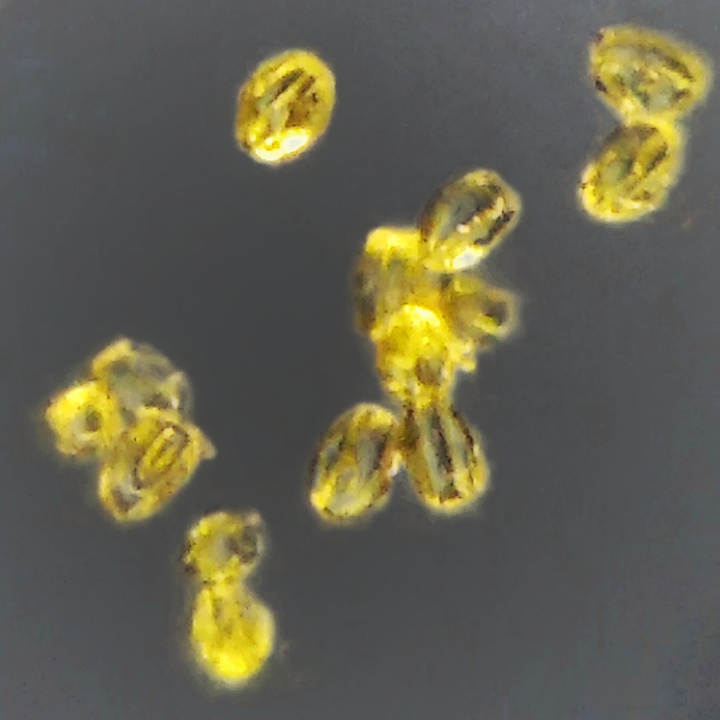
Phomopsis Azadirachtae
''Phomopsis azadirachtae'' is a fungus, a species of the genus ''Phomopsis''. It has been identified as the fungus responsible for dieback in ''Azadirachta indica'' (neem ''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus ''Azadirachta'', and is native to the Indian subcontinent and most of the countries in Afr ...) in India. The species was first identified and described by Sateesh et al in 1997.Girish, K.; Shankara Bhat, S. (2008). "''Phomopsis azadirachtae'' – The Die-Back of Neem Pathogen". ''Electronic Journal of Biology'' 4(3):112-119. References * Vedashree, S., Sateesh M.K., Chowdappa, P. and Nirmal Kumar, B. J. 2015. Species-specific PCR-based assay for identification and detection of ''Phomopsis (Diaporthe) azadirachtae'' causing die-back disease in ''Azadirachta indica''. Journal of Phytopathology. DOI: 10.1111/jph.12380 Further reading * * {{Taxonba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phomopsis
''Phomopsis'' is a genus of Ascomycota, ascomycete fungi in the family Valsaceae. Species Species include: * ''Phomopsis arnoldiae'' * ''Phomopsis asparagi'' * ''Phomopsis asparagicola'' * ''Phomopsis azadirachtae'' * ''Phomopsis cannabina'' * ''Phomopsis caricae-papayae'' * ''Phomopsis coffeae'' * ''Phomopsis durionis'' Hans Sydow, Syd. 1932 * ''Phomopsis elaeagni'' * ''Phomopsis ganjae'' * ''Phomopsis javanica'' * ''Phomopsis juniperovora'' * ''Phomopsis lokoyae'' * ''Phomopsis longicolla'' * ''Phomopsis mangiferae'' * ''Phomopsis obscurans'' * ''Phomopsis perseae'' * ''Phomopsis pittospori'' * ''Phomopsis prunorum'' * ''Phomopsis sojae'' * ''Phomopsis scabra'' * ''Phomopsis sclerotioides'' * ''Phomopsis tanakae'' * ''Phomopsis theae'' * ''Phomopsis viticola'' Formerly placed here: *''Phomopsis vaccinii'', now ''Diaporthe vaccinii'' *''Phomopsis leptostromiformis'', now ''Diaporthe toxica'' Dead-arm infection One of the species of this genus, ''Phomopsis viticola, P. viticola' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Dieback
Forest dieback (also "", a German loan word) is a condition in trees or woody plants in which peripheral parts are killed, either by pathogens, parasites or conditions like acid rain, drought, and more. These episodes can have disastrous consequences such as reduced resiliency of the ecosystem, disappearing important symbiotic relationships and thresholds. Some tipping points for major climate change forecast in the next century are directly related to forest diebacks. Definition Forest dieback refers to the phenomenon of a stand of trees losing health and dying without an obvious cause. This condition is also known as forest decline, forest damage, canopy level dieback, and stand level dieback. This usually affects individual species of trees, but can also affect multiple species. Dieback is an episodic event and may take on many locations and shapes. It can be along the perimeter, at specific elevations, or dispersed throughout the forest ecosystem. Forest dieback presents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azadirachta Indica
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus ''Azadirachta'', and is native to the Indian subcontinent and most of the countries in Africa. It is typically grown in tropical and semi-tropical regions. Neem trees also grow on islands in southern Iran. Its fruits and seeds are the source of neem oil. Description Neem is a fast-growing tree that can reach a height of , and rarely . It is deciduous, shedding many of its leaves during the dry winter months. The branches are wide and spreading. The fairly dense crown is roundish and may reach a diameter of . The neem tree is similar in appearance to its relative, the chinaberry (''Melia azedarach''). The opposite, pinnate leaves are long, with 20 to 30 medium to dark green leaflets about long. The terminal leaflet often is missing. The Petiole (botany), petioles are short. White and fragrant flowers are arranged in more-or- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neem
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus ''Azadirachta'', and is native to the Indian subcontinent and most of the countries in Africa. It is typically grown in tropical and semi-tropical regions. Neem trees also grow on islands in southern Iran. Its fruits and seeds are the source of neem oil. Description Neem is a fast-growing tree that can reach a height of , and rarely . It is deciduous, shedding many of its leaves during the dry winter months. The branches are wide and spreading. The fairly dense crown is roundish and may reach a diameter of . The neem tree is similar in appearance to its relative, the chinaberry (''Melia azedarach''). The opposite, pinnate leaves are long, with 20 to 30 medium to dark green leaflets about long. The terminal leaflet often is missing. The petioles are short. White and fragrant flowers are arranged in more-or-less drooping a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Tree Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |