|
Philippe Verdelot
Philippe Verdelot (1480 to 1485–1530 to 1540) was a French composer of the Renaissance, who spent most of his life in Italy. He is commonly considered to be the father of the Italian madrigal, and certainly was one of its earliest and most prolific composers; in addition he was prominent in the musical life of Florence during the period after the recapture of the city by the Medici from the followers of Girolamo Savonarola. Life Verdelot was born in Les Loges, Seine-et-Marne, France. Details of his early life are obscure. He probably came to Italy at an early age, spending the first decade or two of the 16th century at some cities in northern Italy, most likely including Venice. A painting of 1511, described by Vasari but never positively identified, is believed by many musicologists to show Verdelot in Venice with an Italian singer. Verdelot is known to have been ''maestro di cappella '' at the Baptisterium San Giovanni in Florence from 1523 to 1525; and he seems also to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Cappella
''A cappella'' (, also , ; ) music is a performance by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment, or a piece intended to be performed in this way. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Renaissance polyphony and Baroque concertato musical styles. In the 19th century, a renewed interest in Renaissance polyphony, coupled with an ignorance of the fact that vocal parts were often doubled by instrumentalists, led to the term coming to mean unaccompanied vocal music. The term is also used, rarely, as a synonym for ''alla breve''. Early history A cappella could be as old as humanity itself. Research suggests that singing and vocables may have been what early humans used to communicate before the invention of language. The earliest piece of sheet music is thought to have originated from times as early as 2000 B.C. while the earliest that has survived in its entirety is from the first century A.D.: a piece from Greece called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
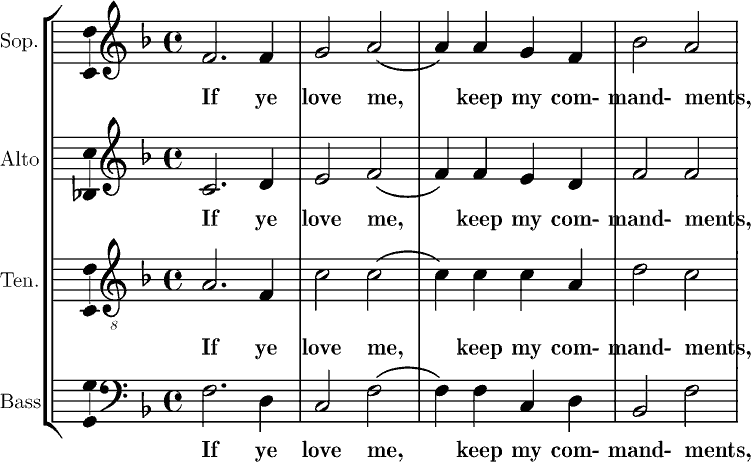
Madrigal Composers
A madrigal is a form of secular vocal music most typical of the Renaissance (15th–16th c.) and early Baroque (1600–1750) periods, although revisited by some later European composers. The polyphonic madrigal is unaccompanied, and the number of voices varies from two to eight, but usually features three to six voices, whilst the metre of the madrigal varies between two or three tercets, followed by one or two couplets. Unlike the verse-repeating strophic forms sung to the same music, most madrigals are through-composed, featuring different music for each stanza of lyrics, whereby the composer expresses the emotions contained in each line and in single words of the poem being sung. As written by Italianized Franco–Flemish composers in the 1520s, the madrigal partly originated from the three-to-four voice frottola (1470–1530); partly from composers' renewed interest in poetry written in vernacular Italian; partly from the stylistic influence of the French chanson; and fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Male Classical Composers
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Classical Composers
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1530s Deaths
Year 153 ( CLIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rusticus and Rufinus (or, less frequently, year 906 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 153 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Minor uprisings occur in Roman Egypt against Roman rule. Asia * Change of era name from ''Yuanjia'' (3rd year) to ''Yongxing'' of the Chinese Han Dynasty. Births * Didia Clara, daughter of Didius Julianus * Kong Rong, Chinese official and warlord (d. 208) * Zhang Hong, Chinese official and politician (d. 212 Year 212 ( CCXII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asper and Camilius (or, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1480s Births
148 may refer to: * 148 (number), a natural number *AD 148, a year in the 2nd century AD * 148 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC * 148 (album), an album by C418 Daniel Rosenfeld (born 9 May 1989), better known by his stage/online name C418 (pronounced "see four eighteen"), is a German musician, producer and sound engineer, best known as the composer and sound designer for the sandbox video game ''Minec ... * 148 (Meiktila) Battery Royal Artillery * 148 (New Jersey bus) See also * List of highways numbered 148 * {{Number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan McClary
Susan Kaye McClary (born October 2, 1946) is an American musicologist associated with " new musicology". Noted for her work combining musicology with feminist music criticism, McClary is professor of musicology at Case Western Reserve University. Early life and education McClary was born in St. Louis, Missouri, and received her BA in 1968 from Southern Illinois University. She attended graduate school at Harvard University where she received her MA in 1971 and her PhD in 1976. Her doctoral dissertation was on the transition from modal to tonal organization in Monteverdi's works. The first half of her dissertation was later reworked and expanded in her 2004 book, ''Modal Subjectivities: Self-fashioning in the Italian Madrigal''. She taught at the University of Minnesota (1977–1991), McGill University (1991–1994), University of California, Berkeley (1993), and University of California, Los Angeles (1994–2011), before becoming a Professor of Musicology at Case Western Reserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustave Reese
Gustave Reese ( ; 29 November 1899 – 7 September 1977) was an American musicologist and teacher. Reese is known mainly for his work on medieval and Renaissance music, particularly with his two publications ''Music in the Middle Ages'' (1940) and ''Music in the Renaissance'' (1954); these two books remain the standard reference works for these two eras, with complete and precise bibliographical material, allowing for almost every piece of music mentioned to be traced back to a primary source. Early life and education Reese was born in New York City on 29 November 1899. He was an avid scholar and had interests in many areas outside music, including art, architecture, and literature. He studied law at New York University, graduating in 1921. Though he was admitted to the New York State Bar, he opted to re-enroll and pursue a Bachelor of Music from NYU, which he received in 1930. Career In 1927, however, he was already teaching classes at the university in medieval and Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word-painting
Word painting, also known as tone painting or text painting, is the musical technique of composing music that reflects the literal meaning of a song's lyrics or story elements in programmatic music. Historical development Tone painting of words goes at least as far back as Gregorian chant. Musical patterns expressed both emotive ideas and theological meanings in these chants. For instance, the pattern ''fa-mi-sol-la'' signifies the humiliation and death of Christ and his resurrection into glory. ''Fa-mi'' signifies deprecation, while ''sol'' is the note of the resurrection, and ''la'' is above the resurrection, His heavenly glory ("''surrexit Jesus''"). Such musical words are placed on words from the Biblical Latin text; for instance when ''fa-mi-sol-la'' is placed on "''et libera''" (e.g., introit for Sexagesima Sunday) in the Christian faith it signifies that Christ liberates us from sin through his death and resurrection. Word painting developed especially in the late 16th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh out the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was generally believed the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |