|
Perspective Control
Perspective control is a procedure for composing or editing photographs to better conform with the commonly accepted distortions in constructed perspective. The control would: * make all lines that are vertical in reality vertical in the image. This includes columns, vertical edges of walls and lampposts. This is a commonly accepted distortion in constructed perspective; perspective is based on the notion that more distant objects are represented as smaller on the page; however, even though the top of the cathedral tower is in reality further from the viewer than base of the tower (due to the vertical distance), constructed perspective considers only the horizontal distance and considers the top and bottom to be the same distance away; * make all parallel lines (such as four horizontal edges of a cubic room) cross in one point. Perspective distortion occurs in photographs when the film plane is not parallel to lines that are required to be parallel in the photo. A common case is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Notre-Dame De Reims, France
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations with an episcopal hierarchy, such as the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches.New Standard Encyclopedia, 1998 by Standard Educational Corporation, Chicago, Illinois; page B-262c Church buildings embodying the functions of a cathedral first appeared in Italy, Gaul, Spain, and North Africa in the 4th century, but cathedrals did not become universal within the Western Catholic Church until the 12th century, by which time they had developed architectural forms, institutional structures, and legal identities distinct from parish churches, monastic churches, and episcopal residences. The cathedral is more important in the hierarchy than the church because it is from the cathedral that the bishop governs the area under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GIMP
GIMP ( ; GNU Image Manipulation Program) is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation (retouching) and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks. It is not designed to be used for drawing, though some artists and creators have used it for such. GIMP is released under the GPL-3.0-or-later license and is available for Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. History In 1995, Spencer Kimball and Peter Mattis began developing GIMP – originally named ''General Image Manipulation Program –'' as a semester-long project at the University of California, Berkeley for the eXperimental Computing Facility''.'' The acronym was coined first, with the letter ''G'' being added to ''-IMP'' as a reference to "the gimp" in the scene from the 1994 ''Pulp Fiction'' film. In 1996 was the initial public release of GIMP (0.54). The editor was quickly adopted and a community of contributors formed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
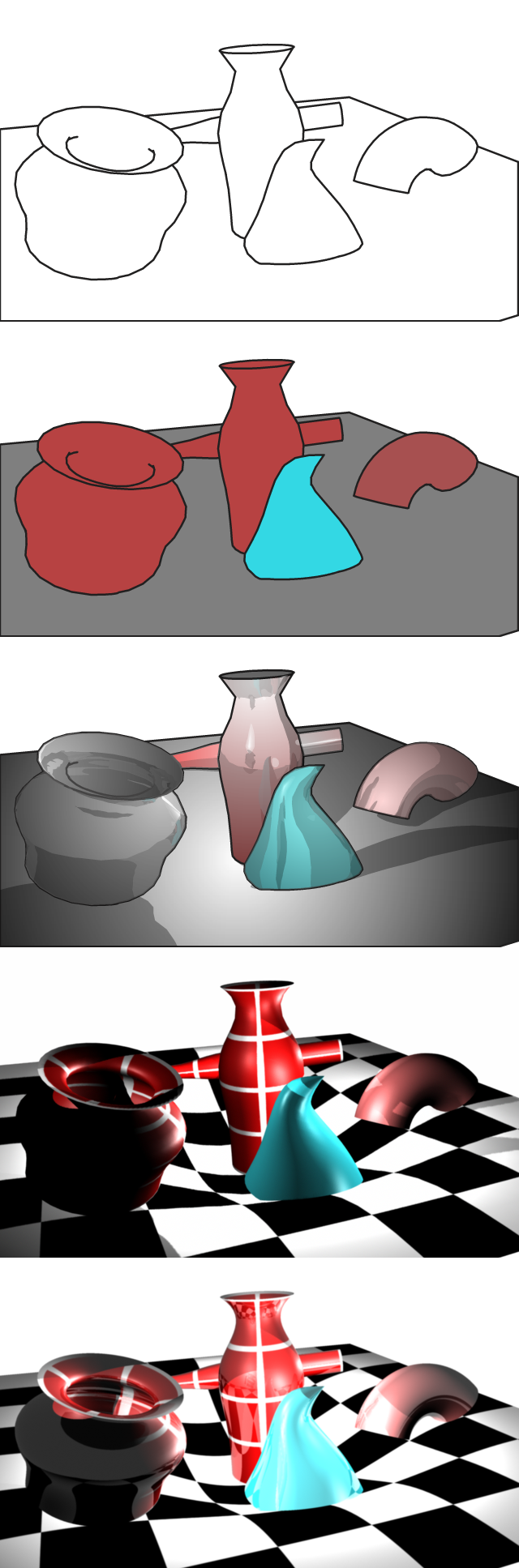
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Scaling
In computer graphics and digital imaging, image scaling refers to the resizing of a digital image. In video technology, the magnification of digital material is known as upscaling or resolution enhancement. When scaling a vector graphic image, the graphic primitives that make up the image can be scaled using geometric transformations, with no loss of image quality. When scaling a raster graphics image, a new image with a higher or lower number of pixels must be generated. In the case of decreasing the pixel number (scaling down) this usually results in a visible quality loss. From the standpoint of digital signal processing, the scaling of raster graphics is a two-dimensional example of sample-rate conversion, the conversion of a discrete signal from a sampling rate (in this case the local sampling rate) to another. Mathematical Image scaling can be interpreted as a form of image resampling or image reconstruction from the view of the Nyquist sampling theorem. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points. In engineering and science, one often has a number of data points, obtained by sampling or experimentation, which represent the values of a function for a limited number of values of the independent variable. It is often required to interpolate; that is, estimate the value of that function for an intermediate value of the independent variable. A closely related problem is the approximation of a complicated function by a simple function. Suppose the formula for some given function is known, but too complicated to evaluate efficiently. A few data points from the original function can be interpolated to produce a simpler function which is still fairly close to the original. The resulting gain in simplicity may outweigh the loss from interpolation error and give better performance in ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Of Field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera. Factors affecting depth of field For cameras that can only focus on one object distance at a time, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus. "Acceptably sharp focus" is defined using a property called the "circle of confusion". The depth of field can be determined by focal length, distance to subject, the acceptable circle of confusion size, and aperture. Limitations of depth of field can sometimes be overcome with various techniques and equipment. The approximate depth of field can be given by: : \text \approx \frac for a given circle of confusion (c), focal length (f), f-number (N), and distance to subject (u). As distance or the size of the acceptable circle of confusion increases, the depth of field increases; however, increasing the size of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resolution is directly connected to angular resolution, other instruments, like synthetic aperture radar or a network of weather stations, produce data whose spatial sampling layout is more related to the Earth's surface, such as in remote sensing and satellite imagery. See also * Image resolution * Ground sample distance * Level of detail * Resel In image analysis, a resel (from ''res''olution ''el''ement) represents the actual spatial resolution in an image or a volumetric dataset. The number of resels in the image may be lower or equal to the number of pixel/voxels in the image. In an act ... References Accuracy and precision {{physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugin (software)
Hugin () is a cross-platform open source panorama photo stitching and HDR merging program developed by Pablo d'Angelo and others. It is a GUI front-end for Helmut Dersch's Panorama Tools and Andrew Mihal's '' Enblend'' and ''Enfuse''. Stitching is accomplished by using several overlapping photos taken from the same location, and using control points to align and transform the photos so that they can be blended together to form a larger image. Hugin allows for the easy (optionally automatic) creation of control points between two images, optimization of the image transforms along with a preview window so the user can see whether the panorama is acceptable. Once the preview is correct, the panorama can be fully stitched, transformed and saved in a standard image format. Features Hugin and the associated tools can be used to * combine overlapping images for panoramic photography * correct complete panorama images, e.g. those that are "wavy" due to a badly levelled panoramic camera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Transformation
In projective geometry, a homography is an isomorphism of projective spaces, induced by an isomorphism of the vector spaces from which the projective spaces derive. It is a bijection that maps lines to lines, and thus a collineation. In general, some collineations are not homographies, but the fundamental theorem of projective geometry asserts that is not so in the case of real projective spaces of dimension at least two. Synonyms include projectivity, projective transformation, and projective collineation. Historically, homographies (and projective spaces) have been introduced to study perspective and projections in Euclidean geometry, and the term ''homography'', which, etymologically, roughly means "similar drawing", dates from this time. At the end of the 19th century, formal definitions of projective spaces were introduced, which differed from extending Euclidean or affine spaces by adding points at infinity. The term "projective transformation" originated in these abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
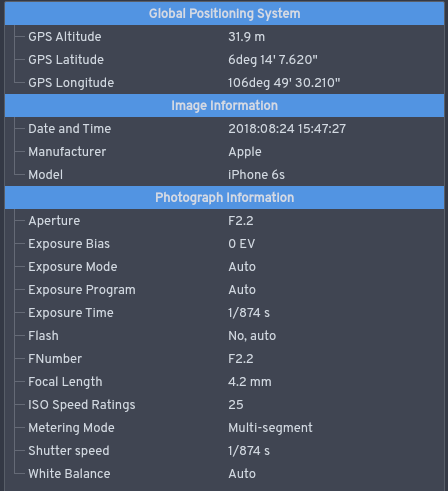
Exif
Exchangeable image file format (officially Exif, according to JEIDA/JEITA/CIPA specifications) is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smartphones), scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing encoding formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG lossy coding for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 (RGB or YCbCr) for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files (linear PCM or ITU-T G.711 μ-law PCM for uncompressed audio data, and IMA-ADPCM for compressed audio data). It does not support JPEG 2000 or GIF encoded images. This standard consists of the Exif image file specification and the Exif audio file specification. Background Exif is supported by almost all camera manufacturers. The metadata tags defined in the Exif standard cover a broad spectrum: * Camera settings: This includes static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35 Mm Equivalent Focal Length
In photography, the 35 mm equivalent focal length is a measure that indicates the angle of view of a particular combination of a camera lens and film or sensor size. The term is popular because in the early years of digital photography, most photographers experienced with interchangeable lenses were most familiar with the 35 mm film format. On any 35 mm film camera, a 28 mm lens is a wide-angle lens, and a 200 mm lens is a long-focus lens. However, now that digital cameras have mostly replaced 35 mm cameras, there is no uniform relation between the focal length of a lens and the angle of view, since the size of the camera sensor also determines angle of view, and sensor size is not standardized as film size was. The 35 mm equivalent focal length of a particular lens–sensor combination is the focal length that one would need for a 35 mm film camera to obtain the same angle of view. Most commonly, the 35 mm equivalent focal length is bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
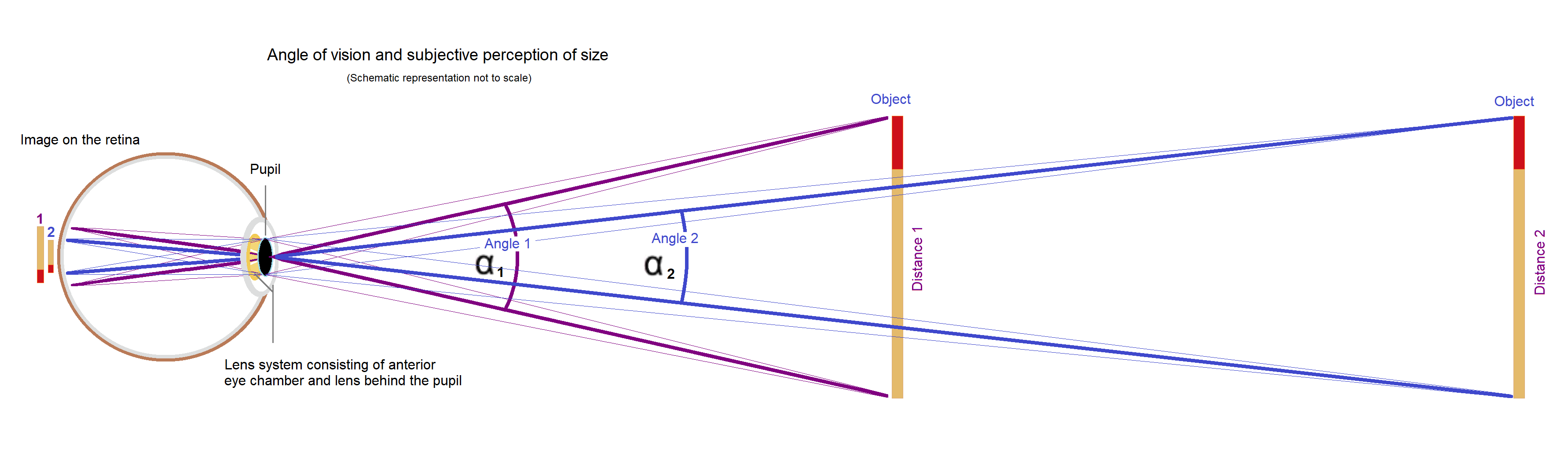
Angle Of View
The angle of view is the decisive variable for the visual perception of the size or projection of the size of an object. Angle of view and perception of size The perceived size of an object depends on the size of the image projected onto the retina. The size of the image depends on the angle of vision. A near and a far object can appear the same size if their edges produce the same angle of vision. With an optical device such as glasses or binoculars, microscope and telescope the angle of vision can be widened so that the object appears larger, which is favourable for the resolving power of the eye (see visual angle). Angle of view in photography In photography, angle of view (AOV) describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view. It is important to distinguish the angle of view from the angle of coverage, which describes the angle range that a lens can image. Typically the image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |