|
Pensacola People
The Pensacola were a Native American people who lived in the western part of what is now the Florida Panhandle and eastern Alabama for centuries before first contact with Europeans until early in the 18th century. They spoke a Muskogean language. They are the source of the name of Pensacola Bay and the city of Pensacola. They lived in the area until the mid-18th century, but were thereafter assimilated into other groups. Pensacola culture The historical Pensacola people lived in part of a region once occupied by a group that archaeologists call the Pensacola culture, a regional variation of the Mississippian culture that lasted from 1100 to 1700 CE. The archaeological culture covers an area stretching from a transitional Pensacola/ Fort Walton culture zone at Choctawhatchee Bay in Florida to the eastern side of the Mississippi River Delta near Biloxi, Mississippi, with the majority of its sites located along Mobile Bay in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta. Sites for the culture stret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottle Creek Indian Mounds
Bottle Creek Indian Mounds ( 1BA2) is an archaeological site owned and monitored by the Alabama Historical Commission located on a low swampy island within the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta north of Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was occupied by the peoples of the Pensacola culture, a regional Mississippian culture variant, and is the largest site of the Mississippian culture on the central Gulf Coast. It is important to understanding the history and culture of the Mobile-Tensaw delta in late prehistoric times and was designated as a National Historic Landmark on March 10, 1995, making it one of only two such sites in Alabama (alongside Moundville Archeological Park). History The site was occupied between 1250 and 1550, and served as the focal point for interaction with other Mississippian culture areas along the coast and the interior of the Southeastern United States. It is located on Mound Island in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta, north of present-day Mobile, and includes 18 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Marcos De Apalache Historic State Park
San Marcos de Apalache Historic State Park is a Florida State Park in Wakulla County, Florida organized around the historic site of a Spanish colonial fort (known as Fort St. Marks by the English and Americans), which was used by succeeding nations that controlled the area. The Spanish first built wooden buildings and a stockade in the late 17th and early 18th centuries here, which were destroyed by a hurricane. The stone fort was built beginning in 1753. It came under successive control by Great Britain, Spain, the United States and, lastly, the Confederacy during the American Civil War. A U.S. Marine Hospital was built from the materials of the fort. The US took control of the site again in 1865, and the fort site was abandoned. On November 13, 1966, the fort area was designated a National Historic Landmark because of its significance and added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. Designated as a National Engineering Landmark, the fort site has been highlighted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachee Province
Apalachee Province was the area in the Panhandle of the present-day U.S. state of Florida inhabited by the Native American peoples known as the Apalachee at the time of European contact. The southernmost extent of the Mississippian culture, the Apalachee lived in what is now Leon County, Wakulla County and Jefferson County. The name was in use during the early period of European exploration. During Spanish colonization, the Apalachee Province became one of the four major provinces in the Spanish mission system, the others being the Timucua Province, (between the St. Johns and Suwanee Rivers), the Mocama Province (along the Atlantic coast of what is now northern Florida and southern Georgia) and the Guale Province (along the Georgia coast north of the Altamaha River). History Around 12,000 years ago, bands of indigenous peoples roamed the hilltops and lake shores of what are now Leon County and Jefferson County. They lived by hunting, fishing and gathering. Eventually they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan De Aspalaga
San Juan de Aspalaga was a Christian mission, mission in the Apalachee Province of Spanish Florida established by Franciscans. It first appears in Spanish records in 1655, when it was located at a distance of 86 League (unit), leagues from St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine (the capital of Spanish Florida), which would place it in the western part of Apalachee Province. By 1675, Aspalaga had moved eastward to the archaeological site known as the Pine Tuft Site, near the present-day town of Wacissa, Florida, about 78 leagues from St. Augustine. By 1695, or at least by 1697, Aspagala had moved back to the western part of Apalachee Province. Aspagala had a population of about 800 in 1675, which had fallen to 250 by 1689. Aspalaga was overrun on June 24, 1704, by Muscogees allied with the Province of Carolina, part of the Apalachee massacre. The site where the mission stood was added to the United States, U.S. National Register of Historic Places on May 7, 1973. See also *Spanish mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parris Island, South Carolina
Parris Island is a district of the city of Port Royal, South Carolina on an island of the same name. It became part of the city with the annexation of the Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island on October 11, 2002. For statistical purposes, the United States Census Bureau previously defined Parris Island as a census-designated place (CDP) when it was an unincorporated area of Beaufort County, South Carolina, Beaufort County. The population was 4,841 at the United States Census, 2000, 2000 census. As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, Parris Island is included within the Beaufort Urban Cluster and the larger Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island–Beaufort, South Carolina, Beaufort Hilton Head Island-Beaufort micropolitan area, Micropolitan Statistical Area. History Parris Island was first colonized by Europeans in 1562, when members of a French expedition led by Jean Ribaut temporarily settled on the island. This was the first semi-permanent European settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Elena (Spanish Florida)
Santa Elena, a Spanish settlement on what is now Parris Island, South Carolina, was the capital of Spanish Florida from 1566 to 1587. It was established under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, the first governor of Spanish Florida. There had been a number of earlier attempts to establish colonies in the area by both the Spanish and the French, who had been inspired by the earlier accounts by Chicora and Hernando de Soto of rich territories in the interior. Menéndez's Santa Elena settlement was intended as the new capital of the Spanish colony of La Florida, shifting the focus of Spanish colonial efforts north from St. Augustine, which had been established in 1565 to oust the French from their colony of Fort Caroline. Santa Elena was ultimately built at the site of the abandoned French outpost of Charlesfort, founded in 1562 by Jean Ribault. In 1565 Menéndez destroyed the French Fort Caroline and then founded Santa Elena. This colony had a sizeable population, including missionaries a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Pensacola, Florida
The history of Pensacola, Florida, begins long before the Spanish claimed founding of the modern city in 1698. The area around present-day Pensacola was inhabited by Native American peoples thousands of years before the historical era. The historical era begins with the arrival of Spanish explorers in the 16th century. In 1559 Tristan de Luna established a short-lived settlement at Pensacola Bay; it was the first multi-year European settlement in what is now the continental United States but was abandoned after two years.John E. Worth, The Tristán de Luna Expedition, 1559-1561, http://uwf.edu/jworth/spanfla_luna.htm "Floripedia: Pensacola, Florida" (history from "The Founding of Pensacola" 1904), University of South Florida, 2005, webpageUSF-Pensac2 In the late 17th century the Spanish returned to the area to found the modern Pensacola as an outpost from which to defend their claims to Spanish Florida. The city's strategic but isolated position, combined with continued Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristán De Luna Y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and Conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://palmm.digital.flvc.org/islandora/object/uwf%3A14851#page/191/mode/1up Biography Born in Borobia, Spain, to a noble family, he came to New Spain, and was sent on an expedition to colonize Florida in 1559. He was a cousin of the viceroy of New Spain, Antonio de Mendoza, and of Juana de Zúñiga, wife of Hernán Cortés. In August of that year, he established an ephemeral colony at modern-day Pensacola, the earliest multi-year European settlement in the continental United States. Pinson, Stev"The Tristan de Luna Expedition" From de-luna.com. Retrieved January 9, 2007. During his years in Mexico, Luna had served with Francisco Vásquez de Coronado on his expedition to the Seven Cities of Cíbola and crushed an Indian rebellion in Oaxaca. Luna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States (through Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and most likely Arkansas). He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River. De Soto's North American expedition was a vast undertaking. It ranged throughout what is now the southeastern United States, both searching for gold, which had been reported by various Native American tribes and earlier coastal explorers, and for a passage to China or the Pacific coast. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River; different sources disagree on the exact location, whether it was what is now Lake Village, Arkansas, or Ferriday, Louisia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabeza De Vaca
In Mexican cuisine, ''cabeza'' (''lit.'' 'head') is the meat from a roasted head of an animal, served as taco or burrito fillings. Typically, the whole head is placed on a steamer or grill, and customers may ask for particular parts of the body meats they favor, such as ''ojo'' (eye), ''oreja'' (ear), ''cachete'' (cheek), ''lengua'' (tongue), or ''labios'' (lips). See also * Brain (as food) * Eggs and brains * Fried-brain sandwich * Maghaz * Phospho-Energon Phospho-Energon, often just called Energon, was a "miracle medicine" produced and distributed in Sweden. Through the sales of Phospho-Energon, the emerging Swedish pharmaceutical company Pharmacia (founded in 1911 out of the ''Elgen'' pharmacy in ... References Beef Brain dishes Mexican cuisine Offal {{meat-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
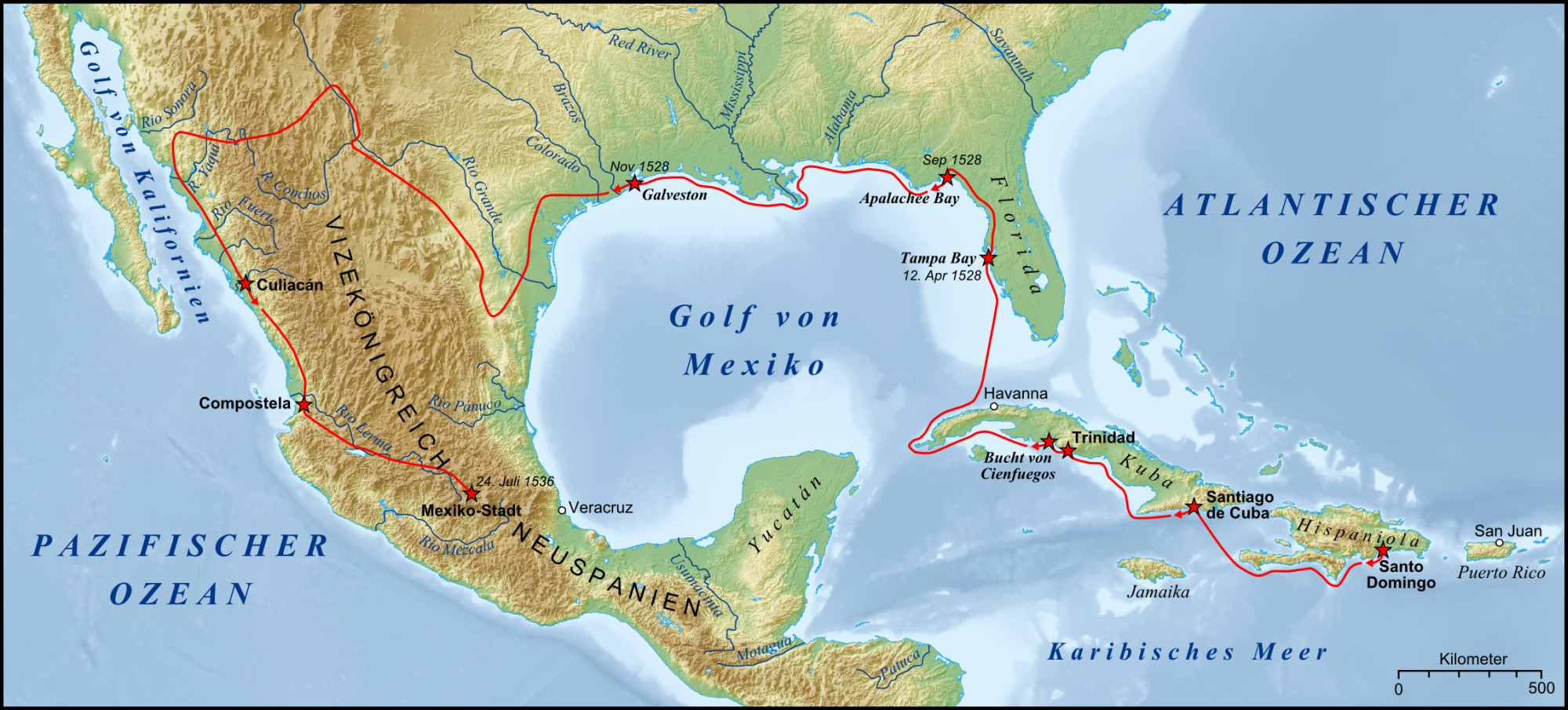
Narváez Expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish journey of exploration and colonization started in 1527 that intended to establish colonial settlements and garrisons in Florida. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. Many more people died as the expedition traveled west along the explored Gulf Coast of the present-day United States and into the American Southwest. Only four of the expedition's original members survived, reaching Mexico City in 1536. These survivors were the first known non-Native Americans to see the Mississippi River, and to cross the Gulf of Mexico and Texas. Narváez's crew initially numbered about 600, including men from Spain, Portugal, Greece, and Italy. The expedition met with disaster almost immediately. Making stops at Hispaniola and Cuba on the way to La Florida, the fleet was devastated by a hurricane, among other storms, and lost two ships. They left Cuba in February 1528. Their intended destination was the Rio de las Palma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |