|
Parrot Training
Parrot training, also called parrot teaching, is the application of training techniques to modify the behavior of household companion parrots. Training is used to deal with behavior problems such as biting anscreaming to train husbandry behaviors such as allowing claw trimming without restraint or accepting a parrot harness, and to teach various tricks. Parrot psychology Although very trainable and intelligent, parrots are a prey species and are naturally more cautious than predatory species such as dogs. They often must be trained more slowly and carefully. Parrots can, however, eventually be taught many complicated tricks and behaviors, and remember them for years. Parrots are often used in shows at zoos and amusement parks. Parrots need to socialize. Some behavior problems may be averted through parrot training. As with any animal, training birds also requires patience, time, and commitment with several short sessions each day. Taming Parrot taming, or teaching, can be mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diopsittaca Nobilis -pet-2
The red-shouldered macaw (''Diopsittaca nobilis'') is a small green South American parrot, a member of a large group of Neotropical parrots called macaws. The species is named for the red coverts on its wings. It is the smallest macaw, being in length - similar in size to the ''Aratinga'' parakeets. It is native to the tropical lowlands, savannah, and swamplands of Brazil, the Guianas, Bolivia, Venezuela, and far south-eastern Peru. It has two distinct subspecies, the noble macaw and the Hahn's macaw, and a possible poorly distinct third subspecies that has longer wings, but is otherwise similar to the noble macaw. The Hahn's subspecies is named for German zoologist Carl-Wilhelm Hahn, who in 1834 began compiling ''Ornithologischer Atlas oder naturgetreue Abbildung und Beschreibung der aussereuropäischen Vögel'' (Engl: Ornithological Atlas or natural depiction and description of birds from outside Europe). Red-shouldered macaws are frequently bred in captivity for the pet trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
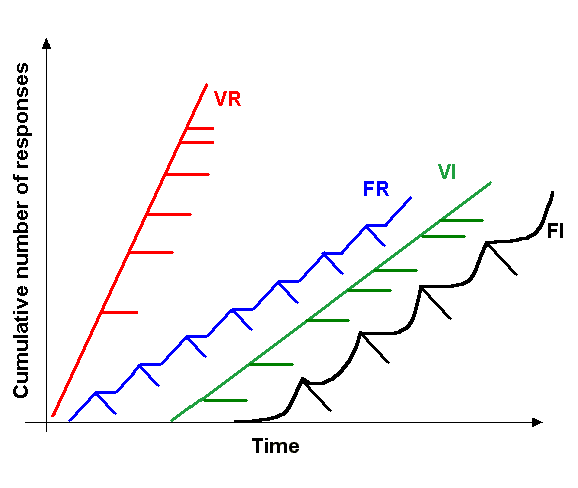
Positive Punishment
In operant conditioning, punishment is any change in a human or animal's surroundings which, occurring after a given behavior or response, reduces the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. As with reinforcement, it is the ''behavior'', not the human/animal, that is punished. Whether a change is or is not punishing is determined by its effect on the rate that the behavior occurs. This is called motivating operations (MO), because they alter the effectiveness of a stimulus. MO can be categorized in abolishing operations, decrease the effectiveness of the stimuli and establishing, increase the effectiveness of the stimuli. For example, a painful stimulus which would act as a punisher for most people may actually reinforce some behaviors of masochistic individuals. There are two types of punishment, positive and negative. Positive punishment involves the introduction of a stimulus to decrease behavior while negative punishment involves the removal of a stimulus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punishment (psychology)
In operant conditioning, punishment is any change in a human or animal's surroundings which, occurring after a given behavior or response, reduces the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. As with reinforcement, it is the ''behavior'', not the human/animal, that is punished. Whether a change is or is not punishing is determined by its effect on the rate that the behavior occurs. This is called motivating operations (MO), because they alter the effectiveness of a stimulus. MO can be categorized in abolishing operations, decrease the effectiveness of the stimuli and establishing, increase the effectiveness of the stimuli. For example, a painful stimulus which would act as a punisher for most people may actually reinforce some behaviors of masochistic individuals. There are two types of punishment, positive and negative. Positive punishment involves the introduction of a stimulus to decrease behavior while negative punishment involves the removal of a stimulus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clicker Training
Clicker training is a positive reinforcement animal training method based on a bridging stimulus ( the clicker) in operant conditioning. The system uses conditioned reinforcers, which a trainer can deliver more quickly and more precisely than primary reinforcers such as food. The term "clicker" comes from a small metal cricket noisemaker adapted from a child's toy that the trainer uses to precisely mark the desired behavior. When training a new behavior, the clicker helps the animal to quickly identify the precise behavior that results in the treat. The technique is popular with dog trainers, but can be used for all kinds of domestic and wild animals. Sometimes, instead of a click to mark the desired behavior, other distinctive sounds are made (such as a "whistle, a click of the tongue, a snap of the fingers, or even a word") [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clicker Training
Clicker training is a positive reinforcement animal training method based on a bridging stimulus ( the clicker) in operant conditioning. The system uses conditioned reinforcers, which a trainer can deliver more quickly and more precisely than primary reinforcers such as food. The term "clicker" comes from a small metal cricket noisemaker adapted from a child's toy that the trainer uses to precisely mark the desired behavior. When training a new behavior, the clicker helps the animal to quickly identify the precise behavior that results in the treat. The technique is popular with dog trainers, but can be used for all kinds of domestic and wild animals. Sometimes, instead of a click to mark the desired behavior, other distinctive sounds are made (such as a "whistle, a click of the tongue, a snap of the fingers, or even a word") [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
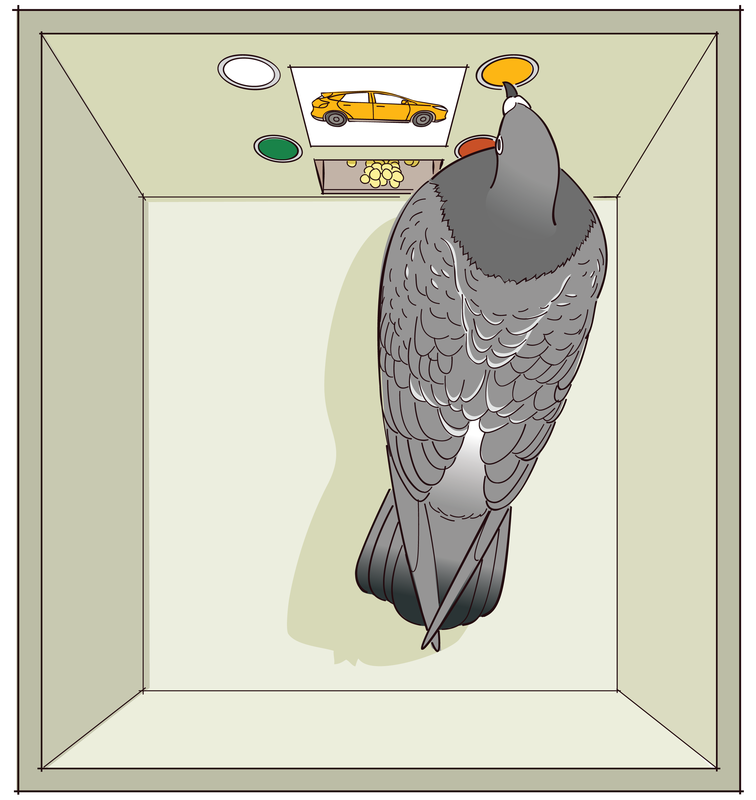
Shaping (psychology)
Shaping is a conditioning paradigm used primarily in the experimental analysis of behavior. The method used is differential reinforcement of successive approximations. It was introduced by B. F. Skinner with pigeons and extended to dogs, dolphins, humans and other species. In shaping, the form of an existing response is gradually changed across successive trials towards a desired target behavior by reinforcing exact segments of behavior. Skinner's explanation of shaping was this: Successive approximations The successive approximations reinforced are increasingly closer approximations of the target behavior set by the trainer. As training progresses the trainer stops reinforcing the less accurate approximations. When the trainer stops reinforcing this behavior, the learner will go through an extinction burst in which they perform many behaviors in an attempt to receive that reinforcement. The trainer will pick one of those behaviors that is a closer approximation to the target beh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene Pepperberg
Irene Maxine Pepperberg (born April 1, 1949) is a scientist noted for her studies in animal cognition, particularly in relation to parrots. She has been a professor, researcher and/or lecturer at multiple universities, and she is currently a research associate and lecturer at Harvard University. Pepperberg also serves on the Advisory Council of METI (Messaging Extraterrestrial Intelligence). She is well known for her comparative studies into the cognitive fundamentals of language and communication, and she was one of the first to work on language learning in animals other than human species (exemplified by the Washoe project), by extension to a bird species. Pepperberg is also active in wildlife conservation, especially in relation to parrots. Early life, family and education Born in 1949 as Irene Platzblatt in Brooklyn, New York City, New York, she was an only child. Her father, Robert Platzblatt, was a biochemist and middle school teacher. Her parents were both first-generati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companion Parrot
A companion parrot is a parrot kept as a pet that interacts abundantly with its human counterpart. Generally, most species of parrot can make excellent companions, but must be carefully managed around other common pet species like dogs and cats as they might be hostile towards them. Species of parrots that are kept as companions include large parrots, such as amazons, greys, cockatoos, eclectus, hawk-headed parrots, and macaws; (Species include hybrids like the Catalina macaw) mid-sized birds, such as caiques, conures, quakers, ''Pionus'', ''Poicephalus'', rose-ringed parakeets, and rosellas; and many of the smaller types, including ''Brotogeris'', budgies, cockatiels, parakeets, lovebirds, parrotlets and lineolated parakeets. Some species of lories and lorikeets are kept as pets but are quite messy, and often more popular as aviary birds. Hanging parrots and fig parrots are normally kept as aviary birds and not as pets. Some species as pygmy parrots and kakapos, night par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |