|
Pathogen Reduction Using Riboflavin And UV Light
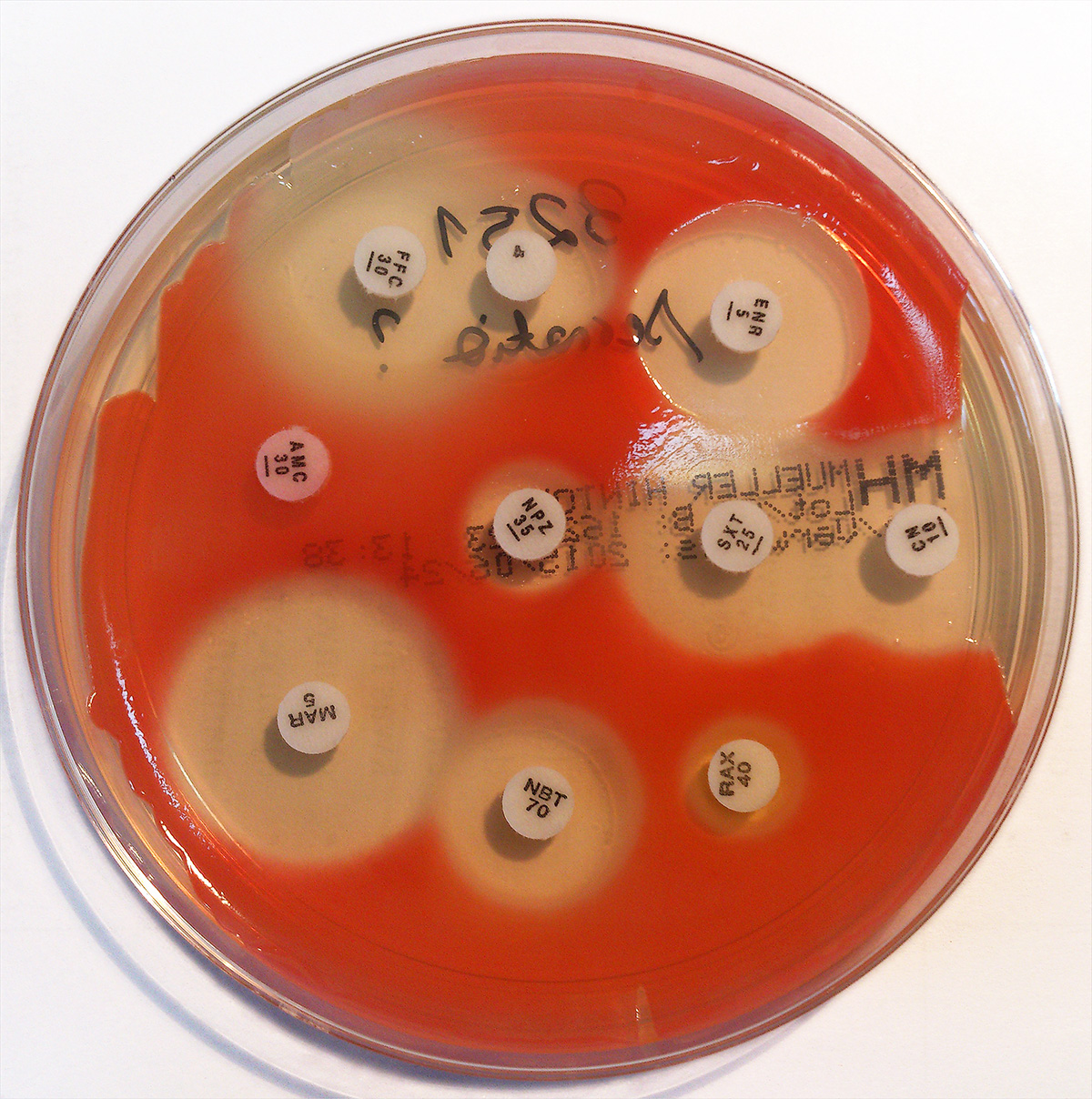
Pathogen reduction using riboflavin and UV light is a method by which infectious pathogens in blood for transfusion are inactivated by adding riboflavin and irradiating with UV light. This method reduces the infectious levels of disease-causing agents that may be found in donated blood components, while still maintaining good quality blood components for transfusion. This type of approach to increase blood safety is also known as “pathogen inactivation” in the industry. Despite measures that are in place in the developed world to ensure the safety of blood products for transfusion, a risk of disease transmission still exists. Consequently, the development of pathogen inactivation/reduction technologies for blood products has been an ongoing effort in the field of transfusion medicine. A new procedure for the treatment of individual units of single-donor (apheresis) or whole blood–derived, pooled, platelets has recently been introduced. This technology uses riboflavin and ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babesiosis
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a ''Babesia'' or ''Theileria'', in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via tick bite is most common in the Northeastern and Midwestern United States and parts of Europe, and sporadic throughout the rest of the world. It occurs in warm weather. People can get infected with ''Babesia'' parasites by the bite of an infected tick, by getting a blood transfusion from an infected donor of blood products, or by congenital transmission (an infected mother to her baby). Ticks transmit the human strain of babesiosis, so it often presents with other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease. After trypanosomes, ''Babesia'' is thought to be the second-most common blood parasite of mammals. They can have major adverse effects on the health of domestic animals in areas without severe winters. In cattle the disease is known as T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yersinia Enterocolitica
''Yersinia enterocolitica'' is a Gram-negative, bacillus-shaped bacterium, belonging to the family Yersiniaceae. It is motile at temperatures of 22–29° C (72–84 °F), but becomes nonmotile at normal human body temperature. ''Y. enterocolitica'' infection causes the disease yersiniosis, which is an animal-borne disease occurring in humans, as well as in a wide array of animals such as cattle, deer, pigs, and birds. Many of these animals recover from the disease and become carriers; these are potential sources of contagion despite showing no signs of disease. The bacterium infects the host by sticking to its cells using trimeric autotransporter adhesins. The genus ''Yersinia'' includes 20 species: '' Y. aldovae'', '' Y. aleksiciae'', '' Y. bercovieri'', '' Y. canariae'', ''Y. enterocolitica'', '' Y. entomophaga'', '' Y. frederiksenii'', '' Y. hibernica'', '' Y. intermedia'', '' Y. kristensenii'', '' Y. massiliensis'', '' Y. mollaretii'', '' Y. nurmii'', '' Y. pekkanenii'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus ''Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' (GABHS) is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berries ( a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Mitis
''Streptococcus mitis'' is a mesophilic alpha-hemolytic species of ''Streptococcus'' that inhabits the oral cavity. It is coccus (spherical shaped), gram-positive, catalase negative, and facultative anaerobe. It was previously classified as ''Streptococcus mitior''. Streptococcus mitis is known to cause several medical conditions one of them being infective endocarditis. Classification Members of the Streptococcus genera belong to lactic acid bacteria defined by the formation of lactic acid as an end-product of carbohydrate metabolism. The family ''Streptococcaceae'' is characterized by based upon its 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis within the low (< 50 mol%) G+C branch. There are over 50 species in the genus which are classified by their 16S rRNA sequences. Habitat ''Streptococcus mitis'' primarily resides in the oral cavity which includes the mouth, nasopharynx, and throat. However, there have also been cases of it in the female genital ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Agalactiae
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a beta-hemolytic, catalase-negative, and facultative anaerobe. ''S. agalactiae'' is the most common human pathogen of streptococci belonging to group B of the Rebecca Lancefield classification of streptococci. GBS are surrounded by a bacterial capsule composed of polysaccharides (exopolysacharide). The species is subclassified into ten serotypes (Ia, Ib, II–IX) depending on the immunologic reactivity of their polysaccharide capsule. The plural term group B streptococci (referring to the serotypes) and the singular term group B streptococcus (referring to the single species) are both commonly encountered (even though ''S. halichoeri'' and ''S. pseudoporcinus'' are also group B Streptococci). In general, GBS is a harmless commensal bacterium being part of the human microbiot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus '' Staphylococcus''. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified salt tolerant strains of ''S. epiderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratia Marcescens
''Serratia marcescens'' () is a species of rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen in humans. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy.Serratia marcescens. (2011, April). Retrieved from https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Serratia_marcescens ''S. marcescens'' is commonly involved in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), also called nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections, and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of HAI cases in the United States. It is commonly found in the respiratory and urinary tracts of hospitalized adults and in the gastrointestinal systems of children. Due to its abundant presence in the environment, and its preference for damp conditions, ''S. marcescens'' is commonly found growing in bathrooms (especially on tile grout, shower corners, toilet water lines, and basins), where it manife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacterium Acnes
''Cutibacterium acnes'' (formerly ''Propionibacterium acnes'') is the relatively slow-growing, typically aerotolerant anaerobic, gram-positive bacterium (rod) linked to the skin condition of acne; it can also cause chronic blepharitis and endophthalmitis, the latter particularly following intraocular surgery. Its genome has been sequenced and a study has shown several genes can generate enzymes for degrading skin and proteins that may be immunogenic (activating the immune system). The species is largely commensal and part of the skin flora present on most healthy adult humans' skin. It is usually just barely detectable on the skin of healthy preadolescents. It lives, among other things, primarily on fatty acids in sebum secreted by sebaceous glands in the follicles. It may also be found throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Originally identified as ''Bacillus acnes'', it was later named ''Propionibacterium acnes'' for its ability to generate propionic acid. In 2016, ''P. ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |