|
Phoenix Mine (Botswana)
Phoenix Mine was an open-pit mining, open pit and underground mining (hard rock), underground mining operation in city of Phoenix, British Columbia, Phoenix in the Boundary Country region of British Columbia, Canada that operated in the early and mid 20th century, run by the Granby Consolidated Mining, Smelting and Power Company. It was discovered in 1891, but was a lower grade copper deposit than the Rossland, British Columbia, Rossland and Slocan, British Columbia, Slocan deposits. The low grade and the nearest railroad being resulted in the Phoenix (and other new deposits) receiving less attention. Discovery & development The first claims in the Phoenix area were staked by Henry White and Matthew Hatter (of the Old Ironsides claim) on July 15, 1891, they were granted in 1896. In 1896, J.F.C. Miner, a rubber footwear manufacturer from Granby, Quebec, mining promoter J.P. Graves of Knob Hill Mining Company and A.L. Little of Old Ironsides (company), Old Ironsides formed the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix, British Columbia
Phoenix is a ghost town in the Boundary Country of British Columbia, Canada, 11 km east of Greenwood. Once called the “highest city in Canada” by its citizens (1,412 metres / 4,633 feet above sea level) it was a booming copper mining community from the late 1890s until 1919. In its heyday it was home to 1,000 citizens and had an opera house, twenty hotels, a brewery and its own city hall. Phoenix’s magistrate, Judge Willie Williams, who served there from 1897 until 1913, became famous for his booming declaration, “I am the highest judge, in the highest court, in the highest city in Canada.” In 1911, Phoenix’s hockey team won the provincial championship and asked for the right to compete for the Stanley Cup, but it was too late to qualify. The Granby Consolidated Mining, Smelting and Power Company operated the Phoenix Mine, a copper mine that produced 13,678,901 tons of ore before operations ceased on June 14, 1919. Boom years Copper was discovered at Phoenix in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Forks, British Columbia
Grand Forks, population 4,112, is a city in the Boundary Country of the West Kootenay region of British Columbia, Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Granby and Kettle Rivers, a tributary of the Columbia River. The city is just north of the Canada–United States border, approximately from Vancouver and from Kelowna and west of the resort area of Christina Lake by road. History In 1894, a new settlement at the North Fork bridge, where the rivers join, was called Grand Forks. However, the valley, dominated by copper mining, was called Grand Prairie, and early settlers equally used that name for the town. The city was laid out in 1895 and Grand Forks was established as a city on 15 April 1897. The adjacent City of Columbia was incorporated on 4 May 1899. By 1902, Grand Forks had three railways, lumber mills, a smelter, mines, a post office, a school and a hospital. The railways servicing Grand Forks were the Canadian Pacific Railway's (CP) Columbia and Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Mines In British Columbia
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 350 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mines In British Columbia
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging * Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mines In British Columbia ...
This is an incomplete list of mines in British Columbia, Canada and includes operating and closed mines, as well as proposed mines at an advanced stage of development (e.g. mining permits applied for). Mines that are in operation are in bold. Past producers which are under re-exploitation, re-development and/or re-promotion are in ''italics''. Also in italics are major projects under development or subject to controversy. See also *List of ghost towns in British Columbia References {{Canada topic, List of mines in * Mines British Columbia British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Shovel
A steam shovel is a large steam-powered excavating machine designed for lifting and moving material such as rock and soil. It is the earliest type of power shovel or excavator. Steam shovels played a major role in public works in the 19th and early 20th century, being key to the construction of railroads and the Panama Canal. The development of simpler, cheaper diesel-powered shovels caused steam shovels to fall out of favor in the 1930s. History Origins and development Grimshaw of Boulton & Watt devised the first steam-powered excavator in 1796. In 1833 William Brunton patented another steam-powered excavator which he provided further details on in 1836. The steam shovel was invented by William Otis, who received a patent for his design in 1839. The first machines were known as 'partial-swing', since the boom could not rotate through 360 degrees. They were built on a railway chassis, on which the boiler and movement engines were mounted. The shovel arm and driving engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mechanics
Rock mechanics is a theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rock and rock masses; compared to geology, it is that branch of mechanics concerned with the response of rock and rock masses to the force fields of their physical environment. 

[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoping (mining Method)
Stoping is the process of extracting the desired ore or other mineral from an underground mine, leaving behind an open space known as a stope. Stoping is used when the country rock is sufficiently strong not to collapse into the stope, although in most cases artificial support is also provided. The earliest forms of stoping were conducted with hand tools or by fire-setting; later gunpowder was introduced. From the 19th century onward, various other explosives, power-tools, and machines came into use. As mining progresses the stope is often backfilled with tailings, or when needed for strength, a mixture of tailings and cement. In old mines, stopes frequently collapse at a later time, leaving craters at the surface. They are an unexpected danger when records of underground mining have been lost with the passage of time. Stoping is considered "productive work", and is contrasted with "deadwork", the work required merely to access the mineral deposit, such as sinking shafts and winz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Set
Philip Deidesheimer was a mining engineer in the Western United States. Deidesheimer was born in 1832, in Darmstadt, Hesse before German unification. He attended the prestigious Freiberg University of Mining (''Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg'') and emigrated to California in 1852. He died on 21 July 1916 in San Francisco, California. Career In 1852, at nineteen, the young mining engineer traveled to the California gold fields to work for several years, including in Georgetown. In April 1860 he was hired by W. F. Babcock, a trustee of the Ophir Mine, part of the Comstock Lode silver mining boom in Nevada, and solved one of the Comstock mines' most critical engineering needs. Comstock Lode Square set timbering Deidesheimer invented a system, now known as square set timbering, using heavy timber "cubes" as supports for underground mining tunnels and shafts, that enabled skilled miners to open three-dimensional cavities of any size. In large openings, the cubes cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
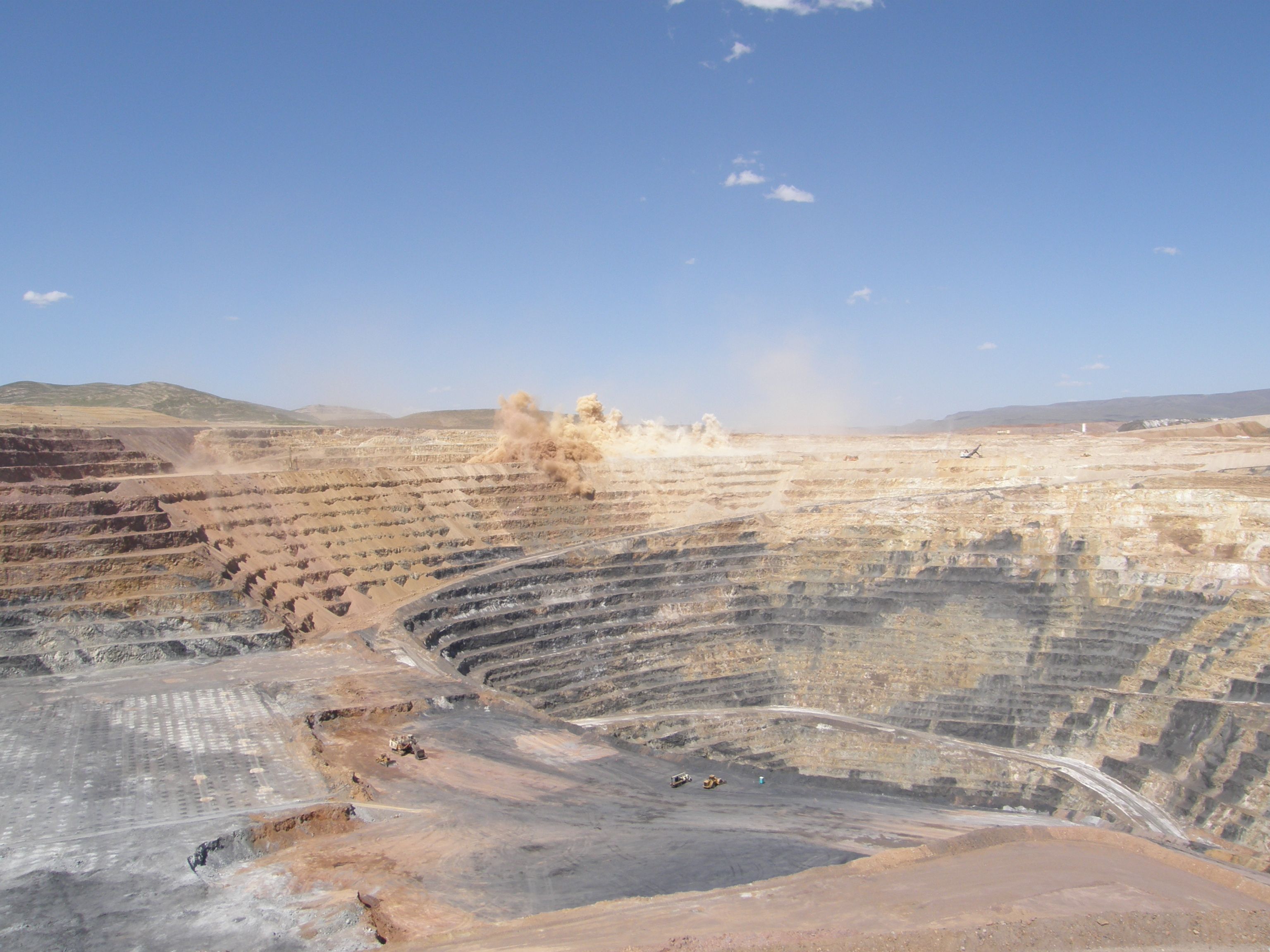
Open-pit Mining
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow. This form of mining differs from extractive methods that require tunnelling into the earth, such as long wall mining. Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or rocks are found near the surface. It is applied to ore or rocks found at the surface because the overburden is relatively thin or the material of interest is structurally unsuitable for tunnelling (as would be the case for cinder, sand, and gravel). In contrast, minerals that have been found underground but are difficult to retrieve due to hard rock, can be reached using a form of underground mining. To create an open-pit mine, the miners must determine the information of the ore that is underground. This is done through drilling of probe holes in the ground, then plotting ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
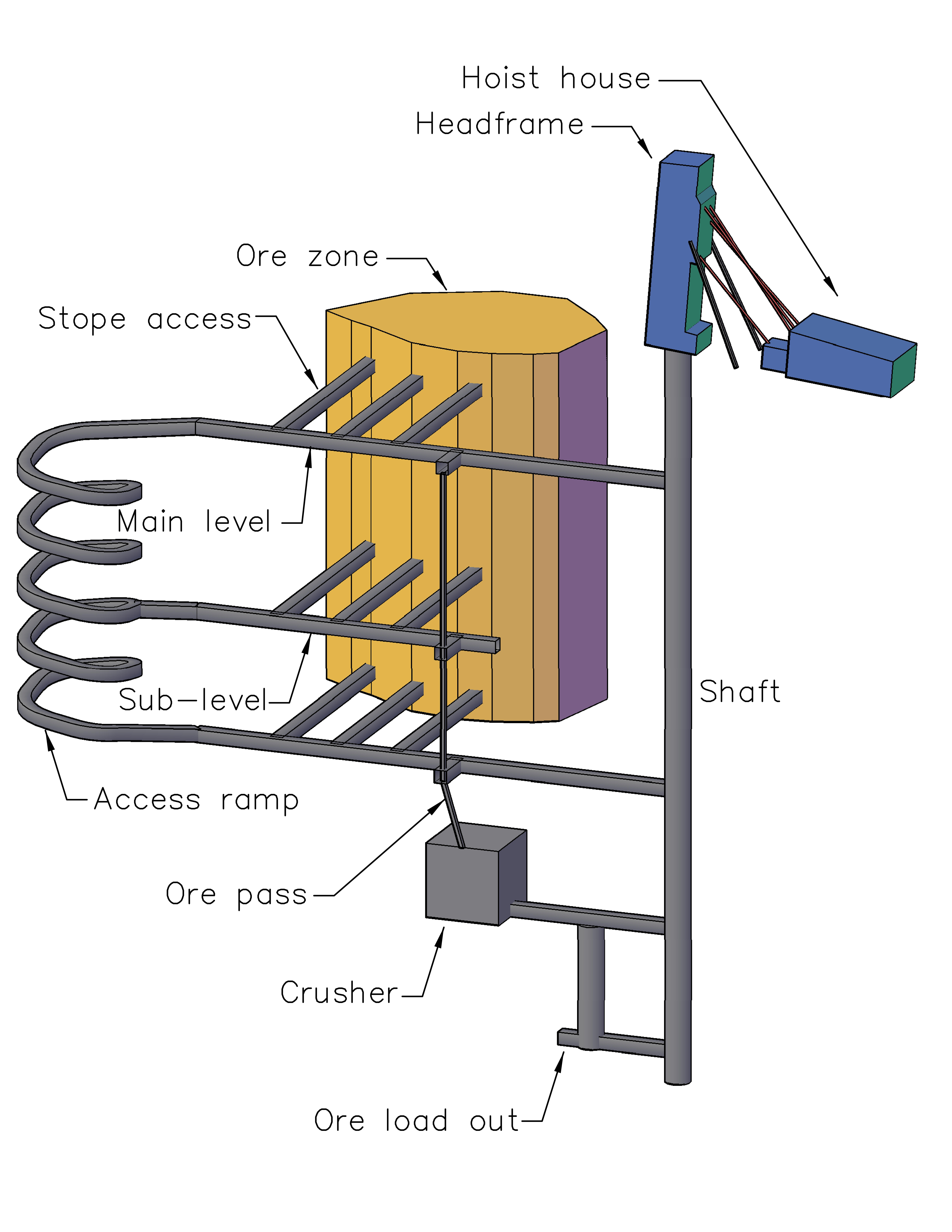
Underground Mining (hard Rock)
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shafts are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |