|
Parischnogaster Nigricans Serrei
''Parischnogaster nigricans serrei'' is a hover wasp subspecies in the family Vespidae, and it is predominantly found in the Java region of Indonesia. Its nest cells are of conical structure, linearly attached to a string-like substratum. The nests are typically found in places open to human interactions, such as gardens, trees, or forests around villages. There is a clear dominance hierarchy within colonies, which often affects the behavioral activities of its members. The wasp’s most common predators are ''Vespa tropica'', also known as the great banded hornet. ''P. nigricans serrei'' defends itself by flying away or giving out alarm calls. Taxonomy and phylogenetics Studies investigating the biology and social behavior of subfamily Stenogastrinae wasps have begun since the early 20th century, but some of their unusual morphological and ethological traits make it hard for them to have a specific systematic allocation in the phylogenetic tree. These wasps also vary a signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Du Buysson
Robert François du Buysson (Born 6 May 1861 - Broût-Vernet (Allier) - Deceased 16 March 1946 - Saint-Rémy-la-Varenne (Maine-et-Loire)), was a French naturalist. Biography He is the son of botanist :fr:François-Charles du Buysson (1825-1906) and Mathilde de Montaignac (1829-1899) and the brother of entomologist :fr:Henri du Buysson. Having developed a taste for herbariums at a very young age and a keen sense of observation, Robert du Buysson began to study the mosses of his native region rapidly expanding his field of study to lichens and vascular cryptogams. From 1888 to 1893 he published an inventory of vascular cryptogams of Europe in the Scientific Review of Bourbonnais and the Centre of France. In the field of bryology, the name of Robert du Buysson remains attached to two species: '' Orthorichum berthoumieui'', named in honor of Father Berthoumieu with whom he studied the mosses around Saint-Pourçain (Allier), and '' Barbula buyssoni''. Robert du Buysson disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parischnogaster Mellyi
''Parischnogaster mellyi'' is a medium-sized species of a hover wasp in the family Vespidae. It is found in Southeast Asia and is widely spread in Thailand and Malaysia. Its nests feature flexible and dynamic qualities, and they are commonly seen under roofs of houses and huts in rural areas. Hovering and patrolling behaviors are the species’ main defining behavioral features, and such activities are closely linked to its mating patterns. Taxonomy and phylogeny All hover wasp species were placed under one genus, ''Stenogaster'', until 1927, when von Schulthess created the new genus, Parischnogaster, for species populated in Asia. ''Parischnogaster'' was synonymized with Holischnogaster by Carpenter in 1982, and it is possibly the largest and the least well known genus. ''P. mellyi'' was first found by De Saussure in 1852. Understanding of phylogenetic background for ''P. mellyi'' is of particular importance because “the independence of origin and range of social organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parischnogaster Alternata
The Black hover wasp, ''Parischnogaster alternata'', is a eusocial wasp in the genus ''Parischnogaster''. It is native to South-East Asia, and builds its nests in cavities located in dark and damp locations.Bolton, A. "Colony Genetic Structure in a Facultatively Eusocial Hover Wasp." Behavioral Ecology 17.6 (2006): 873-80. Web.Coster-Longman, Christina. "Laboratory Observations on the Social Behaviour of ''Parischnogaster Alternata'' (Vespidae Stenogastrinae)."Ethology Ecology & Evolution 6.Sup1 (1994): 31-36. Web. The nests of Black hover wasps are often found in clusters, which serves as a passive defense mechanism against predators.Landi, M., C. Coster-Longman, and S. Turillazzi. "Are the Selfish Herd and the Dilution Effects Important in Promoting Nest Clustering in the Hover Wasp (Stenogastrinae Vespidae Hymenoptera)?" Ethology Ecology & Evolution 14.4 (2002): 297-305. Web. The annual colony cycle begins with nest initiation by a single foundress though colonies typically c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincters
A sphincter is a circular muscle that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage or orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. Sphincters are found in many animals. There are over 60 types in the human body, some microscopically small, in particular the millions of precapillary sphincters. Sphincters relax at death, often releasing fluids and faeces. Functioning Each sphincter is associated with the lumen (opening) it surrounds. As long as the sphincter muscle is contracted, its length is shortened and the lumen is constricted (closed). Relaxation of the muscle causes it to lengthen, opening the lumen and allowing the passage of liquids, solids, or gases. This is evident, for example, in the blowholes of numerous marine mammals. Many sphincters are used every day in the normal course of digestion. For example, the lower oesophageal sphincter (or cardiac sphincter), which resides at the top of the stomach, is closed most of the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropods
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterility (physiology)
Sterility is the physiological inability to effect sexual reproduction in a living thing, members of whose kind have been produced sexually. Sterility has a wide range of causes. It may be an inherited trait, as in the mule; or it may be acquired from the environment, for example through physical injury or disease, or by exposure to radiation. Sterility is the inability to produce a biological child, while infertility is the inability to conceive after a certain period. Sterility is rarely discussed in clinical literature and is often used synonymously with infertility. Infertility affects about 12-15% of couples globally. Still, the prevalence of sterility remains unknown. Sterility can be divided into three subtypes natural, clinical, and hardship. Natural sterility is the couple’s physiological inability to conceive a child naturally. Clinical sterility is natural sterility for which treatment of the patient will not result in conception. Hardship sterility is the inability to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes. Structure The ovaries are considered the female gonads. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
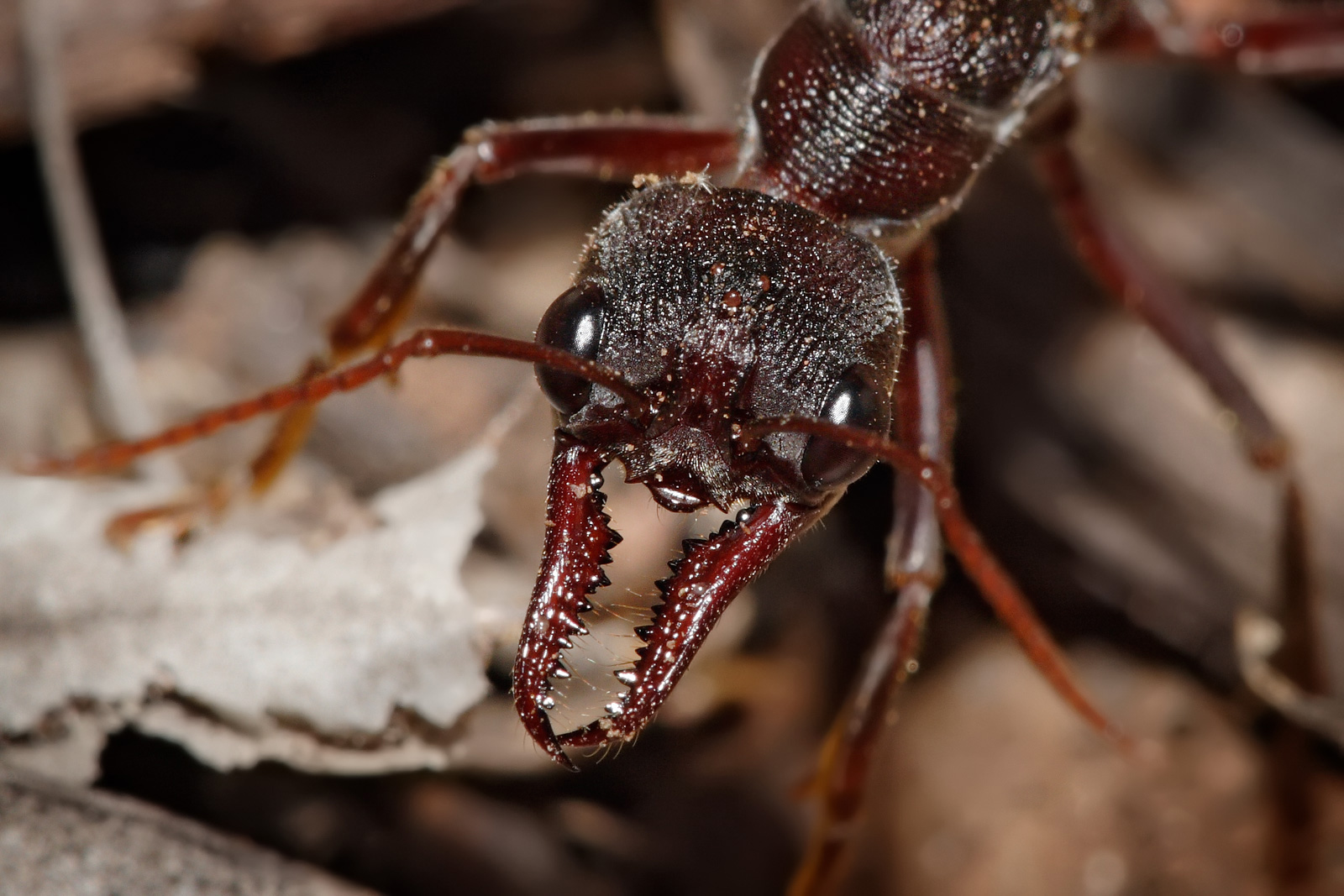
Ants Guard David Baracchi
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of 22,000 species have been classified. They are easily identified by their geniculate (elbowed) Antenna (biology), antennae and the distinctive node-like structure that forms their slender waists. Ants form Ant colony, colonies that range in size from a few dozen predatory individuals living in small natural cavities to highly organised colonies that may occupy large territories and consist of millions of individuals. Larger colonies consist of various castes of sterile, wingless females, most of which are workers (ergates), as well as soldiers (dinergates) and other specialised groups. Nearly all ant colonies also have some fertile males called "drones" and one or more fertile females ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
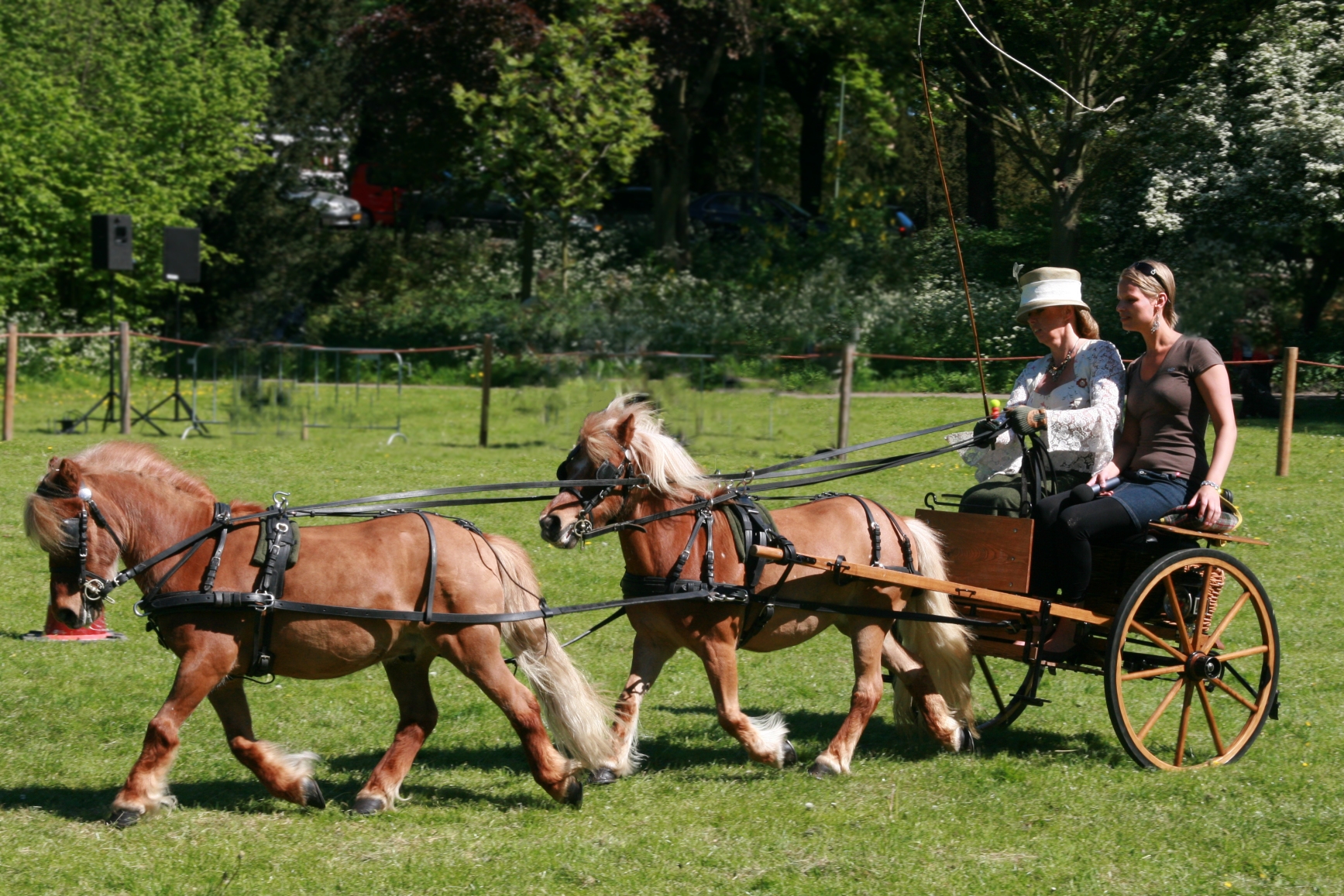
Tandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which a team of machines, animals or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction. The original use of the term in English was in ''tandem harness'', which is used for two or more draft horses, or other draft animals, harnessed in a single line one behind another, as opposed to a pair, harnessed side by side, or a team of several pairs. The tandem harness allows additional animals to provide pulling power for a vehicle designed for a single animal. The English word ''tandem'' derives from the Latin adverb , meaning ''at length'' or ''finally''. It is a word play, using the Latin phrase (referring to time, not position) for English "at length, lengthwise". Tandem bicycles are named for their tandem seating, a more common arrangement than side-by-side "sociable" seating. ''Tandem'' can also be used more generally to refer to any group of persons or objects working together, not necessarily in line. Automob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mulberr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parischnogaster Nigricans Serrei
''Parischnogaster nigricans serrei'' is a hover wasp subspecies in the family Vespidae, and it is predominantly found in the Java region of Indonesia. Its nest cells are of conical structure, linearly attached to a string-like substratum. The nests are typically found in places open to human interactions, such as gardens, trees, or forests around villages. There is a clear dominance hierarchy within colonies, which often affects the behavioral activities of its members. The wasp’s most common predators are ''Vespa tropica'', also known as the great banded hornet. ''P. nigricans serrei'' defends itself by flying away or giving out alarm calls. Taxonomy and phylogenetics Studies investigating the biology and social behavior of subfamily Stenogastrinae wasps have begun since the early 20th century, but some of their unusual morphological and ethological traits make it hard for them to have a specific systematic allocation in the phylogenetic tree. These wasps also vary a signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |