|
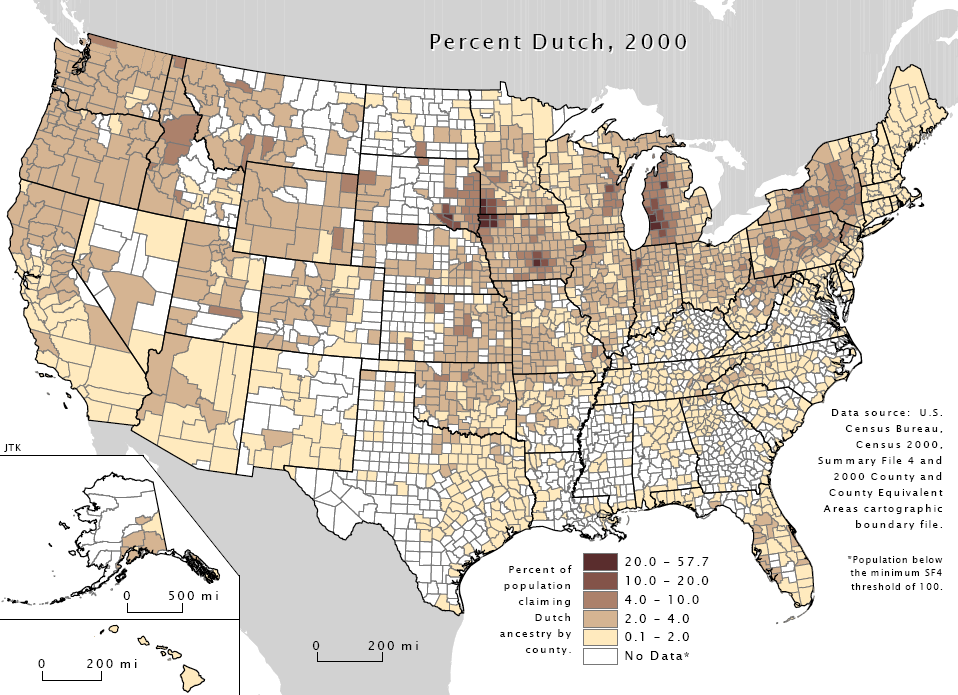
Pella Dutch Dialect
Pella Dutch, also known as Iowa Dutch, is a dialect of the Dutch language spoken in Pella, Iowa. It is a subdialect of South Guelderish. Pella Dutch's origins began with the migration of a group of 800 Dutch settlers under the leadership of Dominee (Reverend) H. P. Scholte in 1847. In 1860, the Pella Weekblad, Pella's first Dutch language Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. '' Afrikaans'' ... newspaper, debuted. The paper continued to be published weekly until 1941. Language use was strongly affected by Governor William L. Harding's controversial 1917 Babel Proclamation, which banned the speaking of languages other than English in public. Semi-speakers of the dialect have been attested as recently as 2011. References Pella, Iowa Dutch-American culture in Iowa Dutch dialects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pella, Iowa
Pella is a city in Marion County, Iowa, United States, with a population of 10,464 at the time of the 2020 U.S. Census The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of .... Founded by immigrants from the Netherlands, it is forty miles southeast of Des Moines, Iowa, Des Moines. Pella is the home of Central College (Iowa), Central College, as well as several manufacturing companies, including Pella (company), Pella Corporation and Vermeer Company, Vermeer Manufacturing Company. History In 1847, 800 Dutch people, Dutch immigrants led by Dominee (Minister (Christianity), Minister) Hendrik "Henry" P. Scholte settled the area known as Pella. The name "Pella" is a reference to Pella, Jordan, Pella of the Decapolis, where the Christians of Jerusalem had found refuge during the Siege of Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of Standard language, unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germanic Languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English language, English and Frisian languages, Frisian, Istvaeonic, which includes Dutch language, Dutch and its close relatives, and Irminonic, which includes German language, German and its close relatives and variants. English language, English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German language, German, and Dutch language, Dutch. Frisian languages, Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser-Rhine Germanic
Weser-Rhine Germanic is a proposed group of prehistoric West Germanic dialects which would have been both directly ancestral to Dutch, as well as being a notable substratum influencing West Central German dialects. The term was introduced by the German linguist Friedrich Maurer as a replacement for the older term Istvaeonic, with which it is essentially synonymous. The term ''Rhine-Weser-Germanic'' is sometimes preferred. Nomenclature The term ''Istvaeonic'' is derived from the Istvæones (or Istvaeones), a culturo-linguistic grouping of Germanic tribes, mentioned by Tacitus in his ''Germania''. Pliny the Elder further specified its meaning by claiming that the Istævones lived near the Rhine. Maurer used Pliny to refer to the dialects spoken by the Franks and Chatti around the northwestern banks of the Rhine, which were presumed to be descendants of the earlier Istvaeones. The Weser is a river in Germany, east of and parallel to the Rhine. The terms ''Rhine-Weser'' or ''Weser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Franconian Languages
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay: ''The History of English: A Linguistic Introduction'', Wardja Press, 2008, p. 73. (Having "Old Low Franconian" and mentioning "Old Low Frankish" and "Old Netherlandic".) is a linguistic category used to classify a number of historical and contemporary West Germanic varieties closely related to, and including, the Dutch language. Most dialects and languages included within the category are spoken in the Netherlands, northern Belgium (Flanders), in the Nord department of France, in western Germany (Lower Rhine), as well as in Suriname, South Africa and Namibia. Terminology The term ''Frankish'' or ''Franconian'' as a modern linguistic category was coined by the German linguist Wilhelm Braune (1850–1926). He divided Franconian which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language spoken country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Guelderish
South Guelderish ( nl, Zuid-Gelders , german: Südgeldersch, ''Kleverländisch'') refers to the easternmost group of Dutch dialects spoken along the lower Rhine (Dutch Nederrijn and German Niederrhein). In its narrower sense, the term refers strictly to the Rivierenlands ( nl), Nijmeegs, and Liemers sub-dialects; in its broader sense, the term encompasses also North Limburgish in the Netherlands and Kleverlander (around Cleves; Dutch ''Kleverlands'', German ''Kleverländisch'') in Germany. South Guelderish (in the narrow sense) — especially Rivierenlands — is sometimes included as part of Brabantic, a more widely spoken Dutch dialect and the closest relative of South Guelderish. Alternatively, it is considered to extend southward into Northern Limburg until the Uerdingen line. It is arguably more appropriate to group South Guelderish (narrow sense), North Limburgish and, Kleverlander into one dialect group—East Dutch. In the Netherlands, South Guelderish is spoken in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babel Proclamation
The Babel Proclamation was issued by Iowa's Governor William L. Harding on May 23, 1918. It forbade the speaking of any language besides English in public. The proclamation was controversial, supported by many established English-speaking Iowans and notably opposed by citizens who spoke languages other than English. Harding repealed it on December 4, 1918. The Babel Proclamation marked the peak of a wave of anti-German sentiment in Iowa during World War I. Rise in anti-German sentiment As America became involved in World War I on the side of the Allies and against Germany, the nation saw a rise in anti-German sentiment. Nativism, which had existed before the war, became increasingly mainstream as a result of American intervention. The state of Iowa saw a particularly large rise in anti-German sentiment. On November 23, 1917, the Iowa State Council for Defense determined that German should not be taught in public schools and took actions to that effect, such as burning German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch-American Culture In Iowa
Dutch Americans ( nl, Nederlandse Amerikanen) are Americans of Dutch descent whose ancestors came from the Netherlands in the recent or distant past. Dutch settlement in the Americas started in 1613 with New Amsterdam, which was exchanged with the English for Suriname at the Treaty of Breda (1667) and renamed New York City. The English split the Dutch colony of New Netherland into two pieces and named them New York and New Jersey. Further waves of immigration occurred in the 19th and 20th centuries. Prominent (partial) Dutch American political figures include Presidents Martin Van Buren, Warren G. Harding, and Theodore and Franklin D. Roosevelt and U.S. Senators Philip Schuyler, Nicholas Van Dyke, Hamilton Fish, John C. Ten Eyck, Daniel W. Voorhees, Arthur Vandenberg, Peter G. Van Winkle, Alan Simpson, Fred Thompson, John Hoeven, and Christopher Van Hollen. Two of the Founding Fathers of the United States, Egbert Benson and John Jay, were also of Dutch descent. Governors John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Dialects
Dutch dialects are primarily the dialects that are both cognate with the Dutch language and are spoken in the same language area as the Dutch standard language. Dutch dialects are remarkably diverse and are found in the Netherlands and Flanders, northern Belgium. The province of Friesland is bilingual. The West Frisian language, distinct from Dutch, is spoken here along with standard Dutch and the Stadsfries dialect. A West Frisian standard language has also been developed. First dichotomy In the east, there is the Dutch Low Saxon language area: in Groningen (province), Groningen, Drenthe, Overijssel, major parts of Gelderland, and parts of Flevoland, Friesland and Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The group is not Low Franconian and forms together with the Low Saxon variants in Germany the West Low German, Low Saxon language. Image:Nederfrankisch.png, Map of traditional Low Franconian dialects Image:Koart Leegsaksisch.png, Low Saxon in the Netherlands Extension across the borders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)