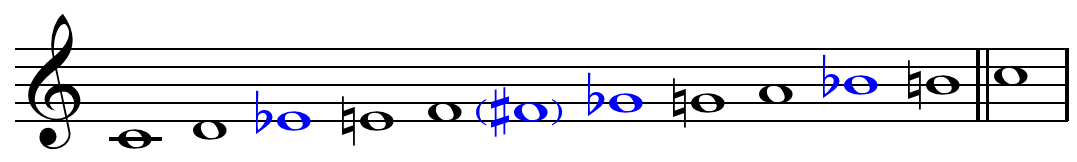|
Parchman Farm (song)
"Parchman Farm" or "Parchman Farm Blues" is a blues song first recorded by American Delta blues musician Bukka White in 1940. It is an autobiographical piece, in which White sings of his experience at the infamous Mississippi State Penitentiary, otherwise known as Parchman Farm. Jazz pianist-vocalist Mose Allison adapted it for his own "Parchman Farm" and "New Parchman", which are among his most popular songs. Numerous artists have recorded their own renditions, usually based on Allison's songs. Background Early in his recording career in 1937, Bukka White was arrested and convicted for a shooting incident and was sentenced to Parchman Farm prison in rural Sunflower County, Mississippi. The institution was operated as a hard-time prison labor work farm, which was notorious for its harsh conditions and use of the trusty system. His recording of " Shake 'Em On Down" became a hit while he was there and as a result, White became somewhat of a celebrity at the prison. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukka White
Booker T. Washington "Bukka" White (November 12, 1906 February 26, 1977) was an American Delta blues guitarist and singer. Biography White was born south of Houston, Mississippi. He was a first cousin of B.B. King's mother (White's mother and King's grandmother were sisters). ''Bukka'' is a phonetic spelling of White's first name; he was named after the African-American educator and civil rights activist Booker T. Washington. He played National resonator guitars, typically with a slide, in an open tuning. He was one of the few, along with Skip James, to use a crossnote tuning in E minor, which he may have learned, as James did, from Henry Stuckey. He also played piano, but less adeptly. White started his career playing the fiddle at square dances. He claimed to have met Charley Patton soon after, but some have doubted this recollection. Nonetheless, Patton was a strong influence on White. "I wants to come to be a great man like Charlie Patton", White told his frien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backbeat Books
In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse (music), pulse (regularly repeating event), of the ''mensural level'' (or ''beat level''). The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when listening to a piece of music, or the numbers a musician counting (music), counts while performing, though in practice this may be technically incorrect (often the first multiple level). In popular use, ''beat'' can refer to a variety of related concepts, including pulse (music), pulse, tempo, meter (music), meter, specific rhythms, and groove (popular music), groove. Rhythm in music is characterized by a repeating sequence of #On-beat and off-beat, stressed and unstressed beats (often called "strong" and "weak") and divided into bar (music), bars organized by time signature and tempo indications. Beats are related to and distinguished from pulse, rhythm (grouping), and meter: Meter (music)#Metric structure, Metric levels faster than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Blues
West Coast blues is a type of blues music influenced by jazz and jump blues, with strong piano-dominated sounds and jazzy guitar solos, which originated from Texas blues players who relocated to California in the 1940s. West Coast blues also features smooth, honey-toned vocals, frequently crossing into rhythm and blues territory. Texas and the West Coast The towering figure of West Coast blues may be the guitarist T-Bone Walker, famous for the song "Call It Stormy Monday (But Tuesday Is Just as Bad)", a relocated Texan, who made his first recordings in the late 1920s. In the early 1940s, Walker moved to Los Angeles,Obrecht, Jas (2000). ''Rollin' and Tumblin': The Postwar Blues Guitarists''. Backbeat Books. p. 7. . where he recorded many enduring sides for Capitol, Black & White, and Imperial. Walker was a crucial figure in the electrification and urbanization of the blues, probably doing more to popularize the electric guitar in the form than anyone else. Much of his mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-Bone Walker
Aaron Thibeaux "T-Bone" Walker (May 28, 1910 – March 16, 1975) was an American blues musician, composer, songwriter and bandleader, who was a pioneer and innovator of the jump blues, West Coast blues, and electric blues sounds. In 2018 ''Rolling Stone'' magazine ranked him number 67 on its list of "The 100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time". Biography 1910–1941: Early years Aaron Thibeaux Walker was born in Linden, Texas, of African-American and Cherokee descent. His parents, Movelia Jimerson and Rance Walker, were both musicians. His stepfather, Marco Washington (a member of the Dallas String Band), taught him to play the guitar, ukulele The ukulele ( ; from haw, ukulele , approximately ), also called Uke, is a member of the lute family of instruments of Portuguese origin and popularized in Hawaii. It generally employs four nylon strings. The tone and volume of the instrumen ..., banjo, violin, mandolin, and piano. Walker began his career as a teenager in Dallas i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jump Blues
Jump blues is an up-tempo style of blues, usually played by small groups and featuring horn instruments. It was popular in the 1940s and was a precursor of rhythm and blues and rock and roll. Appreciation of jump blues was renewed in the 1990s as part of the swing revival. Origins Jump blues evolved from the music of big bands such as those of Lionel Hampton and Lucky Millinder in the early 1940s which produced musicians such as Louis Jordan, Jack McVea, Earl Bostic, and Arnett Cobb. Jordan was the most popular of the jump blues stars; other artists who played the genre include Roy Brown, Amos Milburn, and Joe Liggins, as well as sax soloists Jack McVea, Big Jay McNeely, and Bull Moose Jackson. Hits included singles such as Jordan's "Saturday Night Fish Fry", Roy Brown's "Good Rockin' Tonight" and Big Jay McNeely's "Deacon's Hop". One important stylistic prototype in the development of R&B was jump blues, pioneered by Louis Jordan, with ... His Tympany Five ... thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Jordan
Louis Thomas Jordan (July 8, 1908 – February 4, 1975) was an American saxophonist, multi-instrumentalist, songwriter and bandleader who was popular from the late 1930s to the early 1950s. Known as " the King of the Jukebox", he earned his highest profile towards the end of the swing era. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as an "early influence" in 1987. Specializing in the alto sax, Jordan played all forms of the saxophone, as well as piano and clarinet. He also was a talented singer with great comedic flair, and fronted his own band for more than twenty years. He duetted with some of the biggest solo singing stars of his time, including Bing Crosby, Ella Fitzgerald and Louis Armstrong. Jordan was also an actor and a film personality—he appeared in dozens of "soundies" (promotional film clips) He also made numerous cameos in mainstream features and short films, and starred in two musical feature films: Swing Parade of 1946, probably targeting white viewers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ted Gioia
Ted Gioia (born October 21, 1957) is an American jazz critic and music historian. He is author of eleven books, including ''Music: A Subversive History'', '' The Jazz Standards: A Guide to the Repertoire'', ''The History of Jazz'' and ''Delta Blues''. He is also a jazz musician and one of the founders of Stanford University's jazz studies program. Early years Gioia grew up in an Italian-Mexican household in Hawthorne, California, and later earned degrees from Stanford University and Oxford University, as well as an MBA from the Stanford Graduate School of Business. He served for a period as an adviser to Fortune 500 companies while with the Boston Consulting Group and McKinsey & Company. When Gioia worked amidst Silicon Valley's venture capital community on Sand Hill Road, he was known as the "guy with the piano in his office." Gioia is also owner of one of the largest collections of research materials on jazz and ethnic music in the Western United States. Gioia is the brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
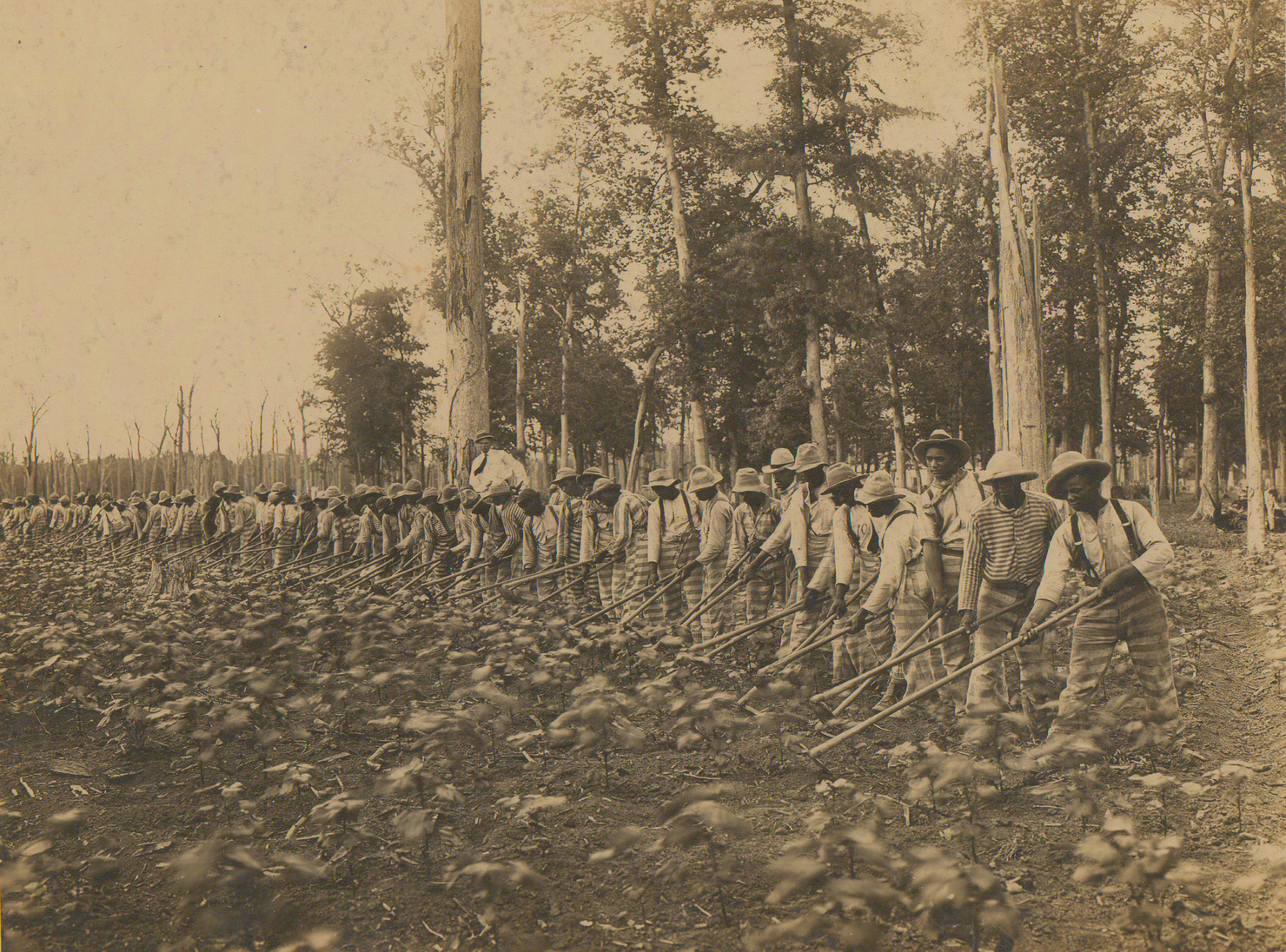
Parchman Prison Convict Labor 1911
Mississippi State Penitentiary (MSP), also known as Parchman Farm, is a maximum-security prison farm located in unincorporated Sunflower County, Mississippi, in the Mississippi Delta region. Occupying about of land,"State Prisons" . . Retrieved January 14, 2011."MDOC Quick Reference" Mississippi Department of Corrections. Retrieved May 21, 2010. Parchman is the only maximum security prison for men in the state of |
Washboard (musical Instrument)
The washboard and frottoir (from Cajun French "frotter", to rub) are used as a percussion instrument, employing the ribbed metal surface of the cleaning device as a rhythm instrument. As traditionally used in jazz, zydeco, skiffle, jug band, and old-time music, the washboard remained in its wooden frame and is played primarily by tapping, but also scraping the washboard with thimbles. Often the washboard has additional traps, such as a wood block, a cowbell, and even small cymbals. Conversely, the frottoir (zydeco rubboard) dispenses with the frame and consists simply of the metal ribbing hung around the neck. It is played primarily with spoon handles or bottle openers in a combination of strumming, scratching, tapping and rolling. The frottoir or '' vest frottoir'' is played as a stroked percussion instrument, often in a band with a drummer, while the washboard generally is a replacement for drums. In Zydeco bands, the frottoir is usually played with bottle openers, to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washboard Sam
Robert Clifford Brown (July 15, 1910 – November 6, 1966), known professionally as Washboard Sam, was an American blues musician and singer. Biography Brown's date and place of birth are uncertain; many sources state that he was born in 1910 in Walnut Ridge, Arkansas, but the researchers Bob Eagle and Eric LeBlanc suggest that he was born in 1903 or 1904, in Jackson, Tennessee, on the basis of Social Security information. When applying for his musicians union card, he gave his birthdate as July 15, 1914. He was reputedly the half-brother of Big Bill Broonzy. He moved to Memphis, Tennessee, in the 1920s, performing as a street musician with Sleepy John Estes and Hammie Nixon. He moved to Chicago in 1932, performing regularly with Broonzy and other musicians, including Memphis Slim and Tampa Red, in many recording sessions for Lester Melrose of Bluebird Records. In 1935, he began recording in his own right for both Bluebird and Vocalion Records, becoming one of the most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Note
In jazz and blues, a blue note is a note that—for expressive purposes—is sung or played at a slightly different pitch from standard. Typically the alteration is between a quartertone and a semitone, but this varies depending on the musical context. Origins and meaning The blue notes are usually said to be the lowered third, lowered fifth, and lowered seventh scale degrees. The lowered fifth is also known as the raised fourth.Ferguson, Jim (1999). ''All Blues Soloing for Jazz Guitar: Scales, Licks, Concepts & Choruses'', p. 20. . Though the blues scale has "an inherent minor tonality, it is commonly 'forced' over major-key chord changes, resulting in a distinctively dissonant conflict of tonalities". A similar conflict occurs between the notes of the minor scale and the minor blues scale, as heard in songs such as " Why Don't You Do Right?", "Happy" and " Sweet About Me". In the case of the lowered third over the root (or the lowered seventh over the dominant), the resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Guitar
Slide guitar is a technique for playing the guitar that is often used in blues music. It involves playing a guitar while holding a hard object (a slide) against the strings, creating the opportunity for glissando effects and deep vibratos that reflect characteristics of the human singing voice. It typically involves playing the guitar in the traditional position (flat against the body) with the use of a slide fitted on one of the guitarist's fingers. The slide may be a metal or glass tube, such as the neck of a bottle. The term bottleneck was historically used to describe this type of playing. The strings are typically plucked (not strummed) while the slide is moved over the strings to change the pitch. The guitar may also be placed on the player's lap and played with a hand-held bar (lap steel guitar). Creating music with a slide of some type has been traced back to African stringed instruments and also to the origin of the steel guitar in Hawaii. Near the beginning of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)