|
Pencoyd (Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania)
Pencoyd (Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania) was a historic house and farm in Bala Cynwyd, Lower Merion Township, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. Located along the north side of what is now City Avenue, the farm originally stretched from the Schuylkill River to Conshohocken State Road (PA Route 23). Settled by John Roberts in 1683, his descendants owned the property for 280 years. The house was built 1684–1690, and demolished in 1964. Welsh Tract Welsh Quakers faced religious discrimination and harassment in their native land. A group of Welsh Quaker businessmen met with William Penn in London in late 1681, and secured a tract of in his new colony of Pennsylvania. The Welsh Tract was to be contiguous and stretch northwestward along the Schuylkill River from the outskirts of Philadelphia to Valley Forge. The understanding of the businessmen was that the Welsh Tract would be a separate county that they would control, and in which business would be conducted in their native language. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pencoyd Restored Architectural Record April 1915 P
Pencoyd is a hamlet and civil parish in Herefordshire, England. The parish, which also includes the hamlet of Netherton and part of the hamlet of Harewood End, both to the east of Pencoyd hamlet, is approximately south from the city and county town of Hereford and west-northwest from the market town of Ross-on-Wye.Extracted fro"Pencoyd" GridReferenceFinder. Retrieved 22 May 2019 History Pencoyd in 1291 was written as "Pencoyt". The name derives from the Celtic 'penn' with 'coid', meaning 'wood's end'. In 1848 the parish was in the Ross (Ross-on-Wye) Union—poor relief provision set up under the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834—and in the upper division of the Hundred of Wormelow (or Weomelow). Inhabitants numbered 225, within an area of . ''Lewis'' states that "the soil is productive, and inferior sandstone is obtained". It was intersected by the road from Hereford to Ross. The living was a perpetual curacy, united to that of Marstow, and endowed with tithes due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
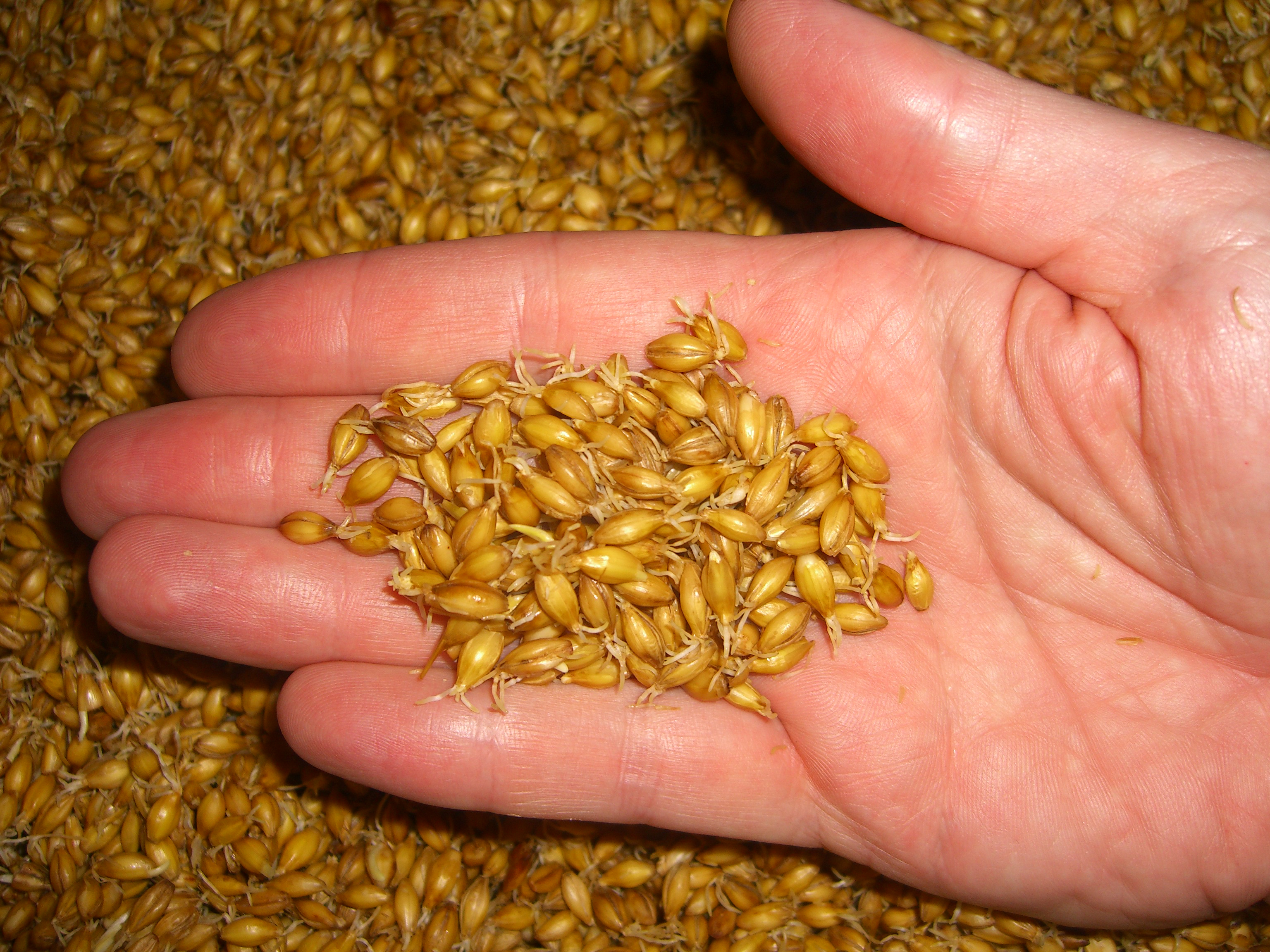
Malt Beer
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air. Malted grain is used to make beer, whisky, malted milk, malt vinegar, confections such as Maltesers and Whoppers, flavored drinks such as Horlicks, Ovaltine, and Milo, and some baked goods, such as malt loaf, bagels, and Rich Tea biscuits. Malted grain that has been ground into a coarse meal is known as "sweet meal". Malting grain develops the enzymes (α-amylase, β-amylase) required for modifying the grains' starches into various types of sugar, including monosaccharide glucose, disaccharide maltose, trisaccharide maltotriose, and higher sugars called maltodextrines. It also develops other enzymes, such as proteases, that break down the proteins in the grain into forms that can be used by yeast. The point at which the malting process is stopped affects the starch-to-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furness & Evans
Furness & Evans was a Philadelphia architectural partnership, established in 1881, between architect Frank Furness and his former chief draftsman, Allen Evans. In 1886, other employees were made partners, and the firm became Furness, Evans & Company. George Howe worked in the firm and later became a partner at Mellor & Meigs, another Philadelphia firm. A number of its works are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. Buildings include (with attribution): * Undine Barge Club, #13 Boat House Row, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1882–83, (Furness & Evans), NRHP-listed. *Hockley Row, 237-241 South 21st Street and 2049 Locust Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1883, (Furness and Evans), NRHP-listed. Allen Evans probably designed this speculative row of houses (his father was the client). * St. Michael's Protestant Episcopal Church, Parish House and Rectory, Mill & Church Streets, Birdsboro, Pennsylvania, 1885–86, (Furness & Evans), NRHP-listed. *Ormonde, East Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen Evans
Allen Evans (December 8, 1849 – February 28, 1925) was an American architect and partner in the Philadelphia firm of Furness & Evans. His best known work may be the Merion Cricket Club. Biography He was the son of Dr. Edmund C. Evans (1813–1881) and Mary S. Allen (1816–1861), of Paoli, Pennsylvania.Sandra L. Tatman"Allen Evans (1849 - 1925),"from Philadelphia Architects and Buildings. He attended schools in West Chester, Pennsylvania, West Chester, followed by Polytechnic College of Pennsylvania, 1866–68. He worked as a draftsman for architect Samuel Sloan (architect), Samuel Sloan, and was working for Frank Furness, Furness & G.W. & W.D. Hewitt, Hewitt by 1872.George E. Thomas, et al., ''Frank Furness: The Complete Works'', (New York: Princeton Architectural Press, revised 1996). When that firm was dissolved in 1875, he remained with Furness, rising to chief draftsman, and partner in 1881. Four other long-term employees were made partners in 1886, and Furness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:George Brooke Roberts
George Brooke Roberts (January 15, 1833 – January 30, 1897) was a civil engineer and the fifth president of the Pennsylvania Railroad (1880–96). Early life and education Roberts was born at his family's farm in the Pencoyd region of Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania. In 1849, he graduated from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and went on to teach there for two years before becoming a rodman for the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR). Beginning in 1852, he worked for the Philadelphia & Erie Railroad, returning to the PRR in 1862 as assistant to the president, J. Edgar Thomson. Roberts oversaw the construction of bridges and other engineering work, including the Connecting Railway Bridge over Schuylkill River in Philadelphia (attributed to John A. Wilson, 1866–67) that connected PRR's southern and northern lines. He became a PRR vice-president in 1869, and succeeded Thomas A. Scott as PRR president in 1880. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 1885. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambrel
A gambrel or gambrel roof is a usually symmetrical two-sided roof with two slopes on each side. (The usual architectural term in eighteenth-century England and North America was "Dutch roof".) The upper slope is positioned at a shallow angle, while the lower slope is steep. This design provides the advantages of a sloped roof while maximizing headroom inside the building's upper level and shortening what would otherwise be a tall roof. The name comes from the Medieval Latin word ''gamba'', meaning horse's hock or leg. The term ''gambrel'' is of American origin, the older, European name being a curb (kerb, kirb) roof. Europeans historically did not distinguish between a gambrel roof and a mansard roof but called both types a mansard. In the United States, various shapes of gambrel roofs are sometimes called Dutch gambrel or Dutch Colonial gambrel with bell-cast eaves, Swedish, German, English, French, or New England gambrel. The cross-section of a gambrel roof is similar to tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic American Buildings Survey, Photocopy, RESTORED PLANS AND ELEVATIONS, 1962
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pencoyd - GBR 1849 Elevation Rotated & Cropped
Pencoyd is a hamlet and civil parish in Herefordshire, England. The parish, which also includes the hamlet of Netherton and part of the hamlet of Harewood End, both to the east of Pencoyd hamlet, is approximately south from the city and county town of Hereford and west-northwest from the market town of Ross-on-Wye.Extracted fro"Pencoyd" GridReferenceFinder. Retrieved 22 May 2019 History Pencoyd in 1291 was written as "Pencoyt". The name derives from the Celtic 'penn' with 'coid', meaning 'wood's end'. In 1848 the parish was in the Ross (Ross-on-Wye) Union—poor relief provision set up under the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834—and in the upper division of the Hundred of Wormelow (or Weomelow). Inhabitants numbered 225, within an area of . ''Lewis'' states that "the soil is productive, and inferior sandstone is obtained". It was intersected by the road from Hereford to Ross. The living was a perpetual curacy, united to that of Marstow, and endowed with tithes due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
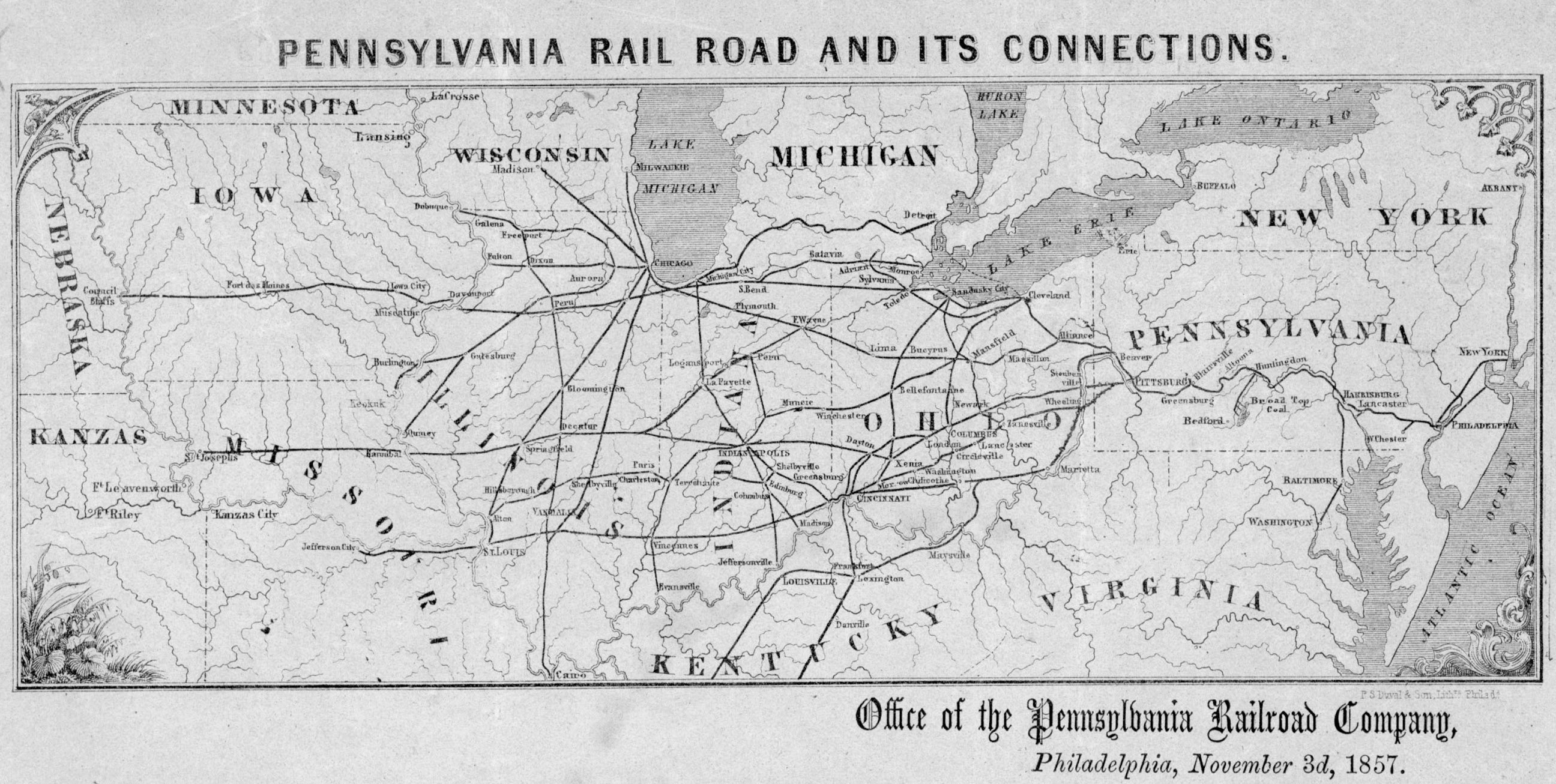
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brooke Roberts
George Brooke Roberts (January 15, 1833 – January 30, 1897) was a civil engineer and the fifth president of the Pennsylvania Railroad (1880–96). Early life and education Roberts was born at his family's farm in the Pencoyd region of Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania. In 1849, he graduated from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and went on to teach there for two years before becoming a rodman for the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR). Beginning in 1852, he worked for the Philadelphia & Erie Railroad, returning to the PRR in 1862 as assistant to the president, J. Edgar Thomson. Roberts oversaw the construction of bridges and other engineering work, including the Connecting Railway Bridge over Schuylkill River in Philadelphia (attributed to John A. Wilson, 1866–67) that connected PRR's southern and northern lines. He became a PRR vice-president in 1869, and succeeded Thomas A. Scott as PRR president in 1880. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 1885. Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Troop Philadelphia City Cavalry
The First Troop Philadelphia City Cavalry, also known as the First City Troop, is a unit of the Pennsylvania Army National Guard. It is one of the oldest military units in the United States still in active service and is among the most decorated units in the U.S. Army. Accordingly, the Troop operates under a number of principles of self-governance unique in the U.S. military, including the election of unit members and officers, voluntarily forgoing pay for military service to the country, continuing to practice horse cavalry skills and tactics, and recruiting a high percentage of its members from veterans of prior active duty service across all branches (many of whom resign past officer commissions to join), as well as older civilian mid-career professionals. It is the only U.S. military unit that owns its own armory building, built with private funds in Philadelphia's Rittenhouse Square neighborhood. As of November 2017, the troop had 46 active members (33 drilling with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Company Of Philadelphia
The Library Company of Philadelphia (LCP) is a non-profit organization based in Philadelphia. Founded in 1731 by Benjamin Franklin as a library, the Library Company of Philadelphia has accumulated one of the most significant collections of historically valuable manuscripts and printed material in the United States. The current collection size is approximately 500,000 books and 70,000 other items, including 2,150 items that once belonged to Franklin, the Mayflower Compact, major collections of 17th-century and Revolution-era pamphlets and ephemera, maps, and whole libraries assembled in the 18th and 19th centuries. The collection also includes first editions of ''Moby-Dick'' and ''Leaves of Grass''. Early history The Library Company was an offshoot of the Junto, a discussion group in colonial Philadelphia, that gravitated around Benjamin Franklin. On July 1, 1731, Franklin and a number of his fellow members among the Junto drew up articles of agreement to found a library, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)