|
Pheidippides
Pheidippides ( grc-gre, Φειδιππίδης, , ; "Son of Pheídippos") or Philippides (Φιλιππίδης) is the central figure in the story that inspired a modern sporting event, the marathon race. Pheidippides is said to have run from Marathon to Athens to deliver news of the victory of the battle of Marathon. The first recorded account showing a courier running from Marathon to Athens to announce victory is from within Lucian's prose on the first use of the word "joy" as a greeting in ''A Slip of the Tongue in Greeting'' (2nd century AD). The traditional story relates that Pheidippides (530–490 BC), an Athenian herald, or ''hemerodrome'' (translated as "day-runner", "courier", "professional-running courier" or "day-long runner"), was sent to Sparta to request help when the Persians landed at Marathon, Greece. He ran about in two days, and then ran back. He then ran the to the battlefield near Marathon and back to Athens to announce the Greek vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phidippides
Pheidippides ( grc-gre, Φειδιππίδης, , ; "Son of Pheídippos") or Philippides (Φιλιππίδης) is the central figure in the story that inspired a modern sporting event, the marathon race. Pheidippides is said to have run from Marathon to Athens to deliver news of the victory of the battle of Marathon. The first recorded account showing a courier running from Marathon to Athens to announce victory is from within Lucian's prose on the first use of the word "joy" as a greeting in ''A Slip of the Tongue in Greeting'' (2nd century AD). The traditional story relates that Pheidippides (530–490 BC), an Athenian herald, or ''hemerodrome'' (translated as "day-runner", "courier", "professional-running courier" or "day-long runner"), was sent to Sparta to request help when the Persians landed at Marathon, Greece. He ran about in two days, and then ran back. He then ran the to the battlefield near Marathon and back to Athens Athens ( ; el, Αθή� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. The Greek army inflicted a crushing defeat on the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars. The first Persian invasion was a response to Athenian involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius had his bow brought to him and then shot an arrow "upwards towards heaven", saying as he did so: "Zeus, that it may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. The Greek army inflicted a crushing defeat on the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars. The first Persian invasion was a response to Athenian involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius had his bow brought to him and then shot an arrow "upwards towards heaven", saying as he did so: "Zeus, that it may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathon Race
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road running, road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair divisions. More than 800 marathons are held throughout the world each year, with the vast majority of competitors being recreational athletes, as larger marathons can have tens of thousands of participants. The marathon was one of the original modern Olympic Games, Olympic events in 1896. The distance did not become standardized until 1921. The distance is also included in the World Athletics Championships, which began in 1983. It is the only running road race included in both championship competitions (walking races on the roads are also contested in both). History Origin The name ''Marathon'' comes from the legend of Philippides (or Pheidippides), the Greek messenger. The legend states that, while he was taking part in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartathlon
Spartathlon is a ultramarathon race held annually in Greece since 1983, between Athens and Sparti, the modern town on the site of ancient Sparta. The Spartathlon is based on the run of Pheidippides, who ran from Athens to Sparta before the Battle of Marathon in a day and a half to seek aid against the Persians. Five Royal Air Force officers attempted the course in 1982 and the competition was started the next year. The winner of the first Spartathlon, Yiannis Kouros, still holds the record for fastest time at 20 hours and 25 minutes. As the race grew more popular, stringent entry criteria were implemented to ensure participants were fit enough to run the course. The race has 75 checkpoints where race officials disqualify runners who fail to meet time cutoffs or who are too tired to continue. Origin The Spartathlon aims to trace the footsteps of Pheidippides, an Athenian messenger sent to Sparta in 490 BC to seek help against the Persians in the Battle of Marathon. Pheidippid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathon, Greece
Marathon (Demotic Greek: Μαραθώνας, ''Marathónas''; Attic/Katharevousa: , ''Marathṓn'') is a town in Greece and the site of the Battle of Marathon in 490 BCE, in which the heavily outnumbered Athenian army defeated the Persians. Legend has it that Pheidippides, a Greek herald at the battle, was sent running from Marathon to Athens to announce the victory, which is how the marathon running race was conceived in modern times. Today it is part of East Attica regional unit, in the outskirts of Athens and a popular resort town and center of agriculture. History The name "Marathon" () comes from the herb fennel, called ''marathon'' () or ''marathos'' () in Ancient Greek,. so ''Marathon'' literally means "a place full of fennel".. It is believed that the town was originally named so because of an abundance of fennel plants in the area. In ancient times, Marathon ( grc, Μαραθών) occupied a small plain in the northeast of ancient Attica, which contained four place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Parthenium
Mount Parthenion ( grc, τὸ Παρθένιον ὄρος) or Parthenius or Parthenium) ("Mount of the Virgin", modern el, Παρθένιο - ''Parthenio'') is a mountain on the border of Arcadia and Argolis, in the Peloponnese, Greece. Its elevation is 1,215 m. It is situated between the villages Achladokampos to the northeast and Partheni to the southwest. It is 16 km east of Tripoli. In antiquity, it divided the little plain of Hysiae from that of Tegea. Mount Parthenion is the mountain where the hero Telephus was exposed. Below its slopes lay Tegea. Pan appeared to Philippides on Mt. Parthenion above Tegea, before the battle of Marathon in 490 BCE. The god called out his name and ordered Philippides ask the Athenians why they paid no honors to him, even though he was well-intentioned toward them, had been helpful to them many times in the past and would be so again in the future. As a result, the Athenians established an altar to Pan at the foot of the Parthenon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histories (Herodotus)
The ''Histories'' ( el, Ἱστορίαι, ; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Written around 430 BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, ''The Histories'' serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that were known in Greece, Western Asia and Northern Africa at that time. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicles beforehand). ''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Persian Empire, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars between the Persian Empire and the Greek city-states in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegea
Tegea (; el, Τεγέα) was a settlement in ancient Arcadia, and it is also a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the Tripoli municipality, of which it is a municipal unit with an area of 118.350 km2. It is near the modern villages of Alea and Episkopi. The legendary founder of Tegea was Tegeates, a son of Lycaon. History Tegea ( grc, Τεγέα; grc-x-ionic, Τεγέη) was one of the most ancient and powerful towns of ancient Arcadia, situated in the southeast of the country. Its territory, called Tegeatis (Τεγεᾶτις), was bounded by Cynuria and Argolis on the east, from which it was separated by Mount Parthenium, by Laconia on the south, by the Arcadian district of Maenalia on the west, and by the territory of Mantineia on the north. The Tegeatae are said to have derived their name from Tegeates, a son of Lycaon, and to have dwelt originally in eight, afterwards nine, demoi or townships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
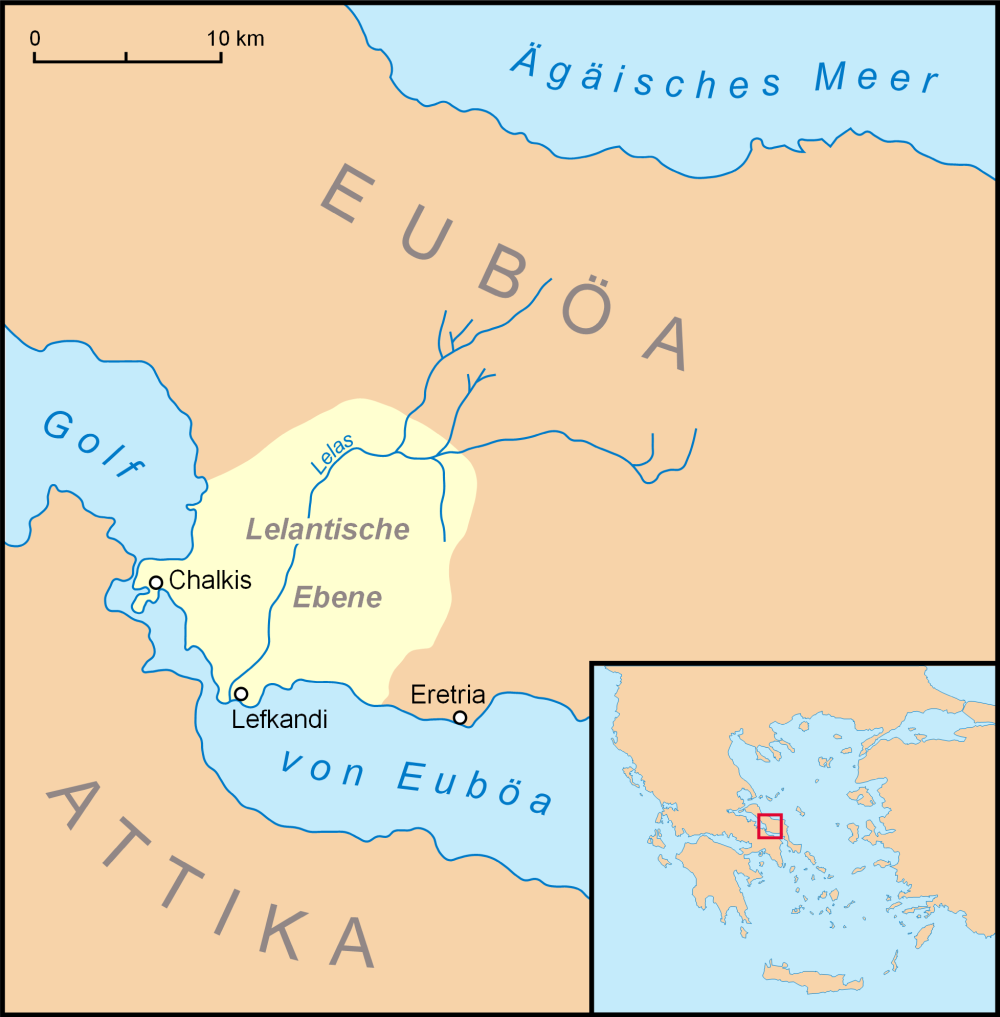
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peisistratos (Athens)
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece containing Athens, along with economic and cultural improvements laid the groundwork for the later preeminence of Athens in ancient Greece. His legacy lies primarily in his institution of the Panathenaic Games, historically assigned the date of 566 BC, and the consequent first attempt at producing a definitive version of the Homeric epics. Peisistratos' championing of the lower class of Athens is an early example of populism. While in power, he did not hesitate to confront the aristocracy and greatly reduce their privileges, confiscating their lands and giving them to the poor. Peisistratos funded many religious and artistic programs, in order to improve the economy and spread the wealth more equally among the Athenian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippias (tyrant)
Hippias ( grc-gre, Ἱππίας; c. 570 BC – 490 BC) was the last tyrant of Athens, ruling from 527 to 510 BC. He was one of a group of tyrants known as the Peisistratids, which was a group of three tyrants in Ancient Greece. Pisistratus first, and then his son, Hippias, followed after him by Hippias' illegitimate son, Hegesistratos. He was deposed when Cleomenes I of Sparta successfully invaded Athens and forced him to flee to Persia. Early life Hippias was born around 570 BC as the eldest son of Pisistratus, the first tyrant of Athens. When his father was forced to flee to Eretria after insulting Megakles by having intercourse with his daughter in an indecent way, Peisistratos held counsel with his sons. Hippias suggested that they should retake the tyranny, which his father agreed to. Preparations began for which Athens fell to Peisistratos for the third time in 546 BC. Tyrant of Athens Hippias succeeded Peisistratos as tyrant of Athens in 528/7 BC when his father d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |