|
Pharnabazus I
Pharnabazus (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', Ancient Greek: ''Φαρνάβαζος''; died before 430 BCE), was a member of the Pharnacid dynasty that governed the province of Hellespontine Phrygia as satraps for the Achaemenid Empire. He is a very obscure figure, almost always mentioned alongside his father Artabazus. He may have succeeded his father as satrap between 455 and 430 BCE, but it is also possible that Artabazus was directly succeeded by his grandson (Pharnabazus' son), Pharnaces II Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithridat .... References Year of birth unknown 430s BC deaths Achaemenid satraps of Hellespontine Phrygia 5th-century BC Iranian people Pharnacid dynasty {{AncientNearEast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Iranian
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian plateau, Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE–900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly-attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Avestan, Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian language, Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian language, Bactrian (from the Kushan Empire, Kushan and Hephthalites, Hephthalite empires). , there were an estimated 150–200 million native speakers of the Iranian languages. ''Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group, with the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnacid Dynasty
The Pharnacid dynasty was a Persian dynasty that ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty from the 5th until the 4th century BCE. It was founded by Artabazus, son of satrap Pharnaces I (younger brother of Hystaspes, who was born shortly before 565 BCE), son of Arsames (died ca. 520 BCE). They were directly related to the Achaemenid dynasty itself. The last member of the dynasty was Pharnabazus III. Before the Pharnacids, Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BCE) had ruled Hellespontine Phrygia for Cyrus the Great and Cambyses II, before being killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, Mitrobates was succeeded by Oebares II (c.493), son of Megabazus, before Artabazus became satrap circa 479 BCE and started the Pharnacid dynasty, which would rule Hellespontine Phrygia until the conquests of Alexander the Great (338 BCE). The residence of the Pharnacid Dynasty was at Dascylium (near modern-day E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
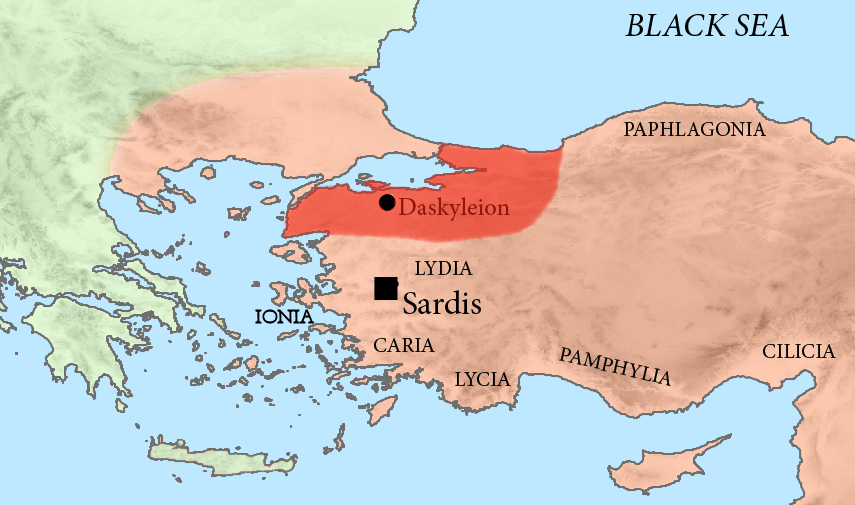
Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of the Hellespont. Its capital was Dascylium, and for most of its existence it was ruled by the hereditary Persian Pharnacid dynasty. Together with Greater Phrygia, it made up the administrative provinces of the wider Phrygia region. History The satrapy was created in the beginning of the fifth century BC, during the time of administrative reorganisations of the territories in western Asia Minor, which were amongst the most important Achaemenid territories. The first Achaemenid ruler of Hellespontine Phrygia was Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BC), who was appointed by Cyrus the Great and continued under Cambises. He was killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of neighbouring Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabazos I Of Phrygia
Artabazos ( grc, Ἀρτάβαζος; fl. 480 BC - 455 BC) was a Persian general in the army of Xerxes I, and later satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia (now northwest Turkey) under the Achaemenid dynasty, founder of the Pharnacid dynasty of satraps. He was the son of Pharnaces, who was the younger brother of Hystaspes, father of Darius I. Artabazos was therefore a first cousin of the great Achaemenid ruler Darius I. General in the Second Persian invasion of Greece Artabazus was one of the generals of Xerxes in the 480 BC Second Persian invasion of Greece, in command of the Parthians and the Chorasmians in the Achaemenid army. He was particularly in charge of the reserve forces guarding the route back to Asia, and responsible for suppressing a revolt in Potidaea. The invasion ended the following year with the Commander in Chief Mardonius, ignoring advice from Artabazus and others, meeting the Greeks in pitched battle at the Battle of Plataea and being defeated (479 BC). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces II Of Phrygia
Pharnaces II (Old Iranian: ''Farnaka''; fl. 430 BCE - 422 BCE) ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty of Persia. Hellespontine Phrygia (Greek: Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία) comprised the lands of Troad, Mysia and Bithynia and had its seat at Daskyleion, south of Cyzicus, Mysia (near modern-day Erdek, Balıkesir Province, Turkey). His grandfather, Artabazos I of Phrygia, was the founder of the Pharnacid dynasty. Pharnaces II followed as satrap either upon the death of his father, Pharnabazus I, or directly upon the death of his grandfather. He was succeeded by his son Pharnabazus II. File:MYSIA, Kyzikos. Circa 460-400 BC.jpg, Coinage of Hellespontine Phrygia at the time of Pharnaces II, Kyzikos, Mysia, circa 460-400 BC File:MYSIA, Kyzikos. Circa 450-400 BC.jpg, Coinage of Hellespontine Phrygia at the time of Pharnaces II, Kyzikos, Mysia Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
430s BC Deaths
43 may refer to: * 43 (number) * one of the years 43 BC, AD 43, 1943, 2043 * Licor 43, also known as "Cuarenta Y Tres" ("Forty-three" in Spanish) * George W. Bush George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ..., 43rd President of the United States, nicknamed "Bush 43" to distinguish from his father * "Forty Three", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' Appalachian Incantation'', 2010 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Satraps Of Hellespontine Phrygia
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |