|
Peace Vallis
Peace Vallis is an ancient stream valley on the northern rim of Gale Crater on the planet Mars. It is notable for its associated alluvial fan which lies near the Mars Science Laboratory ''Curiosity'' landing site (Bradbury Landing). The valley and alluvial fan provide evidence for geologically recent ( Amazonian-aged) fluvial activityNewsom, H.E.; Scuderi, L.A.; Gallegos, Z.E.; Williams, J.M.; Dimitracopoulos, F.D.; Tornabene, L.L.; Wiens, R.C.; Gasnault, O. (2021). Evidence for Glacial and Fluvial Processes on Gale Crater Rim—Dulce Vallis. ''52nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference,'' Abstract #2256. https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2021/pdf/2256.pdf.Ehlmann, B.L.; Buz, J. (2015). Mineralogy and fluvial History of the Watersheds of Gale, Knobel, and Sharp Craters: A Regional Context for the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity's Exploration. ''Geophys. Res. Lett.,'' 42, 264–273, doi:10.1002/2014GL062553. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/2014GL06 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachian
The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain but probably corresponds to the lunar Pre-Nectarian to Early Imbrian periods of 4100 to 3700 million years ago, during the interval known as the Late Heavy Bombardment. Many of the large impact basins on the Moon and Mars formed at this time. The Noachian Period is roughly equivalent to the Earth's Hadean and early Archean eons when the first life forms likely arose. Noachian-aged terrains on Mars are prime spacecraft landing sites to search for fossil evidence of life. During the Noachian, the atmosphere of Mars was denser than it is today, and the climate possibly warm enough to allow rainfall. Large lakes and rivers were present in the southern hemisphere, and an ocean may have covered the low-lying northern plains. Extensive volc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiltration Capacity
Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. It is commonly used in both hydrology and soil sciences. The infiltration capacity is defined as the maximum rate of infiltration. It is most often measured in meters per day but can also be measured in other units of distance over time if necessary. The infiltration capacity decreases as the soil moisture content of soils surface layers increases. If the precipitation rate exceeds the infiltration rate, runoff will usually occur unless there is some physical barrier. Infiltrometers, permeameters and rainfall simulators are all devices that can be used to measure infiltration rates. Infiltration is caused by multiple factors including; gravity, capillary forces, adsorption and osmosis. Many soil characteristics can also play a role in determining the rate at which infiltration occurs. Factors that affect infiltration Precipitation Precipitation can impact infiltration in many ways. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Density
Drainage density is a quantity used to describe physical parameters of a drainage basin. First described by Robert E. Horton, drainage density is defined as the total length of channel in a drainage basin divided by the total area, represented by the following equation: D_=\frac The quantity represents the average length of channel per unit area of catchment and has units \frac, which is often reduced to \left ^\right/math>. Drainage density depends upon both climate and physical characteristics of the drainage basin. Soil permeability (infiltration difficulty) and underlying rock type affect the runoff in a watershed; impermeable ground or exposed bedrock will lead to an increase in surface water runoff and therefore to more frequent streams. Rugged regions or those with high relief will also have a higher drainage density than other drainage basins if the other characteristics of the basin are the same. When determining the total length of streams in a basin, both perennial and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colluvium
Colluvium (also colluvial material or colluvial soil) is a general name for loose, unconsolidated sediments that have been deposited at the base of hillslopes by either rainwash, sheetwash, slow continuous downslope creep, or a variable combination of these processes. Colluvium is typically composed of a heterogeneous range of rock types and sediments ranging from silt to Rock (geology), rock fragments of various sizes. This term is also used to specifically refer to sediment deposited at the base of a hillslope by unconcentrated surface runoff or sheet erosion. Location Colluviation refers to the buildup of colluvium at the base of a hillslope.Jackson, JA, J Mehl, and K. Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. Goodie, AS (2003) ''Colluvium'' in A. S. Goodie, ed., pp. 173, Encyclopedia of Geomorphology Volume 1, A–I. Routledge, New York, New York. 1200 pp. Colluvium is typically loosely consolidated angular materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erode, transport, and deposit materials and are effective agents in regions with sparse vegetation, a lack of soil moisture and a large supply of unconsolidated sediments. Although water is a much more powerful eroding force than wind, aeolian processes are important in arid environments such as deserts. The term is derived from the name of the Greek god Aeolus, the keeper of the winds. Definition and setting ''Aeolian processes'' are those processes of erosion, transport, and deposition of sediments that are caused by wind at or near the surface of the earth. Sediment deposits produced by the action of wind and the sedimentary structures characteristic of these deposits are also described as ''aeolian''. Aeolian processes are most important in areas where there is little or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowmelt
In hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many parts of the world, in some cases contributing high fractions of the annual runoff in a watershed. Predicting snowmelt runoff from a drainage basin may be a part of designing water control projects. Rapid snowmelt can cause flooding. If the snowmelt is then frozen, very dangerous conditions and accidents can occur, introducing the need for salt to melt the ice. Energy fluxes related to snowmelt There are several energy fluxes involved in the melting of snow. These fluxes can act in opposing directions, that is either delivering heat to or removing heat from the snowpack. Ground heat flux is the energy delivered to the snowpack from the soil below by conduction. Radiation inputs to the snowpack include net shortwave (solar radiation including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headward Erosion
Headward erosion is erosion at the origin of a stream channel, which causes the origin to move back away from the direction of the stream flow, lengthening the stream channel.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak It can also refer to widening of a canyon by erosion along its very top edge, when sheets of water first enter the canyon from a more roughly planar surface above it, such as at Canyonlands National Park in Utah. When sheets of water on a roughly planar surface first enter a depression in it, this erodes the top edge of the depression. The stream is forced to grow longer at the very top of the stream, which moves its origin back, or causes the canyon formed by the stream to grow wider as the process repeats. Widening of the canyon by erosion inside the canyon, below the canyon side top edge, or origin or the stream, such as erosion caused by the streamflow inside it, is not called headward erosion. Headward erosion is a fluvial process of erosion that leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in a moving medium, such as water, wind, or ice. Types of mass wasting include creep, solifluction, rockfalls, debris flows, and landslides, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place over timescales from seconds to hundreds of years. Mass wasting occurs on both terrestrial and submarine slopes, and has been observed on Earth, Mars, Venus, Jupiter's moons Io, and on many other bodies in the Solar System. Subsidence is sometimes regarded as a form of mass wasting. A distinction is then made between mass wasting by subsidence, which involves little horizontal movement, and mass wasting by slope movement. Rapid mass wasting events, such as landslides, can be deadly and destructive. More gradual mass wasting, such as soil cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
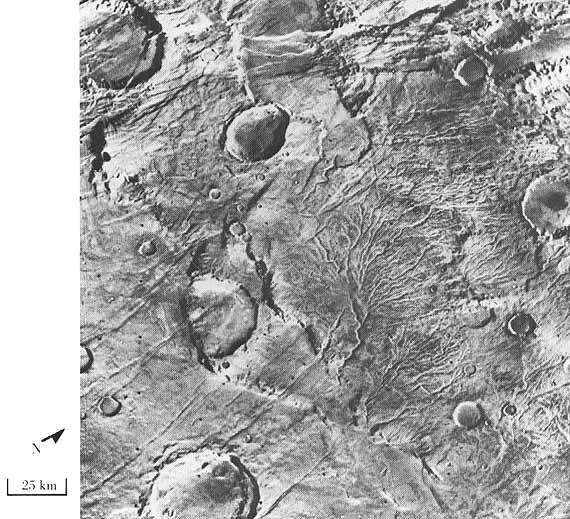
Valley Network (Mars)
Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press. They are found mainly incised into the terrain of the martian southern highlands, and are typically - though not always - of Noachian age (approximately four billion years old). The individual valleys are typically less than 5 kilometers wide, though they may extend for up to hundreds or even thousands of kilometers across the martian surface. The form, distribution, and implied evolution of the valley networks are of great importance for what they may tell us about the history of liquid water on the martian surface, and hence Mars' climate history. Some authors have argued that the properties of the networks demand that a hydrological cycle must have been active on ancient Mars,Craddock, R.A., and Howard, A.D. (2002), The case for rainfall on a warm, wet earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vallis (planetary Geology)
''Vallis'' or ''valles'' (plural ''valles'' ) is the Latin word for ''valley''. It is used in planetary geology to name landform features on other planets. Scientists used ''vallis'' for old river valleys they discovered when they sent the first probes to Mars. The Viking Orbiters caused a revolution in our ideas about water on Mars; finding huge river valleys in many areas. Space craft cameras showed that floods of water broke through dams, carved deep valleys, eroded grooves into bedrock, and traveled thousands of kilometers. Some valles on Mars (Mangala Vallis, Athabasca Vallis, Granicus Vallis, and Tinjar Valles) clearly begin at graben. On the other hand, some of the large outflow channels begin in rubble-filled low areas, called chaos or chaotic terrain. It has been suggested that massive amounts of water were trapped under pressure beneath a thick cryosphere (layer of frozen ground), then the water was suddenly released, perhaps when the cryosphere was broken by a fault. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |