|
Parastatistics
In quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics, parastatistics is one of several alternatives to the better known particle statistics models (Bose–Einstein statistics, Fermi–Dirac statistics and Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics). Other alternatives include anyonic statistics and braid statistics, both of these involving lower spacetime dimensions. Herbert S. Green is credited with the creation of parastatistics in 1953. Formalism Consider the operator algebra of a system of ''N'' identical particles. This is a *-algebra. There is an ''SN'' group (symmetric group of order ''N'') acting upon the operator algebra with the intended interpretation of permuting the ''N'' particles. Quantum mechanics requires focus on observables having a physical meaning, and the observables would have to be invariant under all possible permutations of the ''N'' particles. For example, in the case ''N'' = 2, ''R''2 − ''R''1 cannot be an observable because it changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braid Statistics
In mathematics and theoretical physics, braid statistics is a generalization of the spin statistics of bosons and fermions based on the concept of braid group. While for fermions (Bosons) the corresponding statistics is associated to a phase gain of \pi (2 \pi) under the exchange of identical particles, a particle with braid statistics leads to a rational fraction of \pi under such exchange or even a non-trivial unitary transformation in the Hilbert space (see non-Abelian anyons). A similar notion exists using a loop braid group. Braid statistics are applicable to theoretical particles such as the two-dimensional anyons and their higher-dimensional analogues known as plektons. See also * Braid symmetry * Parastatistics In quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics, parastatistics is one of several alternatives to the better known particle statistics models (Bose–Einstein statistics, Fermi–Dirac statistics and Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics). Other alt ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Statistics
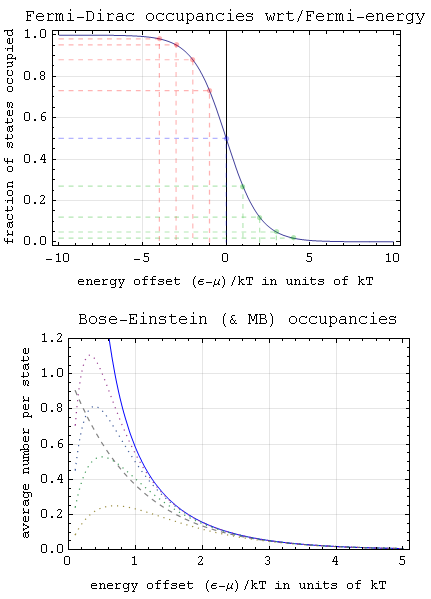
In quantum statistics, Bose–Einstein statistics (B–E statistics) describes one of two possible ways in which a collection of non-interacting, indistinguishable particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states at thermodynamic equilibrium. The aggregation of particles in the same state, which is a characteristic of particles obeying Bose–Einstein statistics, accounts for the cohesive streaming of laser light and the frictionless creeping of superfluid helium. The theory of this behaviour was developed (1924–25) by Satyendra Nath Bose, who recognized that a collection of identical and indistinguishable particles can be distributed in this way. The idea was later adopted and extended by Albert Einstein in collaboration with Bose. The Bose–Einstein statistics applies only to the particles not limited to single occupancy of the same state – that is, particles that do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle restrictions. Such particles have integer values of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac Statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac distribution of particles over energy states. It is named after Enrico Fermi and Paul Dirac, each of whom derived the distribution independently in 1926 (although Fermi derived it before Dirac). Fermi–Dirac statistics is a part of the field of statistical mechanics and uses the principles of quantum mechanics. F–D statistics applies to identical and indistinguishable particles with half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, etc.), called fermions, in thermodynamic equilibrium. For the case of negligible interaction between particles, the system can be described in terms of single-particle energy states. A result is the F–D distribution of particles over these states where no two particles can occupy the same state, which has a considerable ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyonic Statistics
In physics, an anyon is a type of quasiparticle that occurs only in two-dimensional systems, with properties much less restricted than the two kinds of standard elementary particles, fermions and bosons. In general, the operation of exchanging two identical particles, although it may cause a global phase shift, cannot affect observables. Anyons are generally classified as ''abelian'' or ''non-abelian''. Abelian anyons (detected by two experiments in 2020) play a major role in the fractional quantum Hall effect. Non-abelian anyons have not been definitively detected, although this is an active area of research. Introduction The statistical mechanics of large many-body systems obeys laws described by Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics. Quantum statistics is more complicated because of the different behaviors of two different kinds of particles called fermions and bosons. Quoting a recent, simple description:In the three-dimensional world we live in, there are only two types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spin (,, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Bosons are named after physicist Satyendra Nath Bose. Some bosons are elementary particles and occupy a special role in particle physics unlike that of fermions, which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter". Some elementary bosons (for example, gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) gives rise to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, superfluidity arises because composite bosons (bose particles), such as low temperature helium-4 atoms, follow Bose–Ein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable
In physics, an observable is a physical quantity that can be measured. Examples include position and momentum. In systems governed by classical mechanics, it is a real-valued "function" on the set of all possible system states. In quantum physics, it is an operator, or gauge, where the property of the quantum state can be determined by some sequence of operations. For example, these operations might involve submitting the system to various electromagnetic fields and eventually reading a value. Physically meaningful observables must also satisfy transformation laws that relate observations performed by different observers in different frames of reference. These transformation laws are automorphisms of the state space, that is bijective transformations that preserve certain mathematical properties of the space in question. Quantum mechanics In quantum physics, observables manifest as linear operators on a Hilbert space representing the state space of quantum states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory. Group theory The commutator of two elements, and , of a group , is the element : . This element is equal to the group's identity if and only if and commute (from the definition , being equal to the identity if and only if ). The set of all commutators of a group is not in general closed under the group operation, but the subgroup of ''G'' generated by all commutators is closed and is called the ''derived group'' or the '' commutator subgroup'' of ''G''. Commutators are used to define nilpotent and solvable groups and the largest abelian quotient group. The definition of the commutator above is used throughout this article, but many other group theorists define the commutator as :. Identities (group theory) Commutator identities are an important tool in group theory. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticommutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory. Group theory The commutator of two elements, and , of a group , is the element : . This element is equal to the group's identity if and only if and commute (from the definition , being equal to the identity if and only if ). The set of all commutators of a group is not in general closed under the group operation, but the subgroup of ''G'' generated by all commutators is closed and is called the ''derived group'' or the ''commutator subgroup'' of ''G''. Commutators are used to define nilpotent and solvable groups and the largest abelian quotient group. The definition of the commutator above is used throughout this article, but many other group theorists define the commutator as :. Identities (group theory) Commutator identities are an important tool in group theory. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Statistics
Particle statistics is a particular description of multiple particles in statistical mechanics. A key prerequisite concept is that of a statistical ensemble (an idealization comprising the state space of possible states of a system, each labeled with a probability) that emphasizes properties of a large system as a whole at the expense of knowledge about parameters of separate particles. When an ensemble describes a system of particles with similar properties, their number is called the particle number and usually denoted by ''N''. Classical statistics In classical mechanics, all particles ( fundamental and composite particles, atoms, molecules, electrons, etc.) in the system are considered distinguishable. This means that individual particles in a system can be tracked. As a consequence, switching the positions of any pair of particles in the system leads to a different configuration of the system. Furthermore, there is no restriction on placing more than one particle in any given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graded Algebra
In mathematics, in particular abstract algebra, a graded ring is a ring such that the underlying additive group is a direct sum of abelian groups R_i such that R_i R_j \subseteq R_. The index set is usually the set of nonnegative integers or the set of integers, but can be any monoid. The direct sum decomposition is usually referred to as gradation or grading. A graded module is defined similarly (see below for the precise definition). It generalizes graded vector spaces. A graded module that is also a graded ring is called a graded algebra. A graded ring could also be viewed as a graded \Z-algebra. The associativity is not important (in fact not used at all) in the definition of a graded ring; hence, the notion applies to non-associative algebras as well; e.g., one can consider a graded Lie algebra. First properties Generally, the index set of a graded ring is assumed to be the set of nonnegative integers, unless otherwise explicitly specified. This is the case in this ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Algebra
In mathematical physics, the Dirac algebra is the Clifford algebra \text_(\mathbb). This was introduced by the mathematical physicist P. A. M. Dirac in 1928 in developing the Dirac equation for spin-½ particles with a matrix representation of the gamma matrices, which represent the generators of the algebra. The gamma matrices are a set of four 4\times 4 matrices \ = \ with entries in \mathbb, that is, elements of \text_(\mathbb), satisfying :\displaystyle\ = \gamma^\mu \gamma^\nu + \gamma^\nu \gamma^\mu = 2 \eta^, where by convention, an identity matrix has been suppressed on the right-hand side. The numbers \eta^ \, are the components of the Minkowski metric. For this article we fix the signature to be ''mostly minus'', that is, (+,-,-,-). The Dirac algebra is then the linear span of the identity, the gamma matrices \gamma^\mu as well as any linearly independent products of the gamma matrices. This forms a finite-dimensional algebra over the field \mathbb or \mathbb, with d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |