|
Pentalogy Of Cantrell
Pentalogy of Cantrell (or thoraco-abdominal syndrome) is a rare congenital syndrome that causes defects involving the diaphragm, abdominal wall, pericardium, heart and lower sternum. Presentation There are five characteristic findings in pentalogy of Cantrell: # an abdominal wall defect, # lower sternal defect, # congenital heart malformations, # absence of the diaphragmatic pericardium, # and an anterior diaphragmatic defect. Abdominal wall defects in pentalogy of Cantrell occur above the umbilicus (supraumbilical) and in the midline, and have a wide range of presentations. Diastasis recti, hernias, and omphalocele have all been described in conjunction with the pentalogy. Sternal defects too have a range of presentations, from absence of the xiphoid process to shortened or cleft sternum. If the sternal defect is large enough, the neonate may have ectopia cordis, in which the heart is located outside of the thorax. Many congenital heart malformations have been described in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI In Pregnancy
Medical imaging in pregnancy may be indicated because of pregnancy complications, intercurrent diseases or routine prenatal care. Options Options for medical imaging in pregnancy include the following: *Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without MRI contrast agents as well as obstetric ultrasonography are not associated with any risk for the mother or the fetus and are the imaging techniques of choice for pregnant women. February 2016 *Projectional radiography, X-ray computed tomography and nuclear medicine result in some degree of ionizing radiation exposure but have with a few exceptions much lower radiation doses than what is associated with fetal harm. They are indicated when ultrasonography or MRI is not readily available or not feasible for the diagnostic question at hand. :*Radiocontrast agents, when orally administered, are harmless. Intravenous administration of iodinated radiocontrast agents can cross the placenta and enter the fetal circulation, but animal studies hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823. The journal publishes original research articles, review articles ("seminars" and "reviews"), editorials, book reviews, correspondence, as well as news features and case reports. ''The Lancet'' has been owned by Elsevier since 1991, and its editor-in-chief since 1995 has been Richard Horton. The journal has editorial offices in London, New York City, and Beijing. History ''The Lancet'' was founded in 1823 by Thomas Wakley, an English surgeon who named it after the surgical instrument called a lancet (scalpel). Members of the Wakley family retained editorship of the journal until 1908. In 1921, ''The Lancet'' was acquired by Hodder & Stoughton. Elsevier acquired ''The Lancet'' from Hodder & Stoughton in 1991. Impact According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose Of Viterbo
Rose of Viterbo, T.O.S.F. ( it, Rosa da Viterbo; c. 1233 – 6 March 1251), was a young woman born in Viterbo, then a contested commune of the Papal States. She spent her brief life as a recluse, who was outspoken in her support of the papacy. Otherwise leading an unremarkable life, she later became known for her mystical gifts of prophecy and having miraculous powers. She is honoured as a saint by the Catholic Church. Life The chronology of her life remains uncertain, as the acts of her canonization, the chief historical sources, record no dates. Most scholars agree she was probably born around the year 1233. Born of poor and pious parents, even as a child Rose had a great desire to pray and to aid the poor. She prayed much for the conversion of sinners. Rose was not yet 10 years old when the Blessed Virgin Mary is said to have instructed her to take the habit of the Third Order of St. Francis and to preach penance in Viterbo, at that time under the rule of Frederick II, Holy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
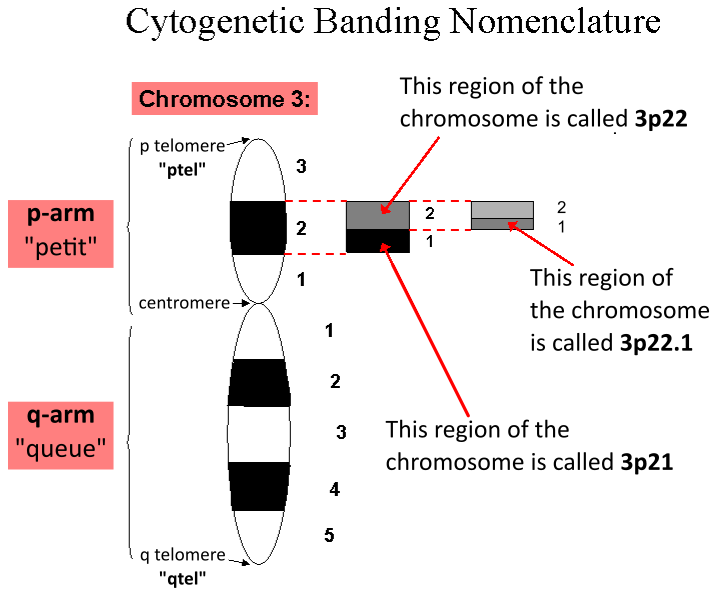
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition Of The Great Vessels
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates. Types Transposed vessels can present with atriovenous, ventriculoarterial and/or arteriovenous discordance. The effects may range from a slight change in blood pressure to an interruption in circulation depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement, and on which specific vessels are involved. Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextrocardia
Dextrocardia (from Latin ''dextro'', meaning "right hand side," and Greek ''kardia'', meaning "heart") is a rare congenital condition in which the apex of the heart is located on the right side of the body, rather than the more typical placement towards the left. There are two main types of dextrocardia: dextrocardia of embryonic arrest (also known as isolated dextrocardia) and dextrocardia ''situs inversus''. Dextrocardia ''situs inversus'' is further divided. Classification Dextrocardia of embryonic arrest In this form of dextrocardia, the heart is simply placed further right in the thorax than is normal. It is commonly associated with severe defects of the heart and related abnormalities including pulmonary hypoplasia. Dextrocardia situs solitus Dextrocardia refers to a heart positioned in the right side of the chest. Situs solitus describes viscera that are in the normal position, with the stomach on the left side. Dextrocardia situs inversus Dextrocardia situs inversus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralogy Of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are: *pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the right ventricle; * a ventricular septal defect, which is a hole allowing blood to flow between the two ventricles; * right ventricular hypertrophy, which is thickening of the right ventricular muscle; and * an overriding aorta, which is where the aorta expands to allow blood from both ventricles to enter. At birth, children may be asymptomatic or present with many severe symptoms. Later in infancy, there are typically episodes of bluish colour to the skin due to a lack of sufficient oxygenation, known as cyanosis. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement, they may undergo a "tet spell" where they turn cyanotic, have difficulty breathing, become limp, and occasionally lose consciousness. Other symptoms may include a heart murmur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Outlet Right Ventricle
Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) is a form of congenital heart disease where both of the great arteries connect (in whole or in part) to the right ventricle (RV). In some cases it is found that this occurs on the left side of the heart rather than the right side. Cause Pathogenesis DORV occurs in multiple forms, with variability of great artery position and size, as well as of ventricular septal defect (VSD) location. It can occur with or without transposition of the great arteries. The clinical manifestations are similarly variable, depending on how the anatomical defects affect the physiology of the heart, in terms of altering the normal flow of blood from the RV and left ventricle (LV) to the aorta and pulmonary artery. For example: :*in DORV with a subaortic VSD, blood from the LV flows through the VSD to the aorta and blood from the RV flows mainly to the pulmonary artery, yielding physiology similar to ventricular septal defect :*in DORV with a subpulmonic VSD (cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonic Stenosis
Pulmonic stenosis, is a dynamic or fixed obstruction of flow from the right ventricle of the heart to the pulmonary artery. It is usually first diagnosed in childhood. Signs and symptoms Cause Pulmonic stenosis is usually due to isolated valvular obstruction (pulmonary valve stenosis), but it may be due to subvalvular or supravalvular obstruction, such as infundibular stenosis. It may occur in association with other congenital heart defects as part of more complicated syndromes (for example, tetralogy of Fallot). Pathophysiology When pulmonic stenosis (PS) is present, resistance to blood flow causes right ventricular hypertrophy. If right ventricular failure develops, right atrial pressure will increase, and this may result in a persistent opening of the foramen ovale, shunting of unoxygenated blood from the right atrium into the left atrium, and systemic cyanosis. If pulmonary stenosis is severe, congestive heart failure occurs, and systemic venous engorgement will be noted. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Diverticulum
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)