|
Paterson Institute For Cancer Research
The Christie NHS Foundation Trust in Withington, Manchester, manages the Christie Hospital, one of the largest cancer treatment centres of its type in Europe. The Christie became a NHS Foundation Trust in 2007 and is also an international leader in cancer research and development, home to the Paterson Institute for Cancer Research. History Foundation of the Christie Hospital The Christie Hospital had its beginnings in the largesse of Sir Joseph Whitworth, a wealthy Mancunian inventor who left money in his will in 1887. He wanted this to be spent on good causes in Manchester and entrusted his bequest to three legatees, one of whom was Richard Copley Christie. Consequently, some of that money was used to buy land off Oxford Road, adjacent to Owens College and intended to allow the movement of the central Manchester hospitals out of the crowded city centre. A committee chaired by Christie was established in 1890 and, partly funded by a legacy of £10,000 from Daniel Proctor, a Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Manchester
Greater Manchester is a metropolitan county and combined authority, combined authority area in North West England, with a population of 2.8 million; comprising ten metropolitan boroughs: City of Manchester, Manchester, City of Salford, Salford, Metropolitan Borough of Bolton, Bolton, Metropolitan Borough of Bury, Bury, Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, Oldham, Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, Rochdale, Metropolitan Borough of Stockport, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford and Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, Wigan. The county was created on 1 April 1974, as a result of the Local Government Act 1972, and designated a functional Manchester City Region, city region on 1 April 2011. Greater Manchester is formed of parts of the Historic counties of England, historic counties of Cheshire, Lancashire and the West Riding of Yorkshire. Greater Manchester spans , which roughly covers the territory of the Greater Manchester Built-up Area, the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, second most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Royal Infirmary
Manchester Royal Infirmary (MRI) is a large NHS teaching hospital in Chorlton-on-Medlock, Manchester, England. Founded by Charles White in 1752 as part of the voluntary hospital movement of the 18th century, it is now a major regional and national medical centre. It is the largest Hospital within Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust, and based on its Oxford Road Campus in South Manchester where it shares a site with the Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester Royal Eye Hospital and Saint Mary's Hospital as well as several other educational and research facilities. The Hospital is also a key site for medical educational within Manchester, serving as a main teaching hospital for School of Medical Sciences, University of Manchester. History The first premises was a house in Garden Street, off Withy Grove, Manchester, which were opened on Monday 27 July 1752, financed by subscriptions. Government of the institution was in the hands of the trustees. Any subscriber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre
The University of Manchester Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre (WMIC) is a purpose-built molecular imaging research facility. Based on the site of the Christie Hospital in Manchester, the Centre aims to develop clinical research and development in medical imaging in areas of oncology, neuroscience and psychiatry research. Facilities and equipment The centre is equipped with cyclotron and radiochemistry facilities including: a hot cell laboratory, 2 advanced high-resolution PET scanners, supporting chemical analysis laboratories and data analysis facilities. There is also a 1.5T MRI scanner in the centre. The Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre is part of the Imaging Facilities of the University of Manchester. The Imaging Facilities also own a 3T MRI scanner at the Manchester Clinical Research Facility and in 2015 a GE SIGNA PET-MR scanner was installed at St Mary's Hospital, funded by the Medical Research Council as part of the Dementias Platform UK initiative (DPUK). History D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Cancer Research Centre
The Manchester Cancer Research Centre (MCRC) was established in 2006 by the University of Manchester, Cancer Research UK and The Christie NHS Foundation Trust. It has since been expanded through the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre to include Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester Mental Health and Social Care Trust and Salford Clinical Commissioning Group. See also * Cancer in the United Kingdom The passing of the Cancer Act 1939 marked the political significance of cancer treatment. It envisaged a system of co-ordination of diagnosis and treatment under the control of County Councils and County Borough Councils which preceded the establis ... References 2006 establishments in England Academic health science centres Cancer organisations based in the United Kingdom Health in Greater Manchester Medical education in England Medical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Manchester Fire And Rescue Service
Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service (GMFRS) is the statutory emergency fire and rescue service for the metropolitan county of Greater Manchester, England. It is part of the Greater Manchester Combined Authority. GMFRS covers an area of approximately . The service has 41 fire stations which until 2006 were organised into three territorial Area Commands (South, East and West), each one with an Area Command Headquarters, based at Stretford, Rochdale and Bolton respectively. When the brigade altered the command area's structure they divided the three area commands from South, East and West to 11 Borough Commands, aligned to the 10 local authorities in the county: Bolton, Bury, Manchester (North/South), Oldham, Rochdale, Salford, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford and Wigan. The service employs 2,200 personnel, of which 1,200 are frontline firefighters, and 403 non-uniformed support staff. The service's headquarters is located in Pendlebury, Salford. History The service was crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Dexter
(Thomas) Michael Dexter FRS (born 15 May 1945) is a British haematologist and director of the Wellcome Trust, from 1998 to 2003. Education Dexter was inspired to take A levels at night school and went on study physiology and zoology at the University of Salford. After graduating, he continued in academia and received a PhD from the University of Manchester in 1974 for research into Leukemia. Dexter also received a Doctor of Science degree from the University of Salford in 1982. Career Dexter was visiting fellow at the Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center and a professor of haematology at the University of Manchester from 1985 to 1998. He was director of the Paterson Institute for Cancer Research and the Wellcome Trust. He has authored over 360 articles in scientific journals including ''Nature Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derek Crowther
Professor Derek Crowther FRCP, FRCR (born 1937) is a British oncologist, and Professor Emeritus, School of Medical Sciences, University of Manchester. Crowther was educated at University of Cambridge and studied medicine at St Bartholomew's Hospital, graduating in 1963. In 1973, he became the first Professor of Medical Oncology at the Christie Cancer Centre, University of Manchester. He was the second professor of medical oncology in the UK (the first being Gordon Hamilton Fairley). He retired in 1997. He served as chair of the Leukemia Research Fund Clinical Trials Advisory Panel, and president of the Association of Cancer Physicians. He is a foundation scholar at Clare College, Cambridge Clare College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. The college was founded in 1326 as University Hall, making it the second-oldest surviving college of the University after Peterhouse. It was refounded .... He was a member of the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
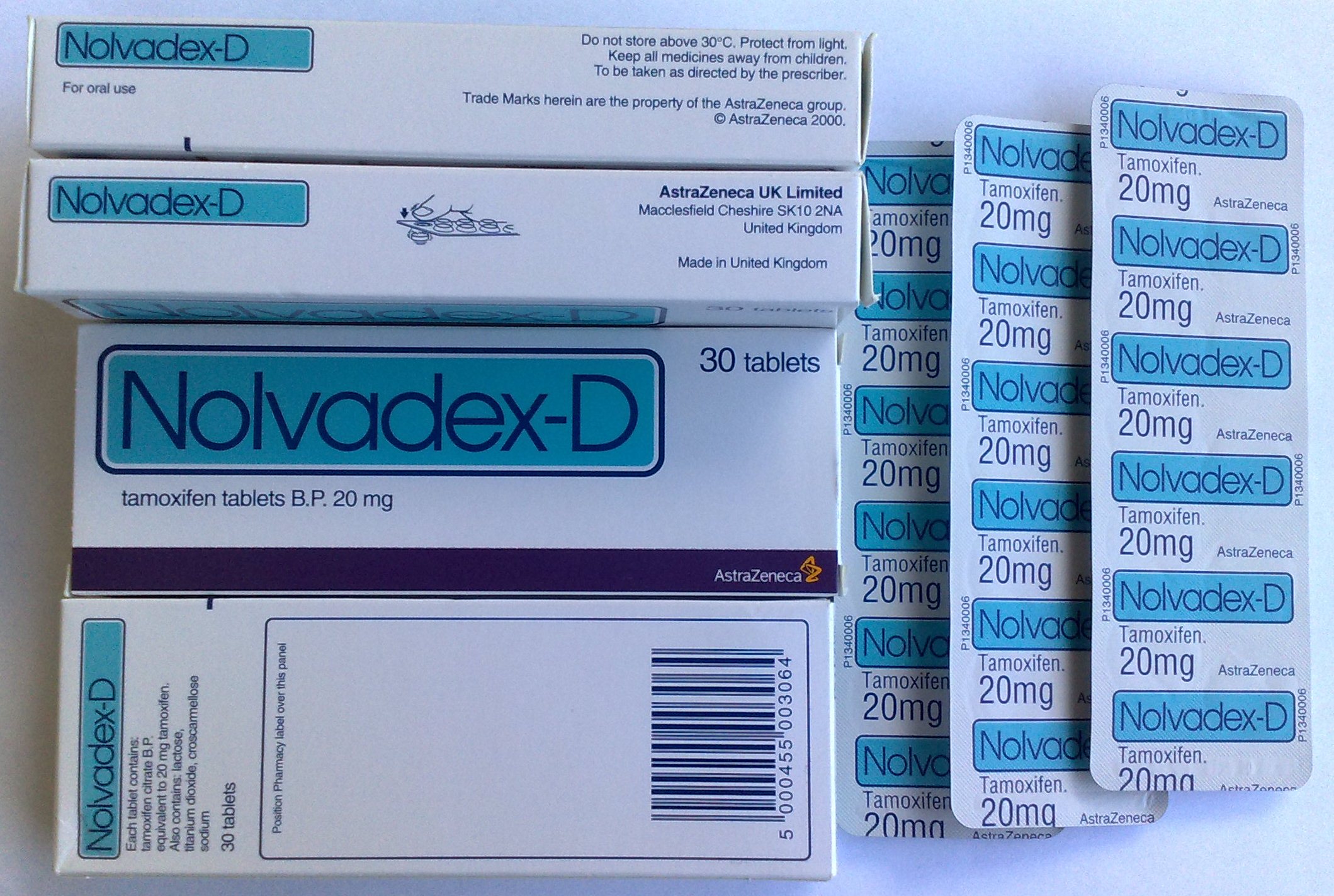
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and treat breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome. Tamoxifen is typically taken daily by mouth for five years for breast cancer. Serious side effects include a small increased risk of uterine cancer, stroke, vision problems, and pulmonary embolism. Common side effects include irregular periods, weight loss, and hot flashes. It may cause harm to the baby if taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM) and works by decreasing the growth of breast cancer cells. It is a member of the triphenylethylene group of compounds. Tamoxifen was initially made in 1962, by chemist Dora Richardson. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Tamoxifen is available as a generic medication. In 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency, treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer, and other uses. By 2007, it was only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. In 2011, Hoover and colleagues reported on adverse health outcomes linked to DES including infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preeclampsia, preterm birth, stillbirth, infant death, menopause prior to age 45, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and vaginal cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance, vaginal, topical, and by injection. DES is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors, the biological target of estroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mule Spinners' Cancer
Mule spinners' cancer or mule-spinners' cancer was a cancer, an epithelioma of the scrotum. It was first reported in 1887 in a cotton mule spinner. In 1926, a British Home Office committee strongly favoured the view that this form of cancer was caused by the prolonged action of mineral oils on the skin of the scrotum, and of these oils, shale oil was deemed to be the most carcinogenic. From 1911 to 1938, there were 500 deaths amongst cotton mule-spinners from cancer of the scrotum, but only three amongst wool mule spinners. Introduction About 1900, there was a high incidence of scrotal cancer detected in former mule spinners. The cancer was limited to cotton mule spinners and did not affect woollen or condenser mule spinners. The cause was attributed to the blend of vegetable and mineral oils used to lubricate the spindles. The spindles, when running, threw out a mist of oil at crotch height, that was captured by the clothing of anyone piecing an end. In the 1920s, much attenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Manchester
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity , established = 2004 – University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 – UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 – Victoria University of Manchester 1880 – Victoria University 1851 – Owens College 1824 – Manchester Mechanics' Institute , endowment = £242.2 million (2021) , budget = £1.10 billion (2020–21) , chancellor = Nazir Afzal (from August 2022) , head_label = President and vice-chancellor , head = Nancy Rothwell , academic_staff = 5,150 (2020) , total_staff = 12,920 (2021) , students = 40,485 (2021) , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Manchester , country = England, United Kingdom , campus = Urban and suburban , colours = Manchester Purple Manchester Yellow , free_label = Scarf , free = , website = , logo = UniOfManchesterLogo.svg , affiliations = Universities Research Association Sutton 30 Russell Group EUA N8 Group NWUA ACUUniversities UK The Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, nonpainful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Those affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying RS cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg)