|
Pectoral Axillary Lymph Nodes
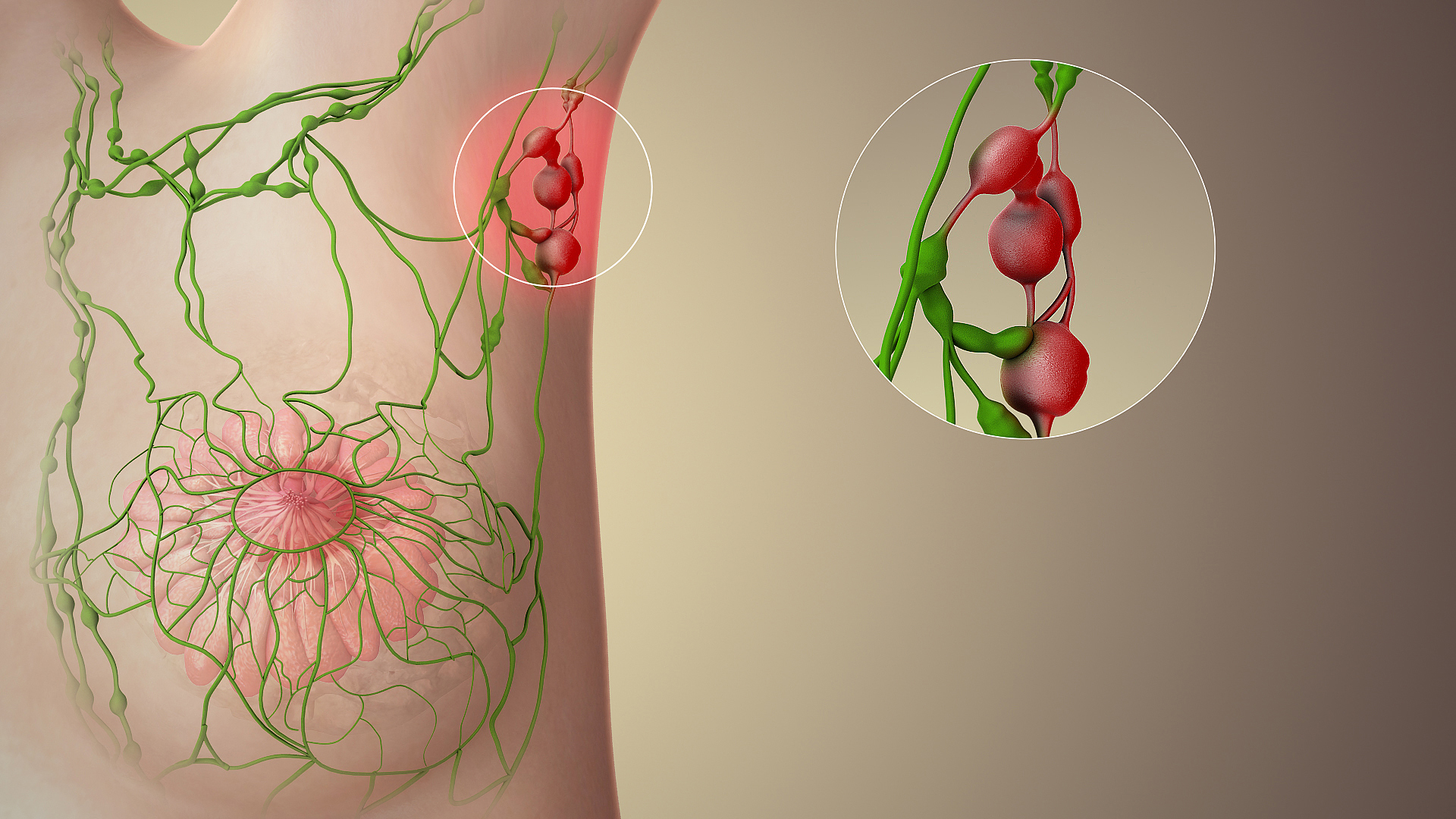
An anterior or pectoral group consists of four or five glands along the lower border of the Pectoralis minor, in relation with the lateral thoracic artery. Their afferents drain the skin and muscles of the anterior and lateral thoracic walls, and the central and lateral parts of the mamma; their efferents pass partly to the central and partly to the subclavicular groups of axillary glands The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the .... Additional images File:Illu lymph chain03.jpg, Lymph Nodes of the Upper Limb and Breast References External links * () Lymphatics of the upper limb {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Lymph Nodes
A central or intermediate group of three or four large glands is imbedded in the adipose tissue near the base of the axilla. Its afferent lymphatic vessels are the efferent vessels of all the preceding groups of axillary glands; its efferents pass to the subclavicular group An apical (or medial or subclavicular) group of six to twelve glands is situated partly posterior to the upper portion of the Pectoralis minor and partly above the upper border of this muscle. Its only direct territorial afferents are those that .... Additional images Image:Illu lymph chain03.jpg, Lymph Nodes of the Upper Limb and Breast References External links * () Lymphatics of the upper limb {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoralis Minor
Pectoralis minor muscle () is a thin, triangular muscle, situated at the upper part of the chest, beneath the pectoralis major in the human body. Structure Attachments Pectoralis minor muscle arises from the upper margins and outer surfaces of the third, fourth, and fifth ribs, near their costal cartilages and from the aponeuroses covering the intercostalis. The fibers pass superior and lateral and converge to form a flat tendon. This tendon inserts onto the medial border and upper surface of the coracoid process of the scapula. Relations Pectoralis minor muscle forms part of the anterior wall of the axilla. It is covered anteriorly (superficially) by the clavipectoral fascia. The medial pectoral nerve pierces the pectoralis minor and the clavipectoral fascia. In attaching to the coracoid process, the pectoralis minor forms a 'bridge' - structures passing into the upper limb from the thorax will pass directly underneath.http://www.teachmeanatomy.com/muscles-of-the-pector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Thoracic Artery
In human anatomy, the lateral thoracic artery (or external mammary artery) is a blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the lateral structures of the thorax and breast. It originates from the axillary artery and follows the lower border of the Pectoralis minor muscle to the side of the chest, supplies the Serratus anterior muscle and the Pectoralis major muscle, and sends branches across the axilla to the axillary lymph nodes and Subscapularis muscle. It anastomoses with the internal thoracic artery, subscapular, and intercostal arteries, and with the pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial artery. In the female it supplies an external mammary branch which turns round the free edge of the Pectoralis major and supplies the breast The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
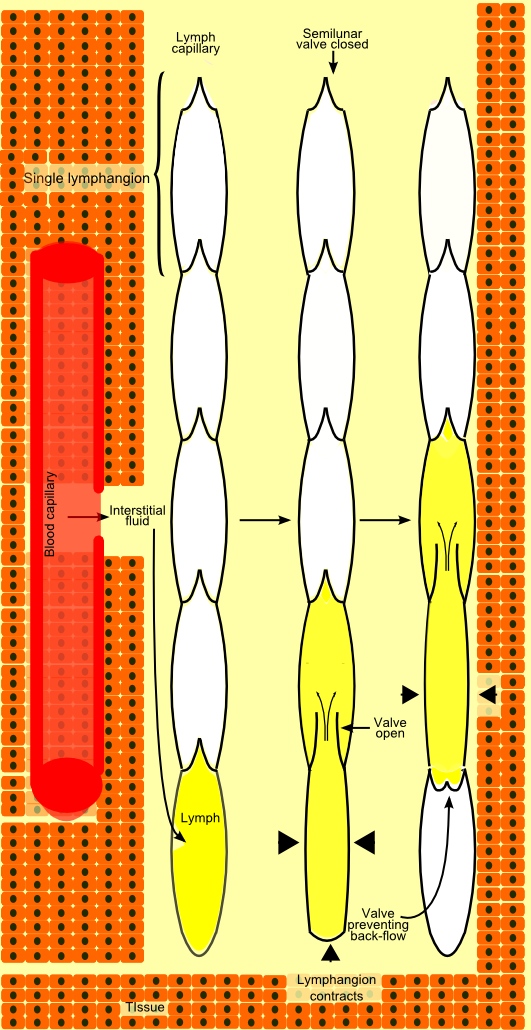
Afferent Lymphatic Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Walls
The thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity. Structure The bony skeletal part of the thoracic wall is the rib cage, and the rest is made up of muscle, skin, and fasciae. The chest wall has 10 layers, namely (from superficial to deep) skin (epidermis and dermis), superficial fascia, deep fascia and the invested extrinsic muscles (from the upper limbs), intrinsic muscles associated with the ribs (three layers of intercostal muscles), endothoracic fascia and parietal pleura. However, the extrinsic muscular layers vary according to the region of the chest wall. For example, the front and back sides may include attachments of large upper limb muscles like pectoralis major or latissimus dorsi, while the sides only have serratus anterior. Function Diving reflex When not breathing for long and dangerous periods of time in cold water, a person's body undergoes great temporary changes to try to prevent death. It achieves this through the activation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamma (anatomy)
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to a much lesser e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efferent Lymphatic Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclavicular Groups
An apical (or medial or subclavicular) group of six to twelve glands is situated partly posterior to the upper portion of the Pectoralis minor and partly above the upper border of this muscle. Its only direct territorial afferents are those that accompany the cephalic vein, and one that drains the upper peripheral part of the mamma. However, it receives the efferents of all the other axillary glands. The efferent vessels of the subclavicular group unite to form the subclavian trunk, which opens either directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins or into the jugular lymphatic trunk; on the left side it may end in the thoracic duct In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the right .... A few efferents from the subclavicular glands usually pass to the inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Glands
The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease. Structure The axillary lymph nodes are arranged in six groups: # Anterior (pectoral) group: Lying along the lower border of the pectoralis minor behind the pectoralis major, these nodes receive lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast and superficial vessels from the anterolateral abdominal wall above the level of the umbilicus. # Posterior (subscapular) group: Lying in front of the subscapularis muscle, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |