|
Paʻao
Paao is a figure from Hawaii. He is most likely a Hawaiian historical character retold through Hawaiian legend. According to Hawaiian tradition and folklore, he is said to have been a high priest from Kahiki, specifically "Wewaʻu" and "ʻUpolu." In Hawaiian prose and chant, the term "Kahiki" is applied in reference to any land outside of Hawaii, although the linguistic root is conclusively derived from Tahiti. "Wewaʻu" and "Upolu" point to actual places in the Society Islands, Samoa, and Hawaiian scholars and royal commentators consistently claim Paao came from Samoa; he was a Samoan priest with properties in both Tonga and Samoa. He arrived on the north shores of the Big Island and named it "Upolu" after Samoa main village (also known as "Western Samoa"). Scholars of Hawaiian lore including David Malo, Samuel M. Kamakau, John Papa ʻĪʻī, Solomon Peleioholani, Teuira Henry, and Stephen L. Desha support the notion that Pili and Pa'ao immigrated from the Society Islands of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands. Hawaii was settled at least 800 years ago with the voyage of Polynesians from the Society Islands. The settlers gradually became detached from their original homeland and developed a distinct Hawaiian culture and identity in their new isolated home. That included the creation of new religious and cultural structures, mostly in response to the new living environment and the need for a structured belief system through which to pass on knowledge. Hence, the Hawaiian religion focuses on ways to live and relate to the land and instills a sense of communal living as well as a specialized spatial awareness. The Hawaiian Kingdom was formed in 1795, when Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oʻ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pili Line
Pili line (House of Pili, Pili dynasty; Hawaiian language: ''Hale o Pili'') was a royal house in ancient Hawaii that ruled over the island of Hawaiʻi with deep roots in the history of Samoa and possibly beyond further to the west, Ao-Po ("gathering of night"; metaphorically: "extreme west", "the land of the dead"), in Pulotu, the Samoan Underworld. It was founded on unknown date by King Pilikaʻaiea (Pili), who either was born in or came from either Upolu, Samoa or Uporu, Tahiti, but came to Hawaii and established his own dynasty of kings (''Aliʻi''). The overall arc of his career describes a brilliant young chief from foreign lands who was eager to share his abundant knowledge of advanced technology with distant frontier rustics. Some stories relate how his ambition got the better of him and damaged his relationships with his subjects. These stories cast him as a libidinous, restless and petty tyrant ever on the move searching for new conquests. According to Samoan lore, Pili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
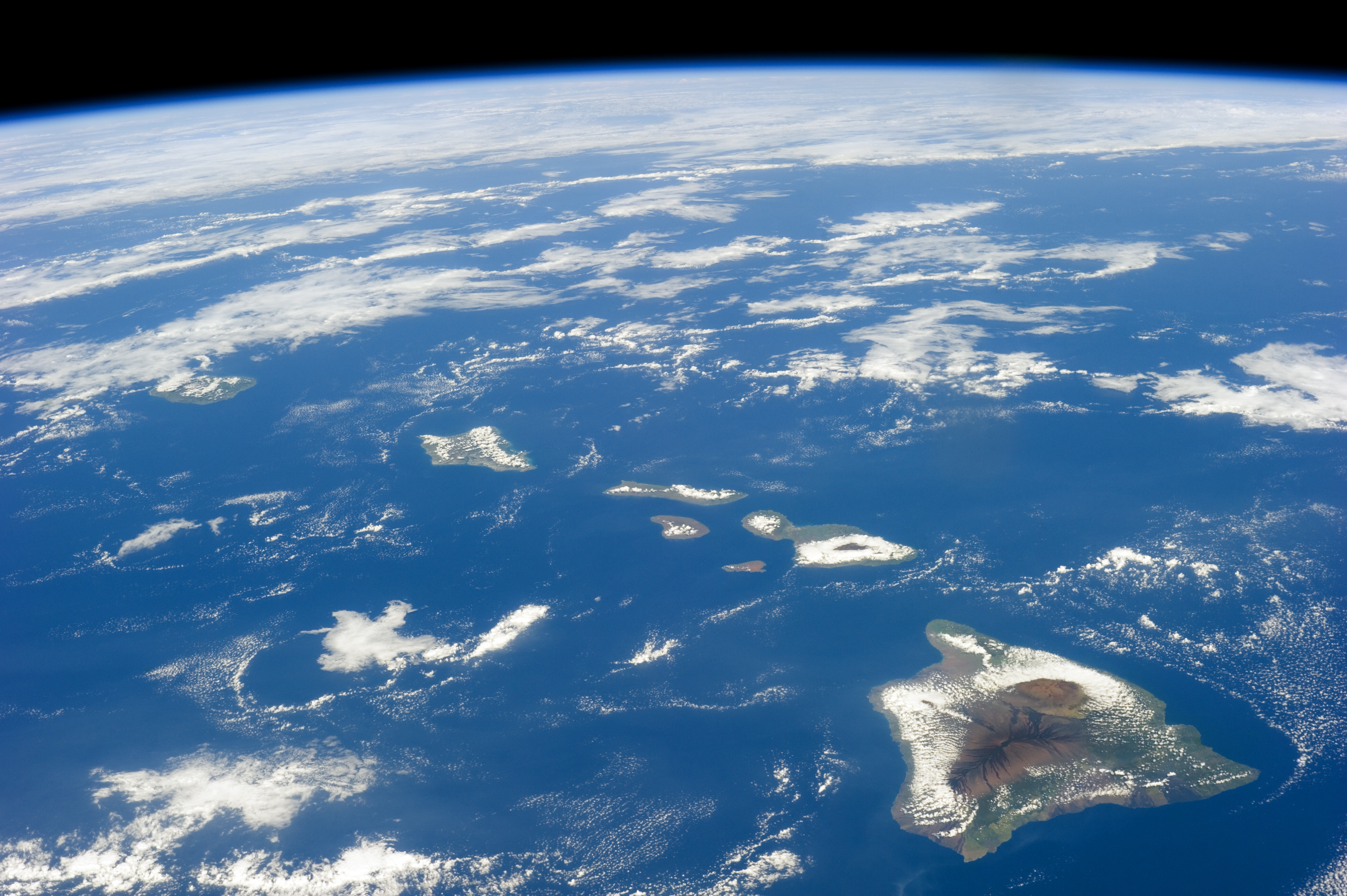
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state geographically located within the tropics. Hawaii comprises nearly the entire Hawaiian archipelago, 137 volcanic islands spanning that are physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lānai, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii—the last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the United States' largest protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonito
Bonitos are a tribe of medium-sized, ray-finned predatory fish in the family Scombridae – a family it shares with the mackerel, tuna, and Spanish mackerel tribes, and also the butterfly kingfish. Also called the tribe Sardini, it consists of eight species across four genera; three of those four genera are monotypic, having a single species each. Bonitos closely resemble the skipjack tuna, which is often called a bonito, especially in Japanese contexts. Etymology The fish's name comes from the Spanish ''bonito'' 'pretty'.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 3rd edition, 2018''s.v.''/ref> An older theory suggests that it comes from an Arabic word ''bainīth'', but that may have been derived from Spanish as well. Species * Genus '' Sarda'' ( Cuvier, 1832) ** Australian bonito, ''S. australis'' (Macleay, 1881) ** '' Sarda chiliensis'' (Cuvier, 1832) *** Eastern Pacific bonito, ''S. c. chiliensis'' (Cuvier, 1832) *** Pacific bonito, ''S. c. lineolata'' ( Girard, 1858) ** Striped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heiau
A ''heiau'' () is a Hawaiian temple. Made in different architectural styles depending upon their purpose and location, they range from simple earth terraces, to elaborately constructed stone platforms. There are heiau to treat the sick (''heiau hōola''), offer first fruits, offer first catch, start rain, stop rain, increase the population, ensure the health of the nation, achieve success in distant voyaging, reach peace, and achieve success in war (''luakini''). Only the luakini was dedicated through human sacrifice. There are two types of luakini. They were called the ''ohia ko'' and ''hakuohia''.Samuel Kamakau, ''Ka Poe Kahiko; The People of Old'' (Honolulu: Bishop Museum Press, 1993), 130. After the official end of Hawaiian religion in 1819 and with later pressure from Christian missionaries (who first arrived in 1820), many were deliberately destroyed, while others were allowed to fall into disrepair. Heiau are still considered sacred by many of the inhabitants of Hawaii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Drake Westervelt
William Drake Westervelt (December 26, 1849 – March 9, 1939) was the author of several books and magazines on Hawaiian history and legends. He drew upon the collections of David Malo, Samuel Kamakau, and Abraham Fornander to popularize Hawaiian folklore in his ''Legends of Maui'' (1910), ''Legends of Old Honolulu'' (1915), ''Legends of Gods and Ghost-Gods'' (1915), ''Hawaiian Legends of Volcanoes'' (1916) and ''Hawaiian Historical Legends'' (1923). Biography Rev. William D. Westervelt was born in Oberlin, Ohio. He graduated from Oberlin College in 1871 with a B.A. degree, and from Oberlin Theological Seminary in 1874 with a B.D. degree. Pastor of churches in Cleveland, Ohio and Colorado, he settled in Hawaii in 1899, marrying a missionary descendant, Caroline Dickinson Castle (1859–1941). After the Hawaiian Historical Society was re-formed, he served as the Corresponding Secretary starting in 1908. He would later serve as treasurer and president. Westervelt's interest in Haw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrum's Hawaiian Annual
''Thrum's Hawaiian Annual'' (fully ''Thrum's Hawaiian Annual and Standard Guide''; alternatively ''All About Hawaii'') is a statistical compendium of Hawaiiana ranging from Hawaiian mythology to Hawaiian language to sites of interest in Hawaii, published by Star-Bulletin Printing Co. The original research was compiled by antiquarian bookman Thomas George Thrum and first published in 1875 as ''The Hawaiian Annual and Almanac''. Contributors to Thrum's Hawaiian Annual include the artist Bessie Wheeler. In 1908 the Hamilton Library acquired the Thrum Hawaiiana collection. Further reading * Thomas G. Thrum, ''More Hawaiian Folk Tales'', Chicago, 1923 * Thomas G. Thrum, Hawaiian Folk Tales: A Collection of Native Legends, International Law & Taxation Publishers, 2001 * Thomas G. Thrum, More Hawaiian Folk Tales: A Collection of Native Legends and Traditions, International Law & Taxation Publishers, 2001 External linksThrum's Hawaiian Annualat University of Hawaii at ManoaThrum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathaniel Bright Emerson
Nathaniel Bright Emerson (July 1, 1839 Waialua, Oahu – July 16, 1915, at sea) was a medical physician and author of Hawaiian mythology. He was the son of Protestant missionaries John S. Emerson and Ursula Newell Emerson, and father of artist Arthur Webster Emerson. He attended Williams College in Williamstown, Massachusetts. He joined the 1st Regiment Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry of the Union Army as a private on September 22, 1862 in Boston during the Civil War. He was wounded three times. After graduating from Williams in 1865, he studied at Harvard and the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York City, from which he graduated in 1869. This was followed by work at Bellevue Hospital in New York City. In New York, Emerson was associated with Willard Parker, a surgeon, as student and assistant. For several years he was also clinical assistant to Dr. Seguin, professor of nervous diseases at the College of Physicians and Surgeons. He served as a doct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martha Warren Beckwith
Martha Warren Beckwith (January 19, 1871 – January 28, 1959) was an American folklorist and ethnographer, appointed to the first chair in Folklore established in the U.S. Early life and education Beckwith was born in Wellesley Heights, Massachusetts to George Ely and Harriet Winslow (née Goodale) Beckwith, both schoolteachers, before the family moved to Maui, Hawaii, where they had relatives descended from early missionaries. There, Beckwith made friends with many locals including members of the wealthy Alexander family who later sponsored her folklore work, and she developed an early interest in Hawaiian folk dancing. Beckwith graduated from Mount Holyoke College in 1893 and taught English at Elmira College, Mount Holyoke, Vassar College, and Smith College. Her formal education in anthropology did not begin till the 1900s. In 1906, she obtained a Master of Arts degree in anthropology after studying under Franz Boas at Columbia University, and she received her Doctor of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheldon Dibble
Sheldon Dibble (January 26, 1809 – January 22, 1845) was a missionary to Hawaii who organized one of the first books on Hawaiian history, and inspired students to write more. Early life Dibble was born in Skaneateles, New York on January 26, 1809. He graduated from Hamilton College in 1827, and the Auburn Theological Seminary in October 1830, where he married Maria M. Tomlinson (1808–1837). They arrived in the fourth company from the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions in 1831 on the ship ''New England'' from New Bedford. He was one of the youngest missionaries, only 22 years old when he arrived. They had a son who died young and a daughter Mary, who died at 18 months in 1831, and is buried in Lahainaluna alongside her parents. After the death of his first wife, he married a cousin of his first wife, Antoinette Tomlinson (1809–1897), in 1839. They had a son Seymour and a daughter Clara. Antoinette and the children moved back to the United States in 1848. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which also includes Molokai, Lānai, and unpopulated Kahoolawe. In 2020, Maui had a population of 168,307, the third-highest of the Hawaiian Islands, behind that of Oahu and Hawaii Island. Kahului is the largest census-designated place (CDP) on the island with a population of 26,337 , and is the commercial and financial hub of the island. Wailuku is the seat of Maui County and is the third-largest CDP . Other significant places include Kīhei (including Wailea and Makena in the Kihei Town CDP, the island's second-most-populated CDP), Lāhainā (including Kāanapali and Kapalua in the Lāhainā Town CDP), Makawao, Pukalani, Pāia, Kula, Haikū, and Hāna. Etymology Native Hawaiian tradition gives the origin of the island's name in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahainaluna High School
Lahainaluna High School is a public high school with the grades 9-12 located in Lahaina (on the island of Maui). Lahainaluna High School is also a public boarding school. It was founded in 1831 as a Protestant missionary school, originally named Lahainaluna Seminary. The early missionaries who arrived in Lahaina in 1823 explained to the Hawaiian Royalty the importance of an educational institution in the American style. A number of the pioneers, students and teachers are buried in a small graveyard behind several buildings on the campus. It was the first formal European-American style school founded in Hawaii and has continued to operate to this day. History and traditions American William Richards founded the missionary station in Lahaina in 1823. In June 1831, Lorrin Andrews was chosen as first principal of a seminary for boys and young men. The site was named Lahainaluna for "upper Lahaina". On September 5, 1831, classes began in thatched huts with 25 Hawaiian young men as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Kamehameha%2C_King_of_the_Sandwich_Islands_by_Louis_Choris%2C_(Russian)%2C_pen_and_watercolor.jpg)