|
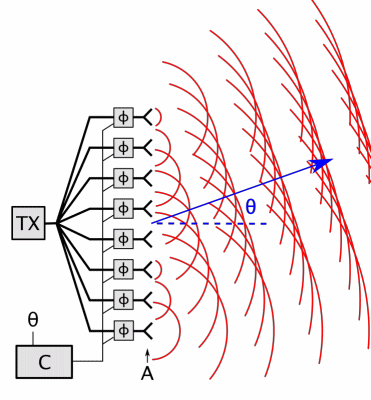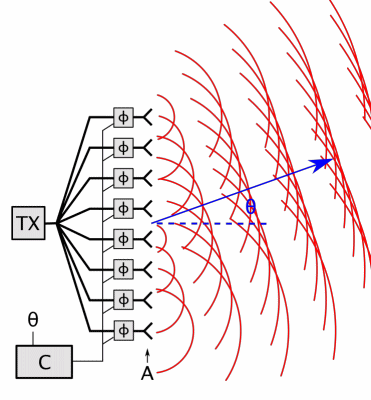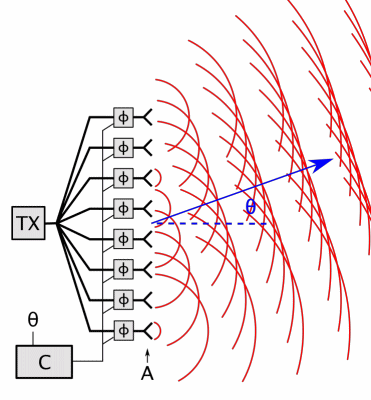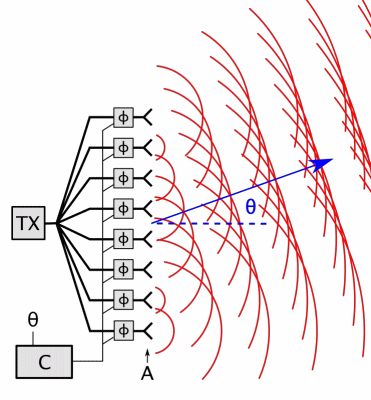
Phased-array Radar
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phased Array Animation With Arrow 10frames 371x400px 100ms
A phaser is an electronic sound processor used to filter a signal, and it has a series of troughs in its frequency-attenutation graph. The position (in Hz) of the peaks and troughs are typically modulated by an internal low-frequency oscillator so that they vary over time, creating a sweeping effect. Phasers are often used to give a "synthesized" or electronic effect to natural sounds, such as human speech. The voice of C-3PO from ''Star Wars'' was created by taking the actor's voice and treating it with a phaser. Process The electronic phasing effect is created by splitting an audio signal into two paths. One path treats the signal with an all-pass filter, which preserves the amplitude of the original signal and alters the phase. The amount of change in phase depends on the frequency. When signals from the two paths are mixed, the frequencies that are out of phase will cancel each other out, creating the phaser's characteristic notches. Changing the mix ratio changes the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound Imaging
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammut Hoarding Radar Illustration
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of the Pleistocene 10,000 to 11,000 years ago. They lived in herds and were predominantly forest-dwelling animals. They generally had a browsing diet, distinct from that of the contemporary Columbian mammoth, which tended towards grazing. ''M. americanum'', the American mastodon, and ''M. pacificus'', the Pacific mastodon, are the youngest and best-known species of the genus. Mastodons disappeared from North America as part of a mass extinction of most of the Pleistocene megafauna, widely believed to have been caused by a combination of climate changes at the end of the Pleistocene and overexploitation by Paleo-Indians. History A Dutch tenant farmer found the first recorded remnant of ''Mammut'', a tooth some in weight, in the village of Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAVE PAWS&BMEWS
PAVE is a United States Air Force program identifier relating to electronic systems. Prior to 1979, Pave was said to be a code word for the Air Force unit responsible for the project. ''Pave'' was used as an inconsequential prefix identifier for a wide range of different programs, though backronyms and alternative meanings have been used. For example, in the helicopters Pave Low and Pave Hawk it was said to mean ''Precision Avionics Vectoring Equipment'', but in Pave Paws it was said to mean ''Precision Acquisition Vehicle Entry''. PAVE systems * Pave Eagle – Modified Beechcraft Bonanza drone aircraft for low altitude sensor monitoring. * Pave Hawk – Sikorsky HH-60 Pave Hawk special operations and combat search and rescue helicopter. * Pave Nail - OV-10 Bronco with Pave Spot target laser designator pod. * Pave Knife – Ford Aerospace AN/AVQ-10 Pave Knife early laser targeting pod. * Pave Low – Sikorsky MH-53 Pave Low special ops and combat search and rescue helicop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAVE PAWS
PAVE PAWS (PAVE Phased Array Warning System) is a complex Cold War early warning radar and computer system developed in 1980 to "detect and characterize a sea-launched ballistic missile attack against the United States". With the first solid-state phased array deployed, the system used a pair of Raytheon AN/FPS-115 phased array radar sets at each site to cover a wide azimuth angle of 240 degrees. Two sites were deployed in 1980 at the periphery of the contiguous United States, then two more in 1987–95, as part of the United States Space Surveillance Network. One system was sold to Taiwan and is still in service. Mission The radar was built in the Cold War to give early warning of a nuclear attack, to allow time for US bombers to get off the ground and land-based US missiles to be launched, to decrease the chance that a preemptive strike could destroy US strategic nuclear forces. The deployment of submarine launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) by the Soviet Union by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braun Phased Array Antenna 1905
Braun is a common surname, originating from the German word for the color brown. The name is the 22nd most common family name in Germany. Many German emigrants to the United States also changed their name to ''Brown'' (''see Brown (surname)''). In German, ''Braun'' is pronounced , except for the "r" equal to the English word "brown". In English, it is often pronounced as "brawn", as in 'Carol Moseley Braun'. Pronunciation is an individual preference and is hard to guess unless one is in a position to hear the person's name spoken. As forename: * Braun Strowman (formerly Braun Stowman), ring name of American professional wrestler Adam Scherr (born 1983) As surname: * Alexander Braun (1805–1877), German botanist * Anna Maria Braun (born 3 July 1979), German business executive and lawyer * Annette Frances Braun (1884–1978), American entomologist * Arthur Michael Braun (1910–1989), American politician and businessman * Ben Braun (born 1953), American college basketball coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformal Antenna , in cartography
{{disambig ...
Conformal may refer to: * Conformal (software), in ASIC Software * Conformal coating in electronics * Conformal cooling channel, in injection or blow moulding * Conformal field theory in physics, such as: ** Boundary conformal field theory ** Coset conformal field theory ** Logarithmic conformal field theory ** Rational conformal field theory * Conformal fuel tanks on military aircraft * Conformal hypergraph, in mathematics * Conformal geometry, in mathematics * Conformal group, in mathematics * Conformal map, in mathematics * Conformal map projection In cartography, a conformal map projection is one in which every angle between two curves that cross each other on Earth (a sphere or an ellipsoid) is preserved in the image of the projection, i.e. the projection is a conformal map in the mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Electronically Scanned Array
An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled array antenna in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna. In the AESA, each antenna element is connected to a small solid-state transmit/receive module (TRM) under the control of a computer, which performs the functions of a transmitter and/or receiver for the antenna. This contrasts with a passive electronically scanned array (PESA), in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver through phase shifters under the control of the computer. AESA's main use is in radar, and these are known as active phased array radar (APAR). The AESA is a more advanced, sophisticated, second-generation of the original PESA phased array technology. PESAs can only emit a single beam of radio waves at a single frequency at a time. The PESA must utilize a Butler matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves (electromagnetic waves of radio frequency) and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation. Radio receivers are essential components of all systems that use radio. The information produced by the receiver may be in the form of sound, video (television), or digital data. A radio receiver may be a separate piece of electronic equipment, or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Radiator
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to: Engineering * Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship * Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag * Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires * Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship * Radio masts and towers , towers that carry antennas * The primary support for a helicopter rotor * The main vertical structure of a forklift truck * Multi-axis shaker table, an automotive test system * Model for assessment of telemedicine, used to assess long-distance medical treatment Biology * Mast (botany), the edible parts of woody plants * Mast Arboretum, at Stephen F. Austin State University in Nacogdoches, Texas * Mast cell, involved in the allergy response * Mast., in botanical naming, the standard author abbreviation for Maxwell T. Masters * Two microtubule-associated serine/threonine-protein kinase enzymes: ** MAST1, an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAST1'' gene ** MAST2, an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAST ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |