|
Phenuiviridae
''Phenuiviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Bunyavirales''. Ruminants, camels, humans, and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Member genus ''Phlebovirus'' is the only genus of the family that has viruses that cause disease in humans (e.g. Rift Valley fever virus) except Dabie bandavirus. Virology Structure Members of ''Phenuiviridae are'' enveloped viruses with helical capsid morphology. Envelope glycoproteins of these viruses are distributed with icosahedral symmetry (T=12). Genome ''Phenuiviridae'' is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus family. Its genome is segmented into three pieces: L segment (encoding RNA-dependent RNA polymerase), M segment, and S segment. Some members of the family have ambisense gene encoding on the S segment ( nucleocapsid proteins). The M segment includes envelope glycoproteins encoded in a polyprotein that is cleaved by host proteases. Multiple different proteins can be encoded on the M segment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyavirales
''Bunyavirales'' is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class ''Ellioviricetes''. The name ''Bunyavirales'' derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species ''Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus'' was first discovered. ''Ellioviricetes'' is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses. Bunyaviruses belong to the fifth group of the Baltimore classification system, which includes viruses with a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. They have an enveloped, spherical virion. Though generally found in arthropods or rodents, certain viruses in this order occasionally infect humans. Some of them also infect plants. In addition, there is a group of bunyaviruses whose replication is restricted to arthropods and is known as insect-specific bunyaviruses. A majority of bunyaviruses are vector-borne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Snatching
The first step of transcription for some negative, single-stranded RNA viruses is cap snatching, in which the first 10 to 20 residues of a host cell RNA are removed (snatched) and used as the 5′ cap and primer to initiate the synthesis of the nascent viral mRNA. The viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) can then proceed to replicate the negative-sense genome from the positive-sense template. Cap-snatching also explains why some viral mRNA have 5’ terminal extensions of 10-20 nucleotides that are not encoded for in the genome. Examples of viruses that engage in cap-snatching include influenza viruses ('' Orthomyxoviridae''), Lassa virus ('' Arenaviridae''), hantaan virus (''Hantaviridae'') and rift valley fever virus (''Phenuiviridae''). Most viruses snatch 15-20 nucleotides except for the families ''Arenaviridae'' and ''Nairoviridae'' and the genus Thogotovirus (''Orthomyxoviridae'') which use a shorter strand. In the influenza virus, cap snatching occurs in the nucleus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative-strand RNA Virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented. Negative-strand RNA viruses constitute the phylum ''Negarnaviricota'', in the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are descended from a common ancestor that was a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus, and they are considered to be a sister clade of reovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dabie Bandavirus
''Dabie bandavirus'', also called SFTS virus, is a tick-borne virus in the genus '' Bandavirus'' in the family ''Phenuiviridae'', order '' Bunyavirales''. The clinical condition it caused is known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). SFTS is an emerging infectious disease that was first described in northeast and central China 2009 and now has also been discovered in Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Taiwan in 2015. SFTS has a fatality rate of 12% and as high as over 30% in some areas. The major clinical symptoms of SFTS are fever, vomiting, diarrhea, multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), leukopenia (low white blood cell count) and elevated liver enzyme levels. Another outbreak occurred in East China in the early half of 2020. History In 2009, Xue-jie Yu and colleagues isolated the SFTS virus (SFTSV) from SFTS patients’ blood. Genome The genome has been sequenced. There are three segments—large (L), medium (M) and small (S). Five pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription (biology), transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus (cell), nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, mRNA, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the Cell (biology), cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of Base pair, complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Ribozyme
The hairpin ribozyme is a small section of RNA that can act as a ribozyme. Like the hammerhead ribozyme it is found in RNA satellites of plant viruses. It was first identified in the minus strand of the tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA where it catalyzes self-cleavage and joining (ligation) reactions to process the products of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. The hairpin ribozyme is similar to the hammerhead ribozyme in that it does not require a metal ion for the reaction. Biological function The hairpin ribozyme is an RNA motif that catalyzes RNA processing reactions essential for replication of the satellite RNA molecules in which it is embedded. These reactions are self-processing, i.e. a molecule rearranging its own structure. Both cleavage and end joining reactions are mediated by the ribozyme motif, leading to a mixture of interconvertible linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. These reactions are imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift Valley Fever Virus
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to the point of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
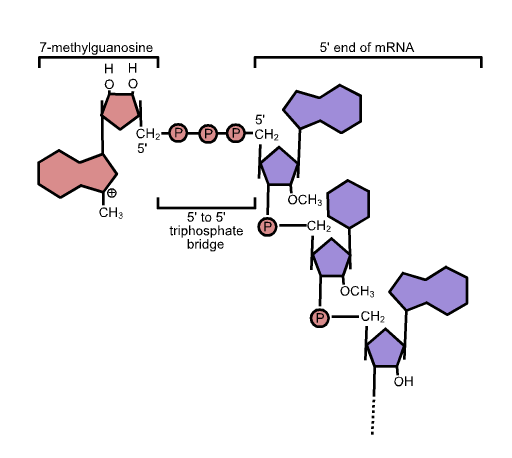
Five-prime Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |