|
Personal Supercomputer
A personal supercomputer (PSC) is a marketing ploy used by computer manufacturers for high-performance computer systems and was a popular term in the mid 2000s to early 2010s. There is no exact definition for what a personal supercomputer is. Many systems have had that label put on them like the Cray CX1 and the Apple Power Mac G4. Generally, though the label is used on computers that are High end Workstations and Servers and have multiple processors and is small enough to fit on a desk or to the side. Other terms like PSC are Desktop/deskside supercomputers and supercomputers in a box. Deskside clusters This is the closest thing to a formal definition of a personal supercomputer as most Computers marketed as personal supercomputers are Deskside clusters like the Cray CX1. A Deskside cluster is as defined binsideHPC.com“Deskside clusters come in a chassis that you can plug into the wall of your office, and they are designed to sit on the floor next to your desk. The chassis ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Surveillance
A surveillance aircraft is an aircraft used for surveillance. They are operated by military forces and other government agencies in roles such as intelligence gathering, battlefield surveillance, airspace surveillance, reconnaissance, observation (e.g. artillery spotting), border patrol and fishery protection. This article concentrates on aircraft used in those roles, rather than for traffic monitoring, law enforcement and similar activities. Surveillance aircraft usually carry no armament, or only limited defensive armament. They do not always require high-performance capability or stealth characteristics, and may be modified civilian aircraft. Surveillance aircraft have also included moored balloons (e.g. TARS) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Definitions The terms “surveillance” and “reconnaissance” have sometimes been used interchangeably, but, in the military context, a distinction can be drawn between surveillance, which monitors a changing situation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel IPSC
The Intel Personal SuperComputer (Intel iPSC) was a product line of parallel computers in the 1980s and 1990s. The iPSC/1 was superseded by the Intel iPSC/2, and then the Intel iPSC/860. iPSC/1 In 1984, Justin Rattner became manager of the Intel Scientific Computers group in Beaverton, Oregon. He hired a team that included mathematician Cleve Moler. The iPSC used a hypercube of connections between the processors internally inspired by the Caltech Cosmic Cube research project. For that reason, it was configured with nodes numbering with power of two, which correspond to the corners of hypercubes of increasing dimension. Intel announced the iPSC/1 in 1985, with 32 to 128 nodes connected with Ethernet into a hypercube. The system was managed by a personal computer of the IBM Personal Computer/AT, PC/AT era running Xenix, the "cube manager". Each node had a 80286 CPU with 80287 math coprocessor, 512K of RAM, and eight Ethernet ports (seven for the hypercube interconnect, and one to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia DGX
Nvidia DGX is a line of Nvidia-produced servers and workstations which specialize in using GPGPU to accelerate deep learning applications. The typical design of a DGX system is based upon a rackmount chassis with motherboard that carries high performance x86 server CPUs (Typically Intel Xeons, though recently the DGX A100 and DGX Station A100 utilize AMD EPYC CPUs). The main component of a DGX system is a set of 4 to 16 Nvidia Tesla GPU modules on an independent system board. DGX systems have large heatsinks and powerful fans to adequately cool thousands of watts of thermal output. The GPU modules are typically integrated into the system using a version of the SXM socket. Models Pascal - Volta DGX-1 DGX-1 servers feature 8 GPUs based on the Pascal or Volta daughter cards with 128GB of total HBM2 memory, connected by an NVLink mesh network. The DGX-1 was announced on the 6th of April in 2016. All models are based on a dual socket configuration of Intel Xeon E5 CPUs, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia Tesla Personal Supercomputer
The Tesla Personal Supercomputer is a desktop computer (personal supercomputer) that is backed by Nvidia and built by various hardware vendors. It is meant to be a demonstration of the capabilities of Nvidia's Tesla GPGPU brand; it utilizes Nvidia's CUDA parallel computing architecture and is powered by up to 2688 parallel processing cores per GPGPU, which allow it to achieve speeds up to 250 times faster than standard PCs, according to Nvidia. See also * Nvidia Tesla * Fastra II The Fastra II is a desktop supercomputer designed for tomography. It was built in late 2009 by the ASTRA (All Scale Tomographic Reconstruction Antwerp) group of researchers of the IBBT (Interdisciplinary institute for BroadBand Technology) Visio ... References External links Tesla Personal Supercomputerwebsite DE Online Nvidia Tesla YouTube channel Nvidia products Computer workstations {{Compu-hardware-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engadget
''Engadget'' ( ) is a multilingual technology blog network with daily coverage of gadgets and consumer electronics. ''Engadget'' manages ten blogs four of which are written in English and six have international versions with independent editorial staff. It has been operated by Yahoo since September 2021. History ''Engadget'' was founded by former '' Gizmodo'' technology weblog editor and co-founder Peter Rojas. ''Engadget'' was the largest blog in Weblogs, Inc., a blog network with over 75 weblogs, including ''Autoblog'' and ''Joystiq,'' which formerly included ''Hackaday''. Weblogs Inc. was purchased by AOL in 2005. Launched in March 2004, ''Engadget'' is updated multiple times a day with articles on gadgets and consumer electronics. It also posts rumors about the technological world, frequently offers opinion within its stories, and produces the weekly Engadget Podcast that covers tech and gadget news stories that happened during the week. On December 30, 2009, ''Engadget' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGI Octane
SGI may refer to: Companies *Saskatchewan Government Insurance *Scientific Games International, a gambling company *Silicon Graphics, Inc., a former manufacturer of high-performance computing products *Silicon Graphics International, formerly Rackable Systems, which acquired the former Silicon Graphics, Inc. *Smoking Gun Interactive, a video game company * Synthetic Genomics, Inc., an alternative fuels company Other uses * Saanich-Gulf Islands, a federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada *Silicon Graphics Image, a graphics file format for Silicon Graphics workstations *Soka Gakkai International, a Nichiren Buddhist movement and also a non-governmental organization (NGO) * SGI, the IATA code for Mushaf Airbase in Pakistan *''Stargate Infinity'', an animated television series *Spheroidal graphite iron, another name for ductile iron * Sustainable Governance Indicators, statistics measuring the need for reform among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyan
Tyan Computer Corporation (泰安電腦科技股份有限公司; also known as Tyan Business Unit, or TBU) is a subsidiary of MiTAC International, and a manufacturer of computer motherboards, including models for both AMD and Intel processors. They develop and produce high-end server, SMP, and desktop barebones systems as well as provide design and production services to tier 1 global OEMs, and a number of other regional OEMs. Founding The company was founded in 1989 by Dr. T. Symon Chang, a veteran of IBM and Intel. At that time, Dr. Chang saw an empty space in the market in which there were no strong players for the SMP server space, and as such he founded Tyan in order to develop, produce and deliver such products, starting with a dual Intel Pentium-series motherboard as well as a number of other single processor motherboards all geared towards server applications. Since then, Tyan has produced a number of single and multi-processor (as well as multi-core) products using te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Analysis
Data analysis is a process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of names, and is used in different business, science, and social science domains. In today's business world, data analysis plays a role in making decisions more scientific and helping businesses operate more effectively. Data mining is a particular data analysis technique that focuses on statistical modeling and knowledge discovery for predictive rather than purely descriptive purposes, while business intelligence covers data analysis that relies heavily on aggregation, focusing mainly on business information. In statistical applications, data analysis can be divided into descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and confirmatory data analysis (CDA). EDA focuses on discovering ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
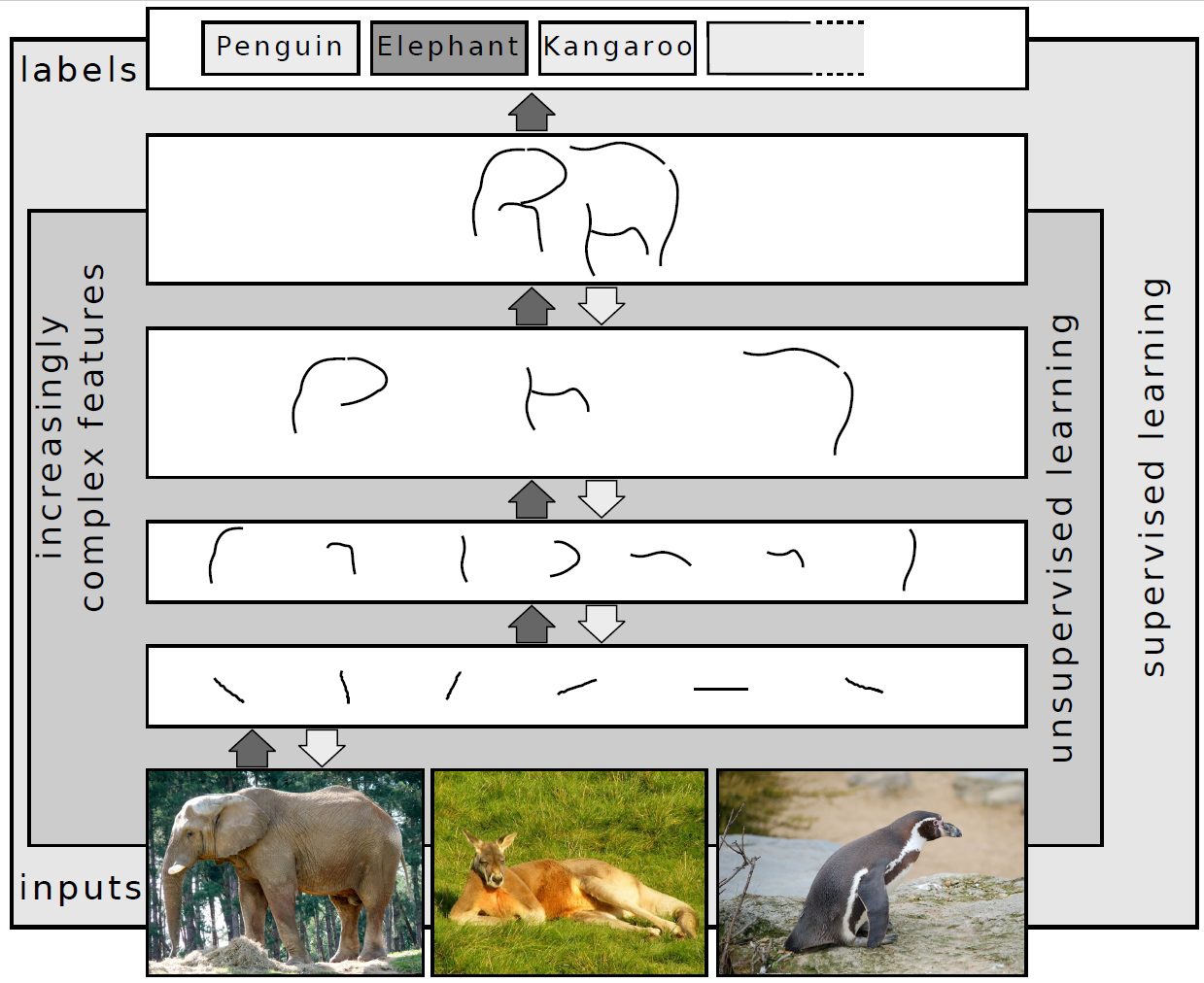
Deep Learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, Climatology, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distributed communication nodes in biological systems. ANNs have various differences from biological brains. Specifically, artificial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain data about the measurement loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |