|
Philip Beachy
Philip Arden Beachy (born October 25, 1958) is Ernest and Amelia Gallo Professor at Stanford University School of Medicine in Palo Alto, California and an Associate at Stanford's Institute of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Early life Beachy was born in Red Lake, Ontario, on October 25, 1958. Beachy spent eight of his early years of life in the hills of central Puerto Rico. His father was a pastor of a rural church. He attended a school taught in Spanish during the day and then learned to read and write English once he came home from school. At nine, Beachy and his family returned to their home base of Goshen, Indiana where he began attending public school. At the early age of 16, Beachy headed off to Goshen College which was very close to home. At this time, Beachy still did not know of his love for science. “Unlike many people who knew they were going to be scientists from a very early age, I didn't decide that I would try to become a scientist until fairly l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Lake, Ontario
Red Lake is a municipality with town status in the Canadian province of Ontario, located northwest of Thunder Bay and less than from the Manitoba border. The municipality consists of six small communities—Balmertown, Cochenour, Madsen, McKenzie Island, Red Lake and Starratt-Olsen—and had a population of 4,107 people in the Canada 2016 Census. Red Lake is an enclave within Unorganized Kenora District. The municipality was formed on 1 July 1998, when the former incorporated townships of Golden and Red Lake were merged along with a small portion of Unorganized Kenora District. The name of the town comes from a local legend telling of two men from the Chippewa tribe who stumbled across a large moose. The men proceeded to kill the moose, the blood of which drained into a nearby lake. The blood turned the lake's waters red in colour, ultimately giving the area its name. The name appears on the Bouchette map of 1875, and was officially approved on 7 December 1909. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
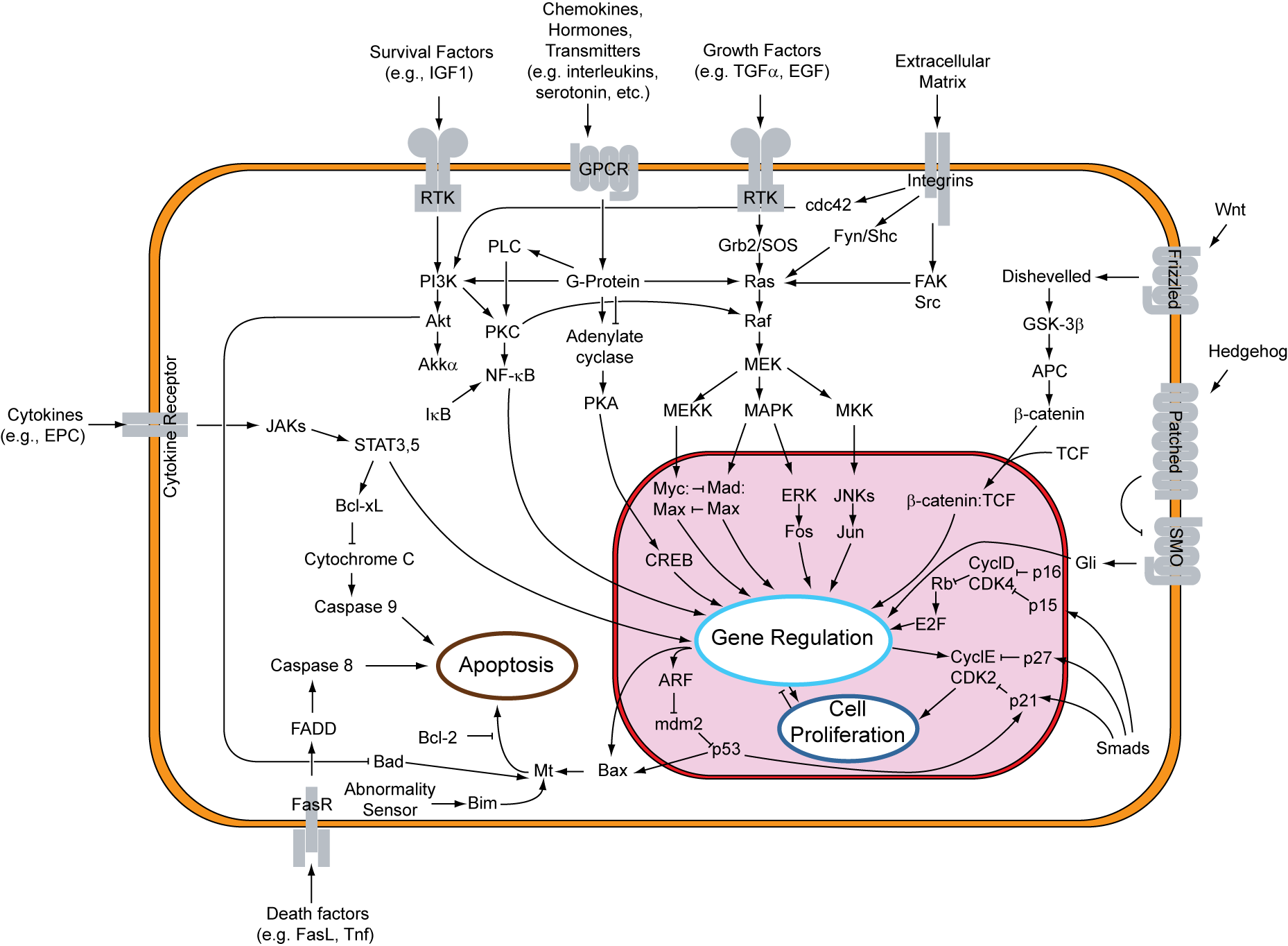
Signal Transduction V1
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
