|
Perspective Machine
A perspective machine is an optical instrument designed to help artists create perspective drawings. The earliest machines were built centuries ago when the theory of perspective was being worked out, and modern versions are still in use. Timeline * 1510: Leonardo da Vinci's ''Draftsman drawing an armillary sphere'' shows an early perspective machine in use. * 1525: Albrecht Dürer, in his illustration ''Man drawing a lute'', shows an artist using a perspective machine to create a drawing. The machine consists of a wooden frame with a taut string passing through it to represent the viewer's line of sight. Dürer built his second model of such a machine in the same year. * c.1765: Scottish engineer James Watt designs a machine based on an easel, with a pantograph mechanism allowing the artist to trace an object using a sight arm and transfer the movement of the sight to a pen drawing on paper. Watt stated that his machine was based on an invention by a Mr Hurst, who lived in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Instrument
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: *Interferometer for measuring the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
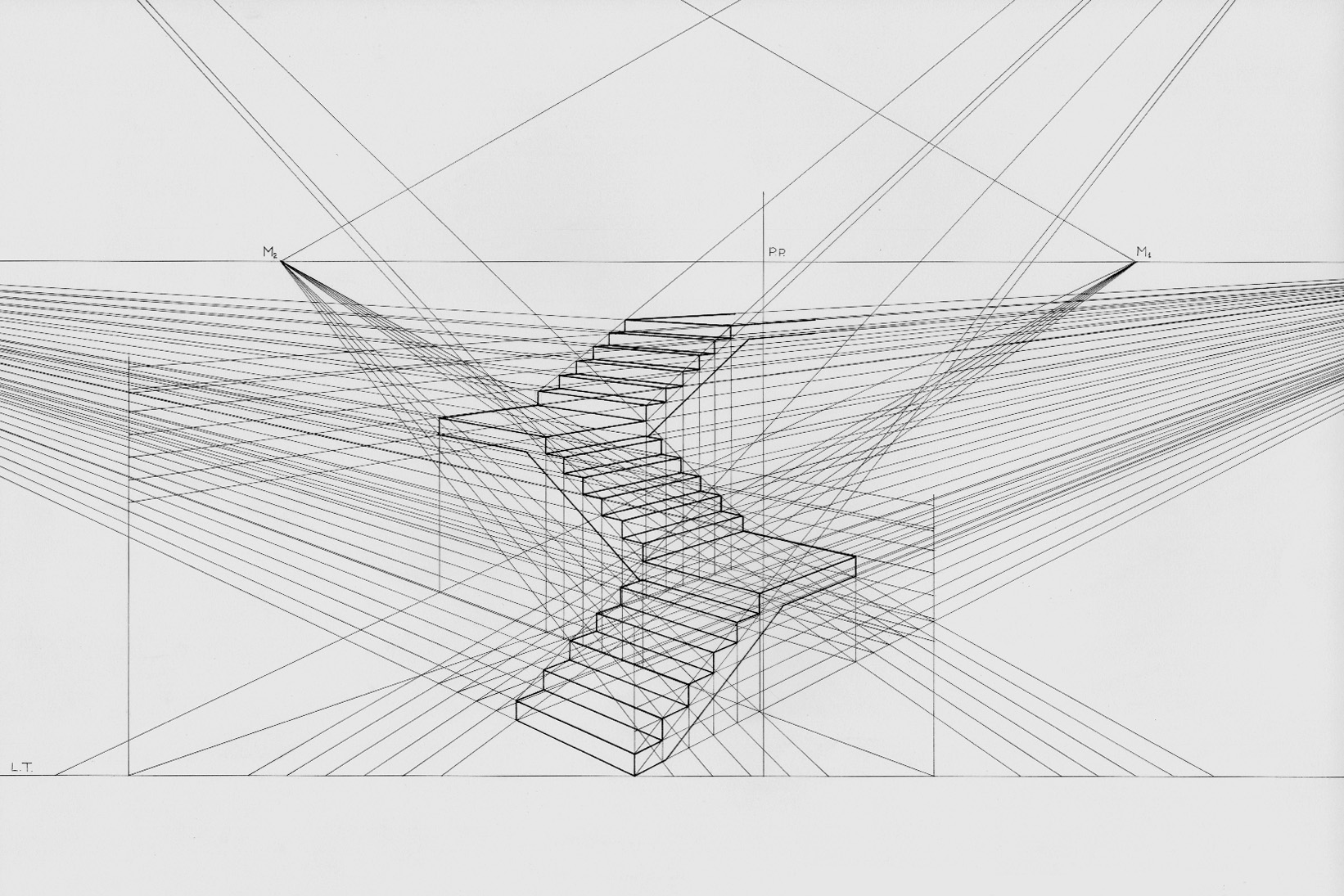
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he also became known for #Journals and notes, his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and paleontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomized the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist ideal, and his List of works by Leonardo da Vinci, collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary, Michelangelo. Born Legitimacy (family law), out of wedlock to a successful Civil law notary, notary and a lower-class woman in, or near, Vinci, Tuscany, Vinci, he was educated in Florence by the Italian painter and sculptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Duerer, was a German painter, printmaker, and theorist of the German Renaissance. Born in Nuremberg, Dürer established his reputation and influence across Europe in his twenties due to his high-quality woodcut prints. He was in contact with the major Italian artists of his time, including Raphael, Giovanni Bellini, and Leonardo da Vinci, and from 1512 was patronized by Emperor Maximilian I. Dürer's vast body of work includes engravings, his preferred technique in his later prints, altarpieces, portraits and self-portraits, watercolours and books. The woodcuts series are more Gothic than the rest of his work. His well-known engravings include the three '' Meisterstiche'' (master prints) '' Knight, Death and the Devil'' (1513), '' Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world. While working as an instrument maker at the University of Glasgow, Watt became interested in the technology of steam engines. He realised that contemporary engine designs wasted a great deal of energy by repeatedly cooling and reheating the cylinder. Watt introduced a design enhancement, the separate condenser, which avoided this waste of energy and radically improved the power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of steam engines. Eventually, he adapted his engine to produce rotary motion, greatly broadening its use beyond pumping water. Watt attempted to commercialise his invention, but experienced great financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easel
An easel is an upright support used for displaying and/or fixing something resting upon it, at an angle of about 20° to the vertical. In particular, easels are traditionally used by painters to support a painting while they work on it, normally standing up, and are also sometimes used to display finished paintings. Artists' easels are still typically made of wood, in functional designs that have changed little for centuries, or even millennia, though new materials and designs are available. Easels are typically made from wood, aluminum or steel. Easel painting is a term in art history for the type of midsize painting that would have been painted on an easel, as opposed to a fresco wall painting, a large altarpiece or other piece that would have been painted resting on the floor, a small cabinet painting, or a miniature created sitting at a desk, though perhaps also on an angled support. It does not refer to the way the painting is meant to be displayed; most easel paintings are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantograph
A pantograph (, from their original use for copying writing) is a mechanical linkage connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line drawing is traced by the first point, an identical, enlarged, or miniaturized copy will be drawn by a pen fixed to the other. Using the same principle, different kinds of pantographs are used for other forms of duplication in areas such as sculpting, minting, engraving, and milling. Because of the shape of the original device, a pantograph also refers to a kind of structure that can compress or extend like an accordion, forming a characteristic rhomboidal pattern. This can be found in extension arms for wall-mounted mirrors, temporary fences, pantographic knives, scissor lifts, and other scissor mechanisms such as the pantograph used on electric locomotives and trams. History The ancient Greek engineer Hero of Alexandria described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Reid
Thomas Reid (; 7 May ( O.S. 26 April) 1710 – 7 October 1796) was a religiously trained Scottish philosopher. He was the founder of the Scottish School of Common Sense and played an integral role in the Scottish Enlightenment. In 1783 he was a joint founder of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. A contemporary of David Hume, Reid was also "Hume's earliest and fiercest critic". Life Reid was born in the manse at Strachan, Aberdeenshire, on 26 April 1710 O.S., the son of Lewis Reid (1676–1762) and his wife Margaret Gregory, first cousin to James Gregory. He was educated at Kincardine Parish School then the O'Neil Grammar School in Kincardine. He went to the University of Aberdeen in 1723 and graduated MA in 1726. He was licensed to preach by the Church of Scotland in 1731 when he came of age. He began his career as a minister of the Church of Scotland but ceased to be a minister when he was given a professorship at King's College, Aberdeen, in 1752. He obtained his doctor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Ronalds
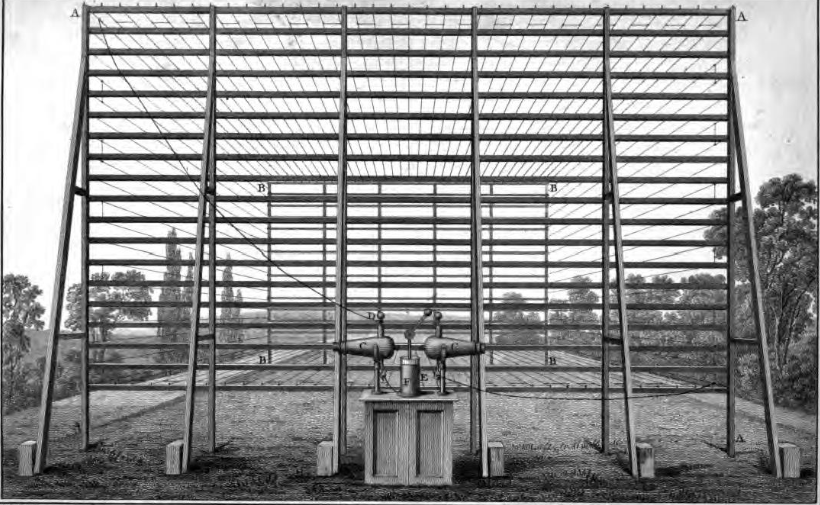
Sir Francis Ronalds FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph over a substantial distance. In 1816 he laid an eight-mile length of iron wire between wooden frames in his mother's garden and sent pulses using electrostatic generators. Upbringing and family Born to Francis Ronalds and Jane (née Field), wholesale cheesemongers, at their business premises in Upper Thames Street, London, he attended Unitarian minister Eliezer Cogan's school before being apprenticed to his father at the age of 14 through the Drapers' Company. He ran the large business for some years. The family later resided in Canonbury Place and Highbury Terrace, both in Islington, at Kelmscott House in Hammersmith, Queen Square in Bloomsbury, at Croydon, and on Chiswick Lane. Several of Ronalds' eleven brothers and sisters also led noteworthy lives. His youngest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



