|
Pentaoxidane
Pentaoxidane is an inorganic compound of hydrogen and oxygen with the chemical formula . This is one of the most unstable hydrogen polyoxides. Synthesis *The compound is prepared as a byproduct of trioxidane production. * has also been synthesized by reaction among peroxy In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where R = any element. The group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable. The most common peroxide is hydrogen ... radicals at low temperature. References {{Hydrides by group Inorganic compounds Oxides Polyoxides Hydrogen compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraoxidane
Tetraoxidane is an inorganic compound of hydrogen and oxygen with the chemical formula . This is one of the unstable hydrogen polyoxides. Synthesis The compound is prepared by a chemical reaction between hydroperoxyl radicals () at low temperatures: ::\mathrm Physical properties This is the fourth member of the polyoxidanes. The first three are water mon)oxidane hydrogen peroxide (dioxidane), and trioxidane Trioxidane (systematically named μ-trioxidanediidodihydrogen), also called dihydrogen trioxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (can be written as or ). It is one of the unstable hydrogen polyoxides. In aqueous solutions, t .... Tetroxidane is more unstable than the previous compounds. The term "tetraoxidane" extends beyond the parent compound to several daughter compounds of the general formula , where R can be hydrogen, halogen atoms, or various inorganic and organic monovalent radicals. The two Rs together can be replaced by a divalent radical, so h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Polyoxide
Hydrogen polyoxides (also known as oxidanes, oxohydrogens, or oxyhydrogens) are chemical compounds that consist only of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, are bonded exclusively by single bonds (i.e., they are saturated), and are acyclic (have molecular structures containing no cycles or loops). They can, therefore, be classed as hydrogen chalcogenides. The simplest possible stable hydrogen polyoxide (the parent molecule) is water, H2O. The general structure of the class of molecules is some number of oxygen atoms single-bonded to each other in a chain. The oxygen atom at each end of this oxygen skeleton is attached to a hydrogen atom. Thus, these compounds form a homologous series with chemical formula in which the members differ by a constant relative molecular mass of 16 (the mass of each additional oxygen atom). The number of oxygen atoms is used to define the size of the hydrogen polyoxide (e.g., hydrogen pentoxide contains a five-oxygen backbone). An oxidanyl group is a fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentoxolane
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, followed by catalytic hydrogenation. A third major industrial route entails hydroformylation of allyl alcohol followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, New Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Quantum Chemistry
The ''International Journal of Quantum Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original, primary research and review articles on all aspects of quantum chemistry, including an expanded scope focusing on aspects of materials science, biochemistry, biophysics, quantum physics, quantum information theory, etc. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.444. It was established in 1967 by Per-Olov Löwdin Per-Olov Löwdin (October 28, 1916 – October 6, 2000) was a Swedish physicist, professor at the University of Uppsala from 1960 to 1983, and in parallel at the University of Florida until 1993. A former graduate student under Ivar Waller, Löwd .... In 2011, the journal moved to an in-house editorial office model, in which a permanent team of full-time, professional editors is responsible for article scrutiny and editorial content. References External links * Chemistry journals Publications established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiley (publisher)
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, New Jer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
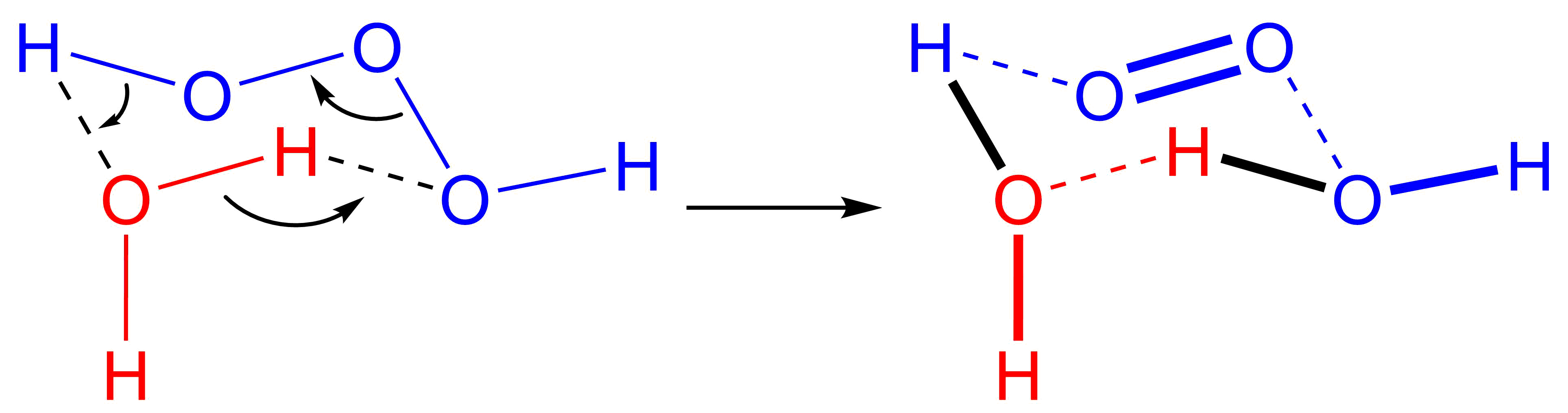
Trioxidane
Trioxidane (systematically named μ-trioxidanediidodihydrogen), also called dihydrogen trioxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (can be written as or ). It is one of the unstable hydrogen polyoxides. In aqueous solutions, trioxidane decomposes to form water and singlet oxygen: The reverse reaction, the addition of singlet oxygen to water, typically does not occur in part due to the scarcity of singlet oxygen. In biological systems, however, ozone is known to be generated from singlet oxygen, and the presumed mechanism is an antibody-catalyzed production of trioxidane from singlet oxygen. Preparation Trioxidane can be obtained in small, but detectable, amounts in reactions of ozone and hydrogen peroxide, or by the electrolysis of water. Larger quantities have been prepared by the reaction of ozone with organic reducing agents at low temperatures in a variety of organic solvents, such as the anthraquinone process. It is also formed during the decomposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxy
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where R = any element. The group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable. The most common peroxide is hydrogen peroxide (), colloquially known simply as "peroxide". It is marketed as solutions in water at various concentrations. Many organic peroxides are known as well. In addition to hydrogen peroxide, some other major classes of peroxides are: * Peroxy acids, the peroxy derivatives of many familiar acids, examples being peroxymonosulfuric acid and peracetic acid, and their salts, one example of which is potassium peroxydisulfate. * Main group peroxides, compounds with the linkage (E = main group element). * Metal peroxides, examples being barium peroxide (), sodium peroxide () and zinc peroxide Zinc peroxide (ZnO2) appears as a bright yellow powder at room temperature. It was historically used as a surgical antiseptic. More recently zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Journal Of Inorganic Chemistry
The ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering inorganic, organometallic, bioinorganic, and solid-state chemistry. It is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of Chemistry Europe. The journal, along with the ''European Journal of Organic Chemistry'', was established in 1998 as the result of a merger of '' Chemische Berichte/Recueil,'' ''Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France,'' '' Bulletin des Sociétés Chimiques Belges,'' ''Gazzetta Chimica Italiana,'' ''Anales de Química,'' ''Chimika Chronika,'' ''Revista Portuguesa de Química, and'' ''ACH-Models in Chemistry.'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 2.551. See also *List of chemistry journals *''European Journal of Organic Chemistry The ''European Journal of Organic Chemistry'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering organic chemistry. It is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of Chemistry Europe. The jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compounds
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |