|
Paschal Vigil
Easter Vigil, also called the Paschal Vigil or the Great Vigil of Easter, is a liturgy held in traditional Christian churches as the first official celebration of the Resurrection of Jesus. Historically, it is during this liturgy that people are baptized and that adult catechumens are received into full communion with the Church. It is held in the hours of darkness between sunset on Holy Saturday and sunrise on Easter Day – most commonly in the evening of Holy Saturday or midnight – and is the first celebration of Easter, days traditionally being considered to begin at sunset. Among liturgical Western Christian churches including the Roman Catholic Church, the Lutheran Churches, the Reformed Churches, the Anglican Communion and the Methodist Churches, the Easter Vigil is the most important liturgy of public worship and Mass of the liturgical year, marked by the first use since the beginning of Lent of the exclamatory "Alleluia", a distinctive feature of the Easter season. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Liturgy
Christian liturgy is a pattern for Christian worship, worship used (whether recommended or prescribed) by a Christian congregation or Christian denomination, denomination on a regular basis. The term liturgy comes from Greek and means "public work". The majority of Christian denominations hold church services on the Lord's Day (with many offering Sunday morning and Sunday evening services); a number of traditions have mid-week Wednesday evening services as well. In some Christian denominations, liturgies are held daily, with these including those in which the canonical hours are prayed, as well as the offering of the Eucharist, Eucharistic liturgies such as Mass (liturgy), Mass, among other forms of worship. In addition to this, many Christians attend services of worship on holy days such as Christmas, Ash Wednesday, Good Friday, Feast of the Ascension, Ascension Thursday, among others depending on the Christian denomination. In most Christian traditions, liturgies are presided o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
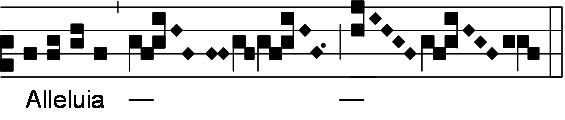
Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of scripture, usually from the Psalms. This chant is commonly used before the proclamation of the Gospel. In Western Christianity, congregations commonly cease using the word "Alleluia" during the period of Lent but restore it into their services at Easter. The form of praise "Alleluia" is used by Christians to thank and glorify God; it finds itself present in many prayers and hymns, especially those related to Eastertide, such as ''Jesus Christ Is Risen Today''. History The Hebrew word ''Hallelujah'' as an expression of praise to God was preserved, untranslated, by the Early Christians as a superlative expression of thanksgiving, joy, and triumph. Thus it appears in the ancient Greek Liturgy of St. James, which is still used to this day b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokeimenon
In the liturgical practice of the Orthodox Church and Byzantine Rite, a prokeimenon (Greek , plural ; sometimes /; lit. 'that which precedes') is a psalm or canticle refrain sung responsorially at certain specified points of the Divine Liturgy or the Divine Office, usually to introduce a scripture reading.Parry (1999), p. 390 It corresponds to the Gradual of the Roman Mass. Prokeimena are not selected based on the personal preference of the priest, reader, or choir director. Rather, the Sunday and weekday prokeimena are taken from the Octoechos, using the particular tone of the day. Many feasts also have their own prokeimena. The basic pattern of a prokeimenon is for the reader to chant a single verse of the psalm or canticle (often announcing the tone as well). This is repeated as a refrain by the choir, as the Reader chants additional verses (exactly how many depends on local practice), followed by the choir singing the first verse in response. The Reader concludes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Covenant
The New Covenant (Hebrew '; Greek ''diatheke kaine'') is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah ( Jeremiah 31:31-34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible). Generally, Christians believe that the promised New Covenant was instituted at the Last Supper as part of the Eucharist, which, in the Gospel of John, includes the New Commandment. Based on the biblical passage which reads that, "For where a testament is, there must also of necessity be the death of the testator. For a testament is of force after men are dead: otherwise it is of no strength at all while the testator liveth", Protestants tend to believe that the New Covenant only came into force with the death of Jesus Christ. The commentary to the Roman Catholic New American Bible also affirms that Christ is the "testator whose death puts his will into effect". Thus, Christians believe that Jesus is the mediator of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Patriarchate Of Jerusalem
The Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem also known as the Armenian Patriarchate of Saint James ( hy, Առաքելական Աթոռ Սրբոց Յակովբեանց Յերուսաղեմ, , ) is located in the Armenian Quarter of Jerusalem. The Armenian Apostolic Church is officially recognised under Israel's confessional system, for the self-regulation of status issues, such as marriage and divorce. Archbishop Nourhan Manougian, previously the Grand Sacristan and the Patriarchal Vicar, became the 97th Armenian Patriarch of Jerusalem on January 24, 2013. Manougian succeeded Archbishop Torkom Manoogian, who died on October 12, 2012, after serving 22 years in the office. The Patriarch, along with a synod of seven clergymen elected by the St. James Brotherhood, oversees the Patriarchate's operations. During World War I, survivors of the Armenian genocide received shelter in the Armenian convent in Jerusalem. The Armenian population of Jerusalem reached at that time 25,000 people. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy ( grc-gre, Θεία Λειτουργία, Theia Leitourgia) or Holy Liturgy is the Eucharistic service of the Byzantine Rite, developed from the Antiochene Rite of Christian liturgy which is that of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. As such, it is used in the Eastern Orthodox, the Greek Catholic Churches, and the Ukrainian Lutheran Church. Although the same term is sometimes applied in English to the Eucharistic service of Armenian Christians, both of the Armenian Apostolic Church and of the Armenian Catholic Church, they use in their own language a term meaning "holy offering" or "holy sacrifice". Other churches also treat "Divine Liturgy" simply as one of many names that can be used, but it is not their normal term. The Greek Catholic and Orthodox Churches see the Divine Liturgy as transcending time and the world. All believers are seen as united in worship in the Kingdom of God along with the departed saints and the angels of heaven. Everything in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonical Hours
In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of fixed times of prayer at regular intervals. A book of hours, chiefly a breviary, normally contains a version of, or selection from, such prayers. In the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, canonical hours are also called ''offices'', since they refer to the official set of prayers of the Church, which is known variously as the ("divine service" or "divine duty"), and the ("work of God"). The current official version of the hours in the Roman Rite is called the Liturgy of the Hours ( la, liturgia horarum) in North America or divine office in Ireland and Britain. In Lutheranism and Anglicanism, they are often known as the daily office or divine office, to distinguish them from the other "offices" of the Church (e.g. the administration of the sacraments). In the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic Churches, the canonical hours may be referred to as the divine services, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and the Malabar coast of South Asia, and ephemerally parts of Persia, Central Asia, the Near East and the Far East. The term does not describe a single communion or religious denomination. Major Eastern Christian bodies include the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Oriental Orthodox Churches, along with those groups descended from the historic Church of the East, as well as the Eastern Catholic Churches (which have either re-established or always retained communion with Rome and maintain Eastern liturgies), and the Eastern Protestant churches (which are Protestant in theology but Eastern in cultural practice). The various Eastern churches do not normally refer to themselves as "Eastern", with the exception of the Assyrian Church of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Orthodoxy
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent one of its oldest branches. As some of the oldest religious institutions in the world, the Oriental Orthodox Churches have played a prominent role in the history and culture of Armenia, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Sudan, Western Asia and India. As autocephalous churches, its bishops are equal by virtue of episcopal ordination. Its doctrines recognizes the validity of only the first three ecumenical councils. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are composed of six autocephalous churches: the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, the Syriac Orthodox Church of Antioch, the Armenian Apostolic Church, the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, and the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church. They consider themselves to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Roman Catholic Church—the Pope—but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognized by them as '' primus inter pares'' ("first among equals"), which may be explained as a representative of the church. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. The Eastern Orthodox Church officially calls itself the Orthodox Catholic Church. Eastern Orthodox theology is based on holy tradition, which incorporates the dogmatic decrees of the seven ecumenical councils, the Scriptures, and the teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunrise Service
Sunrise service is a worship service on Easter Sunday practiced by some Christian denominations, such as the Moravian Church. The sunrise service takes place outdoors, sometimes in a park, and the attendees are seated on outdoor chairs or benches. In the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Lutheran, Methodist, Anglican, and Reformed churches, this ordinarily takes the form of the Easter Vigil, which can begin in the late evening of Holy Saturday or the early morning of Easter Sunday. History The first Easter Sunrise Service recorded took place in 1732 in the Moravian congregation at Herrnhut in the Upper Lusatian hills of Saxony.The Easter Morning Sunrise Service This Month in Moravian History, Number 18, 2007-04, Moravian Archives, Bethlehem NC. After an all-night prayer vigil, the Single Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |