|
Permian Tetrapods
Permian tetrapods were amphibians and reptiles that lived during the Permian Period. During this time, amphibians remained common, including various Temnospondyli and Lepospondyli. Synapsids became the dominant type of animal, represented by the Pelycosaurs during the Early Permian and Therapsids during the Middle and Late Permian, and distinguished by the appearance and possession of mammal-like characteristics (hence the old term "mammal-like reptiles"). These were accompanied by Anapsids or Parareptiles, which included both lizard-like and large herbivorous forms, and primitive diapsids. Classification The following list of families of Permian tetrapods is based mostly on Benton ed. 1993. The classification followBenton 2004 Superclass Tetrapoda * Class Amphibia :::* Order Temnospondyli :::::* Family Edopidae :::::* Family Cochleosauridae :::::* Family Trimerorhachidae :::::* Family Dvinosauridae :::::* Family Saurerpetontidae :::::* Family Brachyopidae :::::* Fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimerorhachidae
Trimerorhachidae is a family of dvinosaurian temnospondyls, including Trimerorhachis and Neldasaurus. They are vertebrates and carnivores. Gallery Trimerorhachis insignis life restoration.jpg, '' Trimerorhachis insignis'', of the early Permian of Texas Neldasaurus wrightae.jpg, '' Neldasaurus wrightae'', of the early Permian of Texas Procuhy nazariensis (cropped).jpg, '' Procuhy nazariensis'', of the early Permian of Brazil Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ... References Dvinosaurs Amphibian families {{Temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematopidae
Trematopidae is a family of dissorophoid temnospondyl spanning the late Carboniferous to the early Permian. Together with Dissorophidae, the family forms Olsoniformes, a clade comprising the medium-large terrestrial dissorophoids. Trematopids are known from numerous localities in North America, primarily in New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas, and from the Bromacker quarry in Germany. History of study The clade Trematopidae was first proposed by American paleontologist S.W. Williston in 1910, although it was named as "Trematopsidae" following the historical (but inaccurate) derivation from the genus "''Trematops''" (now synonymized with ''Acheloma''). British paleontologist D.M.S. Watson proposed a related clade in 1919, Achelomidae, for ''Acheloma'', based on perceived differences separating the taxa; this is now considered a junior synonym of Trematopidae following guidelines of historical precedent. 19th century history In 1882, American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
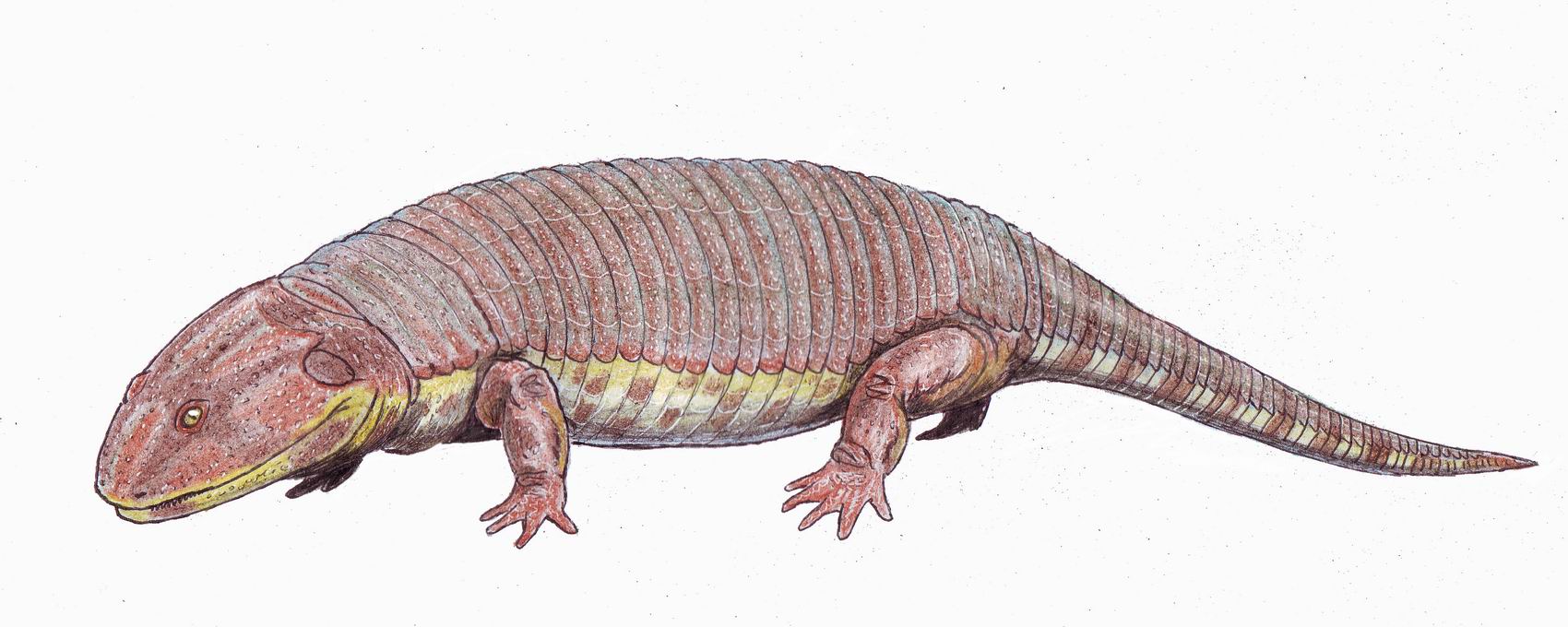
Peltobatrachidae
''Peltobatrachus'' (from Greek ''pelte'', meaning shield and batrakhos, meaning frog) is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the late Permian period of Tanzania. The sole species, ''Peltobatrachus pustulatus'', is also the sole member of the family Peltobatrachidae. Description ''Peltobatrachus'' was a large, slow moving animal, up to in length. It was a fully terrestrial amphibian, only returning to the water to lay its eggs. To protect itself against predators such as the large gorgonopsid therapsids, it had developed an armadillo-like armored plating covering its body and tail. The armor consisted of broad plates on the shoulders and hips and narrower plates on the rest of the body. Although no teeth of the creature have been found, it probably fed on insects, worms, and snail A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parioxyidae
''Parioxys'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Permian of Texas. History of study The type species, ''Parioxys ferricolus'', was named in 1878 by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope based on two badly preserved skulls that were collected from the early Permian Texas red-beds. Egyptian paleontologist Youssef S. Moustafa, described new material of ''P. ferricolus'' from other localities in Texas. This taxon was recently redescribed by Schoch & Sues (2022). Moustafa also described another species, ''P. romeri'', on the basis of an isolated humerus, but this was regarded as being indeterminate. A second definitive species, ''P. bolli'', was described by Canadian paleontologist Robert Carroll in 1964. This taxon is only known from postcranial material. Relationships ''Parioxys'' was historically considered to be closely related to eryopoids, more specifically the well-known '' Eryops megalocephalus'', which was collected from the same locality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eryopidae
Eryopidae were a group of medium to large amphibious temnospondyli, known from North America and Europe. They are defined as all eryopoids with interpterygoid vacuities (spaces in the interpterygoid bone) that are rounded at the front; and large external nares (Laurin and Steyer 2000). Not all of the genera previously included in the Eryopidae (Carroll 1988) are retained under the cladistic revisions. Gallery File:Eryops1DB.jpg, '' Eryops megacephalus'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of North America File:Onchiodon12DB.jpg, ''Onchiodon'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of Europe and North America File:Actinodon frossardi 1DB.jpg, '' Actinodon frossardi'', of the early Permian of France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ... File:Clamorosaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zatrachydidae
Zatracheidae (sometimes mistakenly spelled Zatrachydidae or Zatrachysdidae) is a family of Late Carboniferous and Early Permian temnospondyl amphibians known from North America and Europe. Zatracheidids are distinguished by lateral (sideways) bony protuberances of the quadratojugal bone of the skull, and a large opening in the snout called the internarial fontanelle (sometimes the internarial fenestra) that is bordered by enlarged premaxillae. The skull is flattened, with small orbits or eye sockets set far back. The opening in the snout may have housed a gland for producing a sticky substance so that prey would adhere to the tongue. If so, this indicates that these animals spent a large part of their time on land. History of study There are three genera of zatracheidids: '' Acanthostomatops'' Kuhn, 1961; '' Dasyceps'' Huxley 1859; and '' Zatrachys'' Cope, 1878. Only ''Dascyeps'' is represented by a species in addition to the type species. The name Zatracheidae was first coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinesuchidae
Rhinesuchidae is a family of tetrapods that lived primarily in the Permian period. They belonged to the broad group Temnospondyli, a successful and diverse collection of semiaquatic tetrapods which modern amphibians are probably descended from. Rhinesuchids can be differentiated from other temnospondyls by details of their skulls, most notably the interior structure of their otic notches at the back of the skull. They were among the earliest-diverging members of the Stereospondyli, a subgroup of temnospondyls with flat heads and aquatic habits. Although more advanced stereospondyls evolved to reach worldwide distribution in the Triassic period, rhinesuchids primarily lived in the high-latitude environments of Gondwana (what is now South America and Africa) during the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the Permian. The taxonomy of this family has been convoluted, with more than twenty species having been named in the past; a 2017 review recognized only eight of them (distributed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archegosauridae
Archegosauridae is a family of relatively large and long snouted temnospondyls that lived in the Permian period. They were fully aquatic animals, and were metabolically and physiologically more similar to fish than modern amphibians.Florian Witzmann; Elizabeth Brainerd (2017). "Modeling the physiology of the aquatic temnospondyl Archegosaurus decheni from the early Permian of Germany". Fossil Record. 20 (2): 105–127. doi:10.5194/fr-20-105-2017. The family has been divided into two subfamilies, the longer-snouted Platyoposaurinae and the shorter-snouted Melosaurinae. Gallery Platyoposaurinae File:ArchegosaurusDB3.jpg, '' Archegosaurus decheni'', of the early Permian of Germany File:Prionosuchus BW.jpg, '' Prionosuchus plummeri'', of the early Permian of Brazil File:Platyoposaurus watsoni 1DB.jpg, '' Platyoposaurus watsoni'', of the early to middle Permian of Russia File:Platyoposaurus12DB.jpg, ''Platyoposaurus stuckenbergi'', of the middle Permian of Russia File:Collidosuchus1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intasuchidae
''Intasuchus'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Middle Permian of Russia. It is known from a single species, ''Intasuchus silvicola'', which was named in 1956. ''Intasuchus'' belongs to the family Intasuchidae and is probably its sole member, although other taxa such as '' Syndyodosuchus'' and '' Cheliderpeton'' have been assigned to the family in the past. ''Intasuchus'' most likely belongs to the group Archegosauroidea, Permian relatives of the large, mostly Mesozoic temnospondyl clade Stereospondyli. Description ''Intasuchus'' has a long, flattened skull that narrows slightly toward the front. Prominent ridges run along the skull surface from the eye sockets to the nostril openings. The otic notch at the back of the skull is relatively narrow in comparison to other temnospondyls, although it extends as a groove along the sides of the skull table. ''Intasuchus'' has large teeth on the roof of its mouth, with a large row between two openings of the palate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinodontidae
Eryopidae were a group of medium to large amphibious temnospondyli, known from North America and Europe. They are defined as all eryopoids with interpterygoid vacuities (spaces in the interpterygoid bone) that are rounded at the front; and large external nares (Laurin and Steyer 2000). Not all of the genera previously included in the Eryopidae (Carroll 1988) are retained under the cladistic revisions. Gallery File:Eryops1DB.jpg, '' Eryops megacephalus'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of North America File:Onchiodon12DB.jpg, ''Onchiodon'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of Europe and North America File:Actinodon frossardi 1DB.jpg, '' Actinodon frossardi'', of the early Permian of France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ... File:Clamorosaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |