|
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl Complexes
1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is a cyclic diene with the formula C5Me5H (Me = CH3). 1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is the precursor to the ligand ''1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl'', which is often denoted Cp* (C5Me5) and read as "C P star", the "star" signifying the five methyl groups radiating from the core of the ligand. In contrast to less-substituted cyclopentadiene derivatives, Cp*H is not prone to dimerization. Synthesis Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is commercially available. It was first prepared from tiglaldehyde via 2,3,4,5-tetramethylcyclopent-2-enone. Alternatively, 2-butenyllithium adds to ethyl acetate followed by acid-catalyzed dehydrocyclization: Organometallic derivatives Cp*H is a precursor to organometallic compounds containing the ligand, commonly called Cp*−. Some representative reactions leading to such Cp*–metal complexes follow: :Cp*H + C4H9Li → Cp*Li + C4H10 :Cp*Li + TiCl4 → Cp*TiCl3 + LiCl Some Cp* co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Compound
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present (heterocyclic compounds). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size (e.g., < 17 total atoms) numbers in the many b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula () to the word. Properties and structure is a dense, colourless distillable liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting and boiling points are similar to those of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodium(III) Chloride
Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)''n'', where ''n'' varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of ''n'', the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation. Structures Aqueous solutions of RhCl3(H2O)3 have been characterized by 103Rh NMR spectroscopy, which shows the presence of several species. The proportions of which change with time and depend on the concentration of chloride. The relative distribution of these species determines the colour of the solutions, which can range from yellow (the hexaaquo ion) to "raspberry-red". Some of these species are h(H2O)6sup>3+, hCl(H2O)5sup>2+, ''cis''- and ''trans''- hCl2(H2O)4sup>+, and hCl3(H2O)3 Individual ions have been separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Communications
''ChemComm'' (or ''Chemical Communications''), formerly known as ''Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications'' (1969–1971), ''Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications'' (1972–1995), is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It covers all aspects of chemistry. In January 2012, the journal moved to publishing 100 issues per year. The current chair of the Editorial Board is Douglas Stephan (University of Toronto, Canada), while the executive editor is Richard Kelly. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Chemical Abstracts * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * Scopus * Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 6.065. See also * ''New Journal of Chemistry'' * ''Chemical Society Reviews'' * ''Chemical Science'' * ''RSC Advances ''RSC Advances'' is an online ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridium(III) Chloride
Iridium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula IrCl3. The anhydrous compound is relatively rare, but the related hydrate is useful for preparing other iridium compounds. The anhydrous salt is a dark green crystalline solid. More commonly encountered is the trihydrate IrCl3(H2O)3. Preparation Iridium is separated from the other platinum group metals as crystalline ammonium hexachloroiridate, (NH4)2 rCl6 which can be reduced to iridium metal in a stream of hydrogen. The spongy Ir thus produced reacts with chlorine at 300–400 °C to give iridium(III) chloride. Hydrated iridium trichloride is obtained by heating hydrated iridium(III) oxide with hydrochloric acid. Structure Like the related rhodium compound, IrCl3 adopts the structure seen for aluminium chloride. This is the monoclinic α polymorph. A rhombohedral β polymorph also exists. Both polymorphs have effectively the same anion lattice but differ in the octahedral interstices the iridium ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2021 impact factor of 16.823. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'' ( (print), (online)), and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition'' ( (print), (online)). The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Business model ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron Letters
''Tetrahedron Letters'' is a weekly international journal for rapid publication of full original research papers in the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.415. Indexing ''Tetrahedron Letters'' is indexed in: References See also *''Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...'' *'' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry'' Chemistry journals Weekly journals Publications established in 1959 Elsevier academic journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrohalic Acid
In chemistry, hydrogen halides (hydrohalic acids when in the aqueous phase) are diatomic, inorganic compounds that function as Arrhenius acids. The formula is HX where X is one of the halogens: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine. All known hydrogen halides are gases at Standard Temperature and Pressure.The Acidity of the Hydrogen Halides. (2020, August 21). Retrieved May 5, 2021, from https://chem.libretexts.org/@go/page/3699 Vs. hydrohalic acids The hydrogen halides are diatomic molecules with no tendency to ionize in the gas phase (although liquified hydrogen fluoride is a polar solvent somewhat similar to water). Thus, chemists distinguish hydrogen chloride from hydrochloric acid. The former is a gas at room temperature that reacts with water to give the acid. Once the acid has formed, the diatomic molecule can be regenerated only with difficulty, but not by normal distillation. Commonly the names of the acid and the molecules are not clearly distinguished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl Rhodium Dichloride Dimer
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula C5(CH3)5RhCl2)sub>2, commonly abbreviated p*RhCl2sub>2 This dark red air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry. Structure and preparation The compound has idealized C2h symmetry. Each metal centre is pseudo-octahedral. The compound is prepared by the reaction of rhodium trichloride trihydrate and pentamethylcyclopentadiene in hot methanol, from which the product precipitates: :2 Cp*H + 2 RhCl3(H2O)3 -> ce \text/chem> p*RhCl2sub>2 + 2 HCl + 6 H2O It was first prepared by the reaction of hydrated rhodium trichloride with hexamethyl Dewar benzene Reactions Reductive carbonylation gives p*Rh(CO)2 The Rh-'' μ''-Cl bonds are labile and cleave en route to a variety of adducts of the general formula Cp*RhCl2L. Treatment with silver ions in polar coordinating solvents cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
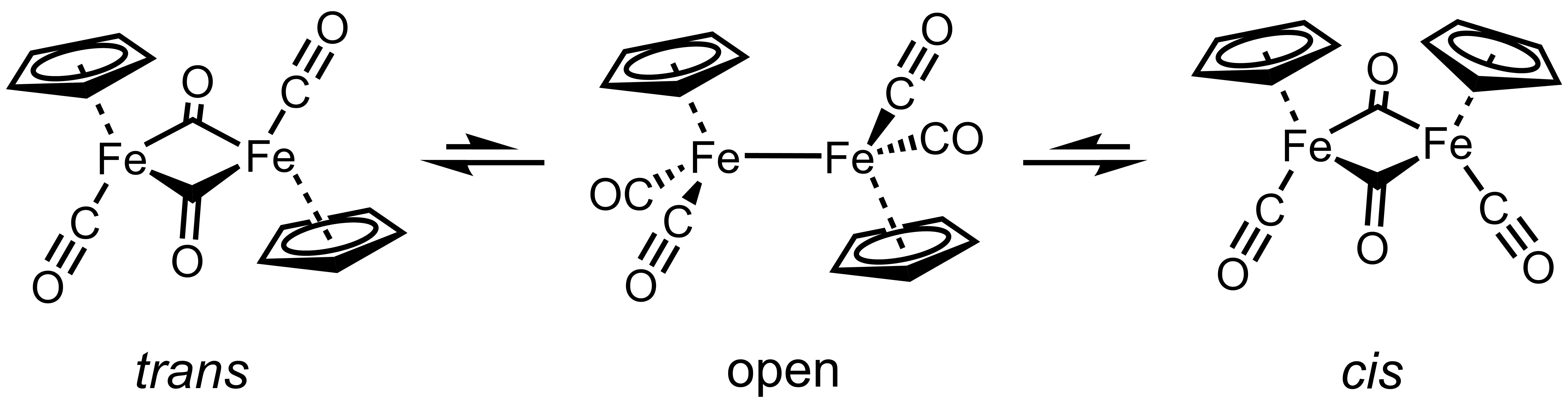
Cyclopentadienyliron Dicarbonyl Dimer
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula ''η''5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2sub>2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, pFe(CO)2sub>2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below). Structure In solution, Cp2Fe2(CO)4 can be considered a dimeric half-sandwich complex. It exists in three isomeric forms: ''cis'', ''trans'', and an unbridged, open form. These isomeric forms are distinguished by the position of the ligands. The ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers differ in the relative position of C5H5 (Cp) ligands. The ''cis'' and ''trans'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |