|
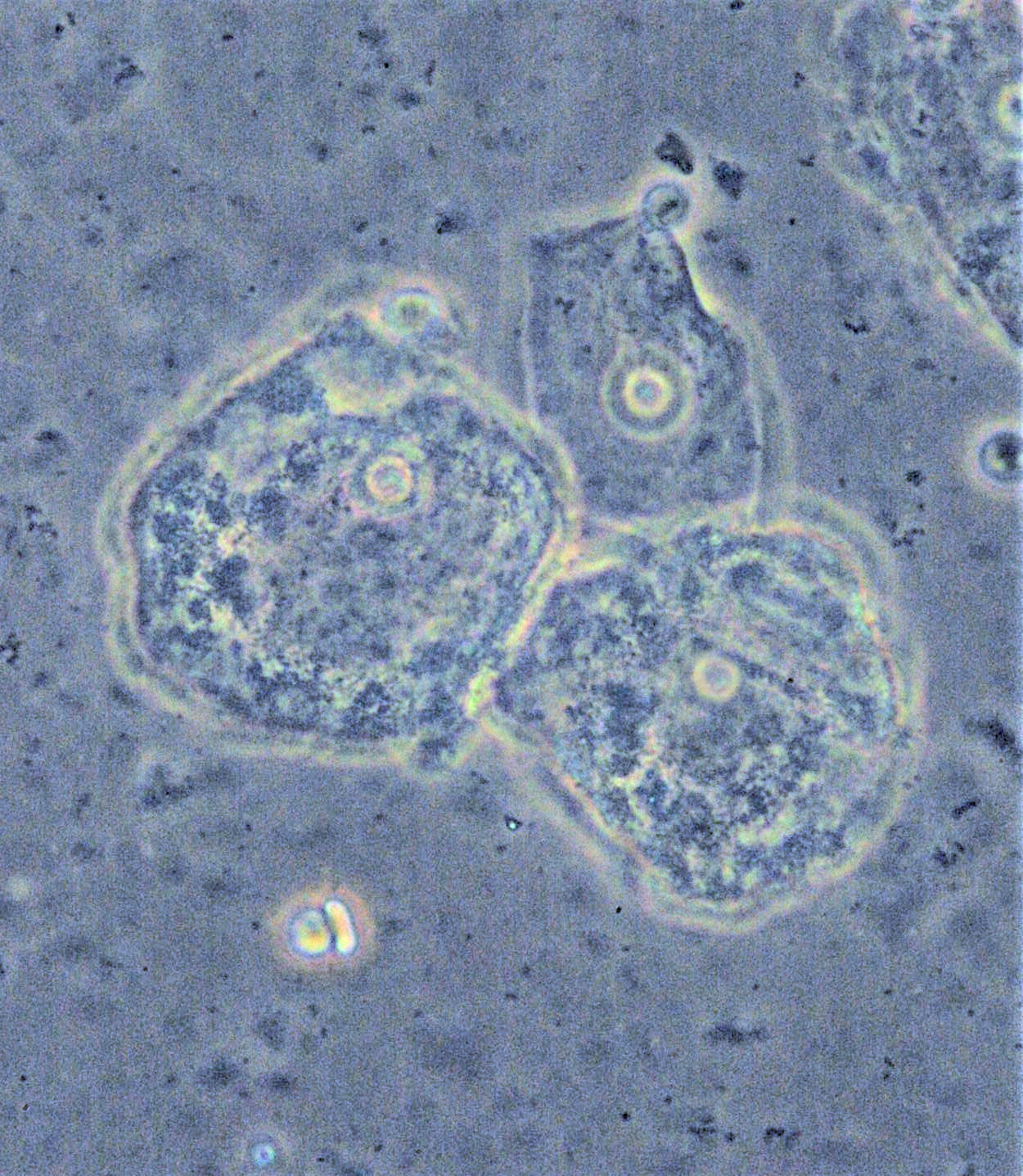
Peptostreptococcus Anaerobius
''Peptostreptococcus anaerobius'' is a species of bacteria belonging to the ''Peptostreptococcus'' genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive, non- spore forming bacteria. The cells are small, spherical, and can occur in short chains, in pairs or individually. ''Peptostreptococcus'' are slow-growing bacteria sometimes resistance to antimicrobial drugs. ''Peptostreptococcus anaerobius'' is present as part of the microbiota of the lower reproductive tract of women and has been recovered from women with pelvic inflammatory disease and bacterial vaginosis Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination .... See also * List of bacterial vaginosis microbiota References External links Type strain of ''Peptostreptococcus anaerobius'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadataba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Sammlung Von Mikroorganismen Und Zellkulturen
The Leibniz Institute DSMZ - German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH (German: ''Leibniz-Institut DSMZ-Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH''), located in Braunschweig, is a research infrastructure in the Leibniz Association. Also the DSMZ is the world's most diverse collection of bioresources (status 2021: 75,000 bioresources). These include microorganisms (including more than 32,000 bacterial strains, 690 archaeal strains, 7,000 strains of yeasts and fungi) as well as more than 840 human and animal cell cultures, over 1. 500 plant viruses, over 940 bacteriophages, and 250 plasmids (status 2021). Since 2010, the scientific director of the Leibniz Institute DSMZ has been Jörg Overmann, a microbiologist with a PhD. He holds a professorship in microbiology at the Technical University of Braunschweig. Since August 2018, he has led the institute in a dual leadership with Bettina Fischer as administrative director. History Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Microbiota Species Of The Lower Reproductive Tract Of Women
This is the list of healthy vaginal microbiota (VMB), which is defined as the group of species and genera that generally are found to have lack of symptoms, absence of various infections, and result in good pregnancy outcomes. VMB is dominated mainly by Lactobacillus species. This is the list of organisms that are found in the lower reproductive tract of sexually mature women who are not immunocompromised. A partial description of pathogens that can be found in the lower and upper reproductive tract of women can be found in the article sexually transmitted disease. The organisms listed below are capable of causing illness if for some reason there is a change in vaginal pH or a change in the ratio of one organism to another. For example, '' Candida'' is a normal inhabitant of a healthy reproductive tract but an overgrowth of this organism can cause candidiasis. Normal microbiota This is the list of the normal flora that are found in the lower reproductive tract of sexually mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
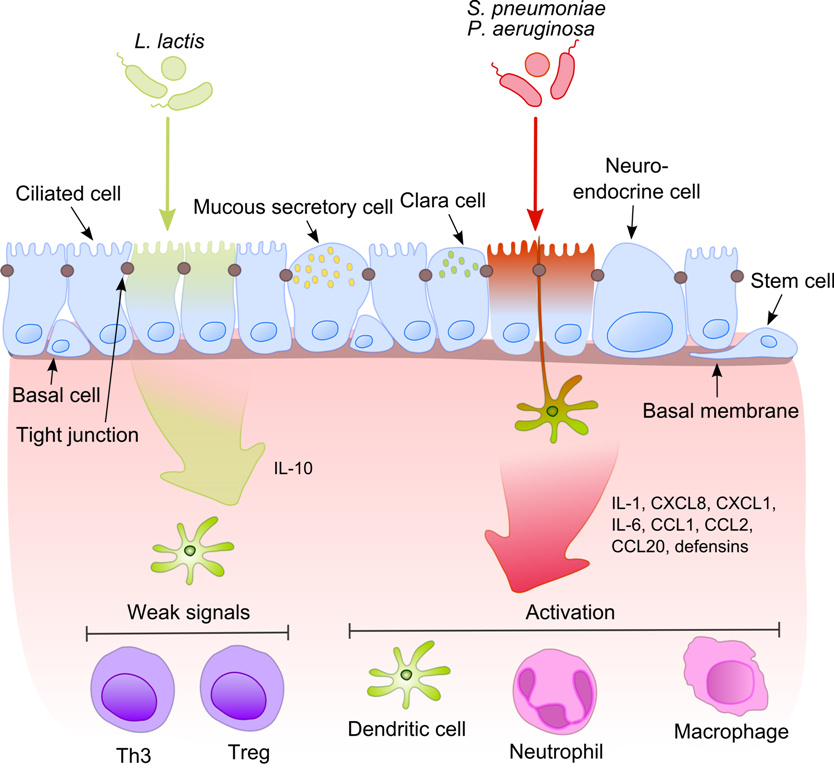
Bacterial Diseases
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptostreptococcaceae
The Peptostreptococcaceae are a family of Gram-positive bacteria in the class Clostridia. Several members of the Peptostreptococcaceae are well known inhabitants of the digestive tract. Microbiome studies of animal feces have corroborated this. Notably, an unclassified group of Peptostreptococcaceae has been reported making up a significant portion of the microbial community in domestic cats, while other studies have not found a significant presence of Peptostreptococcaceae. ''Clostridioides difficile'' is a notable human pathogen in this family. Peptostreptococcaceae have been of interest for several other bowel diseases as biological marker or causative agent. Decreased abundance has been reported for Crohn's disease, while the genus ''Peptostreptococcus ''Peptostreptococcus'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive, non-spore forming bacteria. The cells are small, spherical, and can occur in short chains, in pairs or individually. They typically move using cilia. ''Pepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikidata Link
Wikidata is a collaboratively edited multilingual knowledge graph hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation. It is a common source of open data that Wikimedia projects such as Wikipedia, and anyone else, can use under the CC0 public domain license. Wikidata is a wiki powered by the software MediaWiki, and is also powered by the set of knowledge graph MediaWiki extensions known as Wikibase. Concept Wikidata is a document-oriented database, focused on items, which represent any kind of topic, concept, or object. Each item is allocated a unique, persistent identifier, a positive integer prefixed with the upper-case letter Q, known as a "QID". This enables the basic information required to identify the topic that the item covers to be translated without favouring any language. Examples of items include , , , , and . Item labels need not be unique. For example, there are two items named "Elvis Presley": , which represents the American singer and actor, and , which represents his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bacterial Vaginosis Microbiota
Bacterial vaginosis is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. The normally predominant species of ''Lactobacilli'' are markedly reduced. This is the list of organisms that are found in the vagina that are associated with bacterial vaginosis, an infectious disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of specific bacteria. The census and relationships among the microbiota are altered in BV resulting in a complex bacterial milieu. Some species have been identified relatively recently. Having infections with the listed pathogens increases the risk of acquiring other sexually transmitted infections including HIV/AIDS. Microbiota *'' Actinobacteria'' spp * '' Actinomyces naeslundii'' * ''Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans'' * '' Anaerococcus'' spp *'' Atopobium vaginae'' * '' Bacteroides ureolyticus'' * '' Bifidobacterium'' spp * '' Clostridiales'' spp * '' Collinsella aerofaciens'' * '' Eggerthella lenta'' *'' Eggerthella'' spp * ''Eubac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
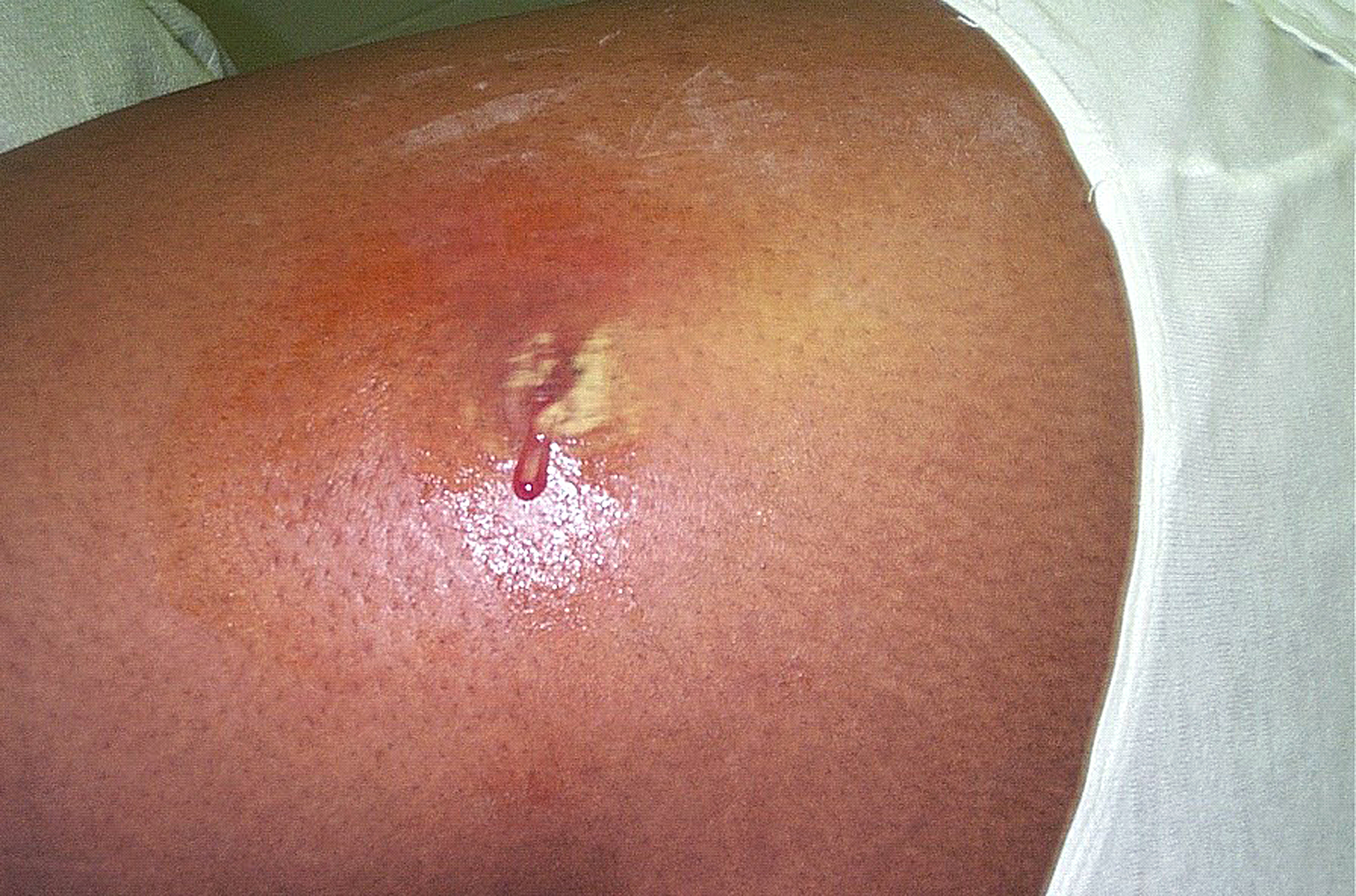
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women. BV is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. There is a change in the most common type of bacteria and a hundred to thousand fold increase in total numbers of bacteria present. Typically, bacteria other than ''Lactobacilli'' become more common. Risk factors include douching, new or multiple sex partners, antibiotics, and using an intrauterine device, among others. However, it is not considered a sexually transmitted infection and, unlike gonorrh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
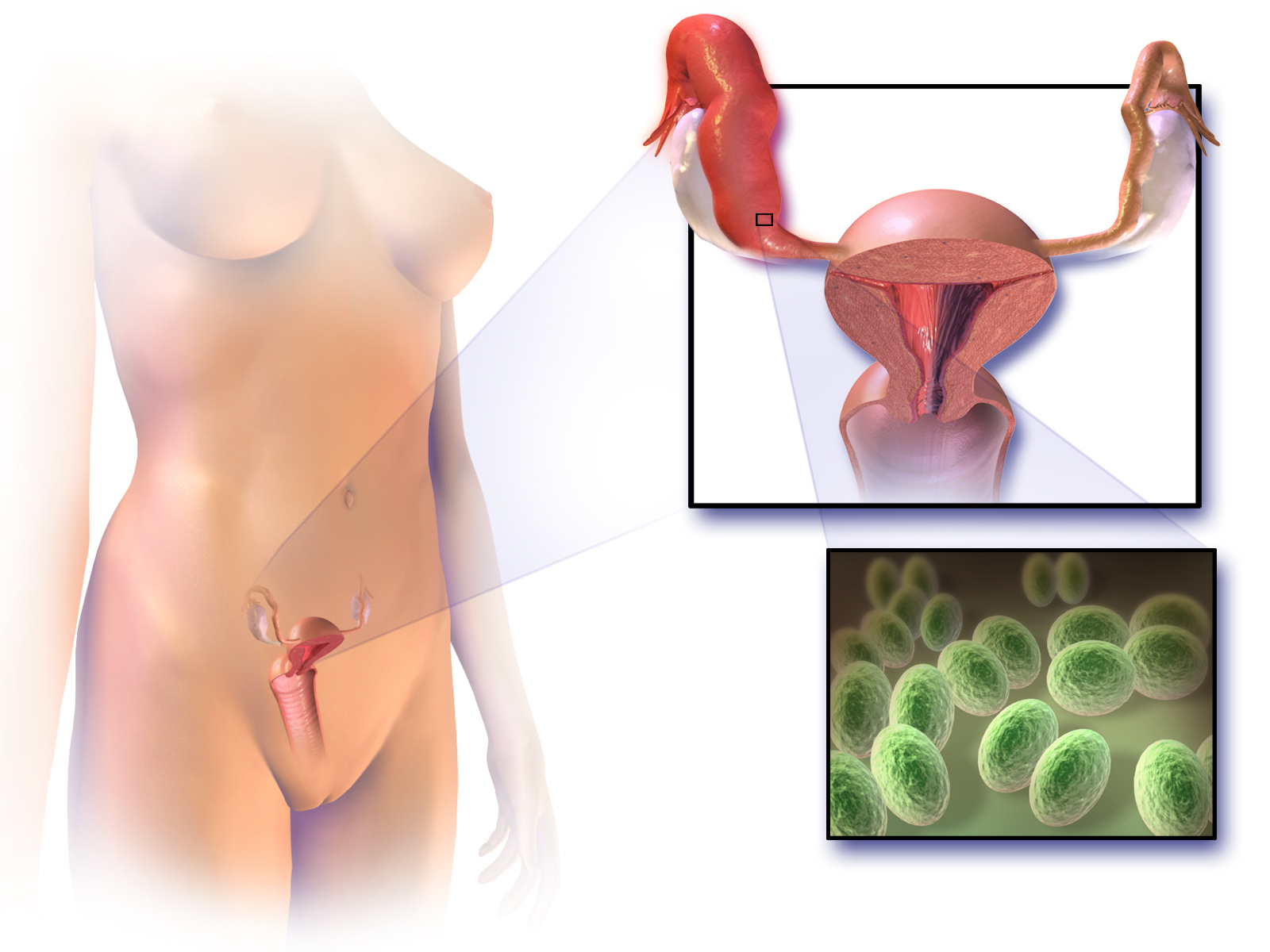
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer. The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often, multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID. Risk factors are generally similar to those of sexua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function. Agents that kill microbes are microbicides, while those that merely inhibit their growth are called bacteriostatic agents. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis. The main classes of antimicrobial agents are disinfectants (non-selective agents, such as bleach), which kill a wide range of microbes on non-living surfaces to prevent the spread of illness, antiseptics (which are applied to living tissue and help reduce infection during surgery), and antibiotics (which destroy microorganisms within the body). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptostreptococcus
''Peptostreptococcus'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive, non-spore forming bacteria. The cells are small, spherical A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the ce ..., and can occur in short chains, in pairs or individually. They typically move using cilia. ''Peptostreptococcus'' are slow-growing bacteria with increasing resistance to antimicrobial drugs. ''Peptostreptococcus'' is a normal List of microbiota species of the lower reproductive tract of women, inhabitant of the healthy lower reproductive tract of women. Pathogenesis ''Peptostreptococcus'' species are commensal organisms in humans, living predominantly in the mouth, skin, gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal, vagina and urinary tracts, and are members of the gut flora, gut microbiota. Under immunosuppresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocci
A coccus (plural cocci) is any bacterium or archaeon that has a spherical, ovoid, or generally round shape. Bacteria are categorized based on their shapes into three classes: cocci (spherical-shaped), bacillus (rod-shaped) and spiral ( of which there are two types: spirillum and spirochete). Coccus refers to the shape of the bacteria, and can contain multiple genera, such as staphylococci or streptococci. Cocci can grow in pairs, chains, or clusters, depending on their orientation and attachment during cell division. In contrast to many bacilli-shaped bacteria, most cocci bacteria do not have flagella and are non-motile. Cocci is an English loanword of a modern or neo-Latin noun, which in turn stems from the Greek masculine noun () meaning 'berry'. Structure The cell wall structure for cocci may vary between gram-positive (thick peptidoglycan layers) and gram-negative (thin peptidoglycan layers). While living in their host organism, cocci can be pathogenic (e.g., streptoco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |