|
Pareto-efficient Envy-free Division
Efficiency and fairness are two major goals of welfare economics. Given a set of resources and a set of agents, the goal is to divide the resources among the agents in a way that is both Pareto efficient (PE) and envy-free (EF). The goal was first defined by David Schmeidler and Menahem Yaari. Later, the existence of such allocations has been proved under various conditions. Existence of PEEF allocations We assume that each agent has a preference-relation on the set of all bundles of commodities. The preferences are complete, transitive, and closed. Equivalently, each preference relation can be represented by a continuous utility function. Weakly-convex preferences ''Theorem 1 (Varian):'' ''If the preferences of all agents are convex and strongly monotone, then PEEF allocations exist.'' ''Proof'': The proof relies on the existence of a competitive equilibrium with equal incomes. Assume that all resources in an economy are divided equally between the agents. I.e, if the total e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare Economics
Welfare economics is a branch of economics that uses microeconomic techniques to evaluate well-being (welfare) at the aggregate (economy-wide) level. Attempting to apply the principles of welfare economics gives rise to the field of public economics, the study of how government might intervene to improve social welfare. Welfare economics also provides the theoretical foundations for particular instruments of public economics, including cost–benefit analysis, while the combination of welfare economics and insights from behavioral economics has led to the creation of a new subfield, behavioral welfare economics. The field of welfare economics is associated with two fundamental theorems. The first states that given certain assumptions, competitive markets produce ( Pareto) efficient outcomes; it captures the logic of Adam Smith's invisible hand. The second states that given further restrictions, any Pareto efficient outcome can be supported as a competitive market equilibrium. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitute Good
In microeconomics, two goods are substitutes if the products could be used for the same purpose by the consumers. That is, a consumer perceives both goods as similar or comparable, so that having more of one good causes the consumer to desire less of the other good. Contrary to complementary goods and independent goods, substitute goods may replace each other in use due to changing economic conditions. An example of substitute goods is Coca-Cola and Pepsi; the interchangeable aspect of these goods is due to the similarity of the purpose they serve, i.e fulfilling customers' desire for a soft drink. These types of substitutes can be referred to as close substitutes. Definition Economic theory describes two goods as being close substitutes if three conditions hold: # products have the same or similar performance characteristics # products have the same or similar occasion for use and # products are sold in the same geographic area Performance characteristics describe what the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Division
Fair division is the problem in game theory of dividing a set of resources among several people who have an entitlement to them so that each person receives their due share. That problem arises in various real-world settings such as division of inheritance, partnership dissolutions, divorce settlements, electronic frequency allocation, airport traffic management, and exploitation of Earth observation satellites. It is an active research area in mathematics, economics (especially social choice theory), dispute resolution, etc. The central tenet of fair division is that such a division should be performed by the players themselves, maybe using a mediator but certainly not an arbiter as only the players really know how they value the goods. The archetypal fair division algorithm is divide and choose. It demonstrates that two agents with different tastes can divide a cake such that each of them believes that he got the best piece. The research in fair division can be seen as an exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Equilibrium Computation
Market equilibrium computation (also called competitive equilibrium computation or clearing-prices computation) is a computational problem in the intersection of economics and computer science. The input to this problem is a ''market'', consisting of a set of ''resources'' and a set of ''agents''. There are various kinds of markets, such as Fisher market and Arrow–Debreu market, with divisible or indivisible resources. The required output is a ''competitive equilibrium'', consisting of a ''price-vector'' (a price for each resource), and an ''allocation'' (a resource-bundle for each agent), such that each agent gets the best bundle possible (for him) given the budget, and the market ''clears'' (all resources are allocated). Market equilibrium computation is interesting due to the fact that a competitive equilibrium is always Pareto efficient. The special case of a Fisher market, in which all buyers have equal incomes, is particularly interesting, since in this setting a competitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weller's Theorem
Weller's theorem is a theorem in economics. It says that a heterogeneous resource ("cake") can be divided among ''n'' partners with different valuations in a way that is both Pareto-efficient (PE) and envy-free (EF). Thus, it is possible to divide a cake fairly without compromising on economic efficiency. Moreover, Weller's theorem says that there exists a price such that the allocation and the price are a competitive equilibrium (CE) with equal incomes (EI). Thus, it connects two research fields which were previously unrelated: fair cake-cutting and general equilibrium. Background Fair cake-cutting has been studied since the 1940s. There is a heterogeneous divisible resource, such as a cake or a land-estate. There are ''n'' partners, each of whom has a personal value-density function over the cake. The value of a piece to a partner is the integral of his value-density over that piece (this means that the value is a nonatomic measure over the cake). The envy-free cake-cutting prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Cake-cutting
Fair cake-cutting is a kind of fair division problem. The problem involves a ''heterogeneous'' resource, such as a cake with different toppings, that is assumed to be ''divisible'' – it is possible to cut arbitrarily small pieces of it without destroying their value. The resource has to be divided among several partners who have different preferences over different parts of the cake, i.e., some people prefer the chocolate toppings, some prefer the cherries, some just want as large a piece as possible. The division should be ''unanimously'' fair - each person should receive a piece that he or she believes to be a fair share. The "cake" is only a metaphor; procedures for fair cake-cutting can be used to divide various kinds of resources, such as land estates, advertisement space or broadcast time. The prototypical procedure for fair cake-cutting is divide and choose, which is mentioned already in the book of Genesis. It solves the fair division problem for two people. The modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
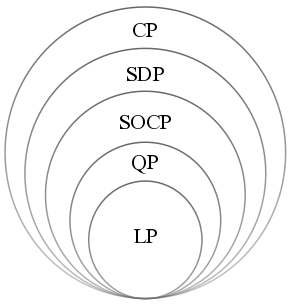
Convex Optimization
Convex optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets (or, equivalently, maximizing concave functions over convex sets). Many classes of convex optimization problems admit polynomial-time algorithms, whereas mathematical optimization is in general NP-hard. Convex optimization has applications in a wide range of disciplines, such as automatic control systems, estimation and signal processing, communications and networks, electronic circuit design, data analysis and modeling, finance, statistics ( optimal experimental design), and structural optimization, where the approximation concept has proven to be efficient. With recent advancements in computing and optimization algorithms, convex programming is nearly as straightforward as linear programming. Definition A convex optimization problem is an optimization problem in which the objective function is a convex function and the feasible set is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjusted Winner Procedure
Adjusted Winner (AW) is a procedure for envy-free item allocation. Given two agents and some goods, it returns a partition of the goods between the two agents with the following properties: # Envy-freeness: Each agent believes that his share of the goods is at least as good as the other share; # Equitable division, Equitability: The "relative happiness levels" of both agents from their shares are equal; # Pareto-optimality: no other allocation is better for one agent and at least as good for the other agent; # At most one good has to be shared between the agents. For two agents, Adjusted Winner is the only Pareto optimal and equitable procedure that divides at most a single good. The procedure can be used in divorce settlements and partnership dissolutions, as well as international conflicts. The procedure was designed by Steven Brams and Alan D. Taylor. It was first published in their book on fair division and later in a stand-alone book. The algorithm has been commercialized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractible Space
In mathematics, a topological space ''X'' is contractible if the identity map on ''X'' is null-homotopic, i.e. if it is homotopic to some constant map. Intuitively, a contractible space is one that can be continuously shrunk to a point within that space. Properties A contractible space is precisely one with the homotopy type of a point. It follows that all the homotopy groups of a contractible space are trivial. Therefore any space with a nontrivial homotopy group cannot be contractible. Similarly, since singular homology is a homotopy invariant, the reduced homology groups of a contractible space are all trivial. For a topological space ''X'' the following are all equivalent: *''X'' is contractible (i.e. the identity map is null-homotopic). *''X'' is homotopy equivalent to a one-point space. *''X'' deformation retracts onto a point. (However, there exist contractible spaces which do not ''strongly'' deformation retract to a point.) *For any space ''Y'', any two maps ''f'',''g'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakutani Fixed-point Theorem
In mathematical analysis, the Kakutani fixed-point theorem is a fixed-point theorem for set-valued functions. It provides sufficient conditions for a set-valued function defined on a convex set, convex, compact set, compact subset of a Euclidean space to have a fixed point (mathematics), fixed point, i.e. a point which is map (mathematics), mapped to a set containing it. The Kakutani fixed point theorem is a generalization of the Brouwer fixed point theorem. The Brouwer fixed point theorem is a fundamental result in topology which proves the existence of fixed points for continuous function (topology), continuous functions defined on compact, convex subsets of Euclidean spaces. Kakutani's theorem extends this to set-valued functions. The theorem was developed by Shizuo Kakutani in 1941, and was used by John Forbes Nash, Jr., John Nash in his description of Nash equilibrium, Nash equilibria. It has subsequently found widespread application in game theory and economics. Statement K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knaster–Kuratowski–Mazurkiewicz Lemma
The Knaster–Kuratowski–Mazurkiewicz lemma is a basic result in mathematical fixed-point theory published in 1929 by Knaster, Kuratowski and Mazurkiewicz. The KKM lemma can be proved from Sperner's lemma and can be used to prove the Brouwer fixed-point theorem. Statement Let \Delta_ be an (n-1)-dimensional simplex with ''n'' vertices labeled as 1,\ldots,n. A KKM covering is defined as a set C_1,\ldots,C_n of closed sets such that for any I \subseteq \, the convex hull of the vertices corresponding to I is covered by \bigcup_C_i. The KKM lemma says that in every KKM covering, the common intersection of all ''n'' sets is nonempty, i.e: :\bigcap_^n C_i \neq \emptyset. Example When n=3, the KKM lemma considers the simplex \Delta_2 which is a triangle, whose vertices can be labeled 1, 2 and 3. We are given three closed sets C_1,C_2,C_3 such that: * C_1 covers vertex 1, C_2 covers vertex 2, C_3 covers vertex 3. * The edge 12 (from vertex 1 to vertex 2) is covered by the sets C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weakly Pareto Optimal
Pareto efficiency or Pareto optimality is a situation where no action or allocation is available that makes one individual better off without making another worse off. The concept is named after Vilfredo Pareto (1848–1923), Italian civil engineer and economist, who used the concept in his studies of economic efficiency and income distribution. The following three concepts are closely related: * Given an initial situation, a Pareto improvement is a new situation where some agents will gain, and no agents will lose. * A situation is called Pareto-dominated if there exists a possible Pareto improvement. * A situation is called Pareto-optimal or Pareto-efficient if no change could lead to improved satisfaction for some agent without some other agent losing or, equivalently, if there is no scope for further Pareto improvement. The Pareto front (also called Pareto frontier or Pareto set) is the set of all Pareto-efficient situations. Pareto originally used the word "optimal" for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)