|
Parapeytoia
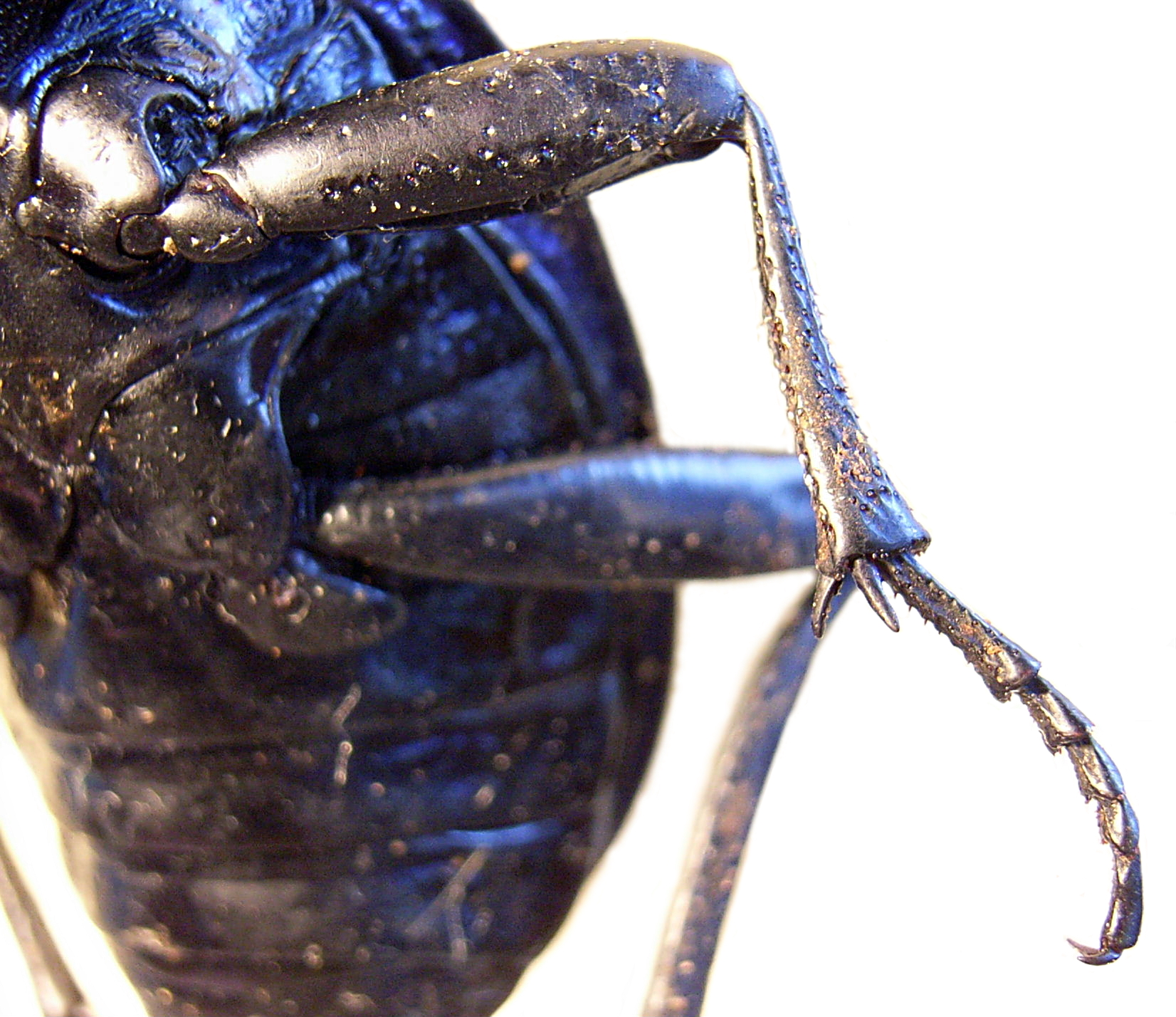
''Parapeytoia'' was a prehistoric arthropod that lived over 530 million years ago (Cambrian Stage 3) in the Maotianshan shales of prehistoric China. It was interpreted as an anomalocaridid (radiodont) with legs, but later studies reveal it was a megacheiran, a group of arthropods which are no longer thought to be closely related to the radiodonts. ''Parapeytoia'' is known from a few incomplete fossil materials with part of its ventral structures preserved. The frontmost appendages were a pair of great appendages that had a peduncle and 4 spines on each of them, a characteristic feature shared by other megacheirans such as ''Yohoia'' and '' Fortiforceps''. Behind the great appendages were 2 or 3 pairs of short appendages, and numerous pairs of well-developed biramous appendages, each formed by a basipod with spiny gnathobase, lobe-like exopod and leg-like endopod with 8 segments. A narrow sternite associated between each of those appendages. Some features originally interpret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalocaridid
Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', '' Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster falcatus'' and '' Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician '' Aegirocassis benmoulai'' and the Devonian ''Schinderhannes bartelsi''. Etymology The name Radiodonta ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megacheira
Megacheira ("great hands") is an extinct class of predatory arthropods that possessed a pair of great appendages, hence the class name as well as the common name "great appendage arthropods". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. Most of them were found in marine environments throughout the world from the lower to middle Cambrian. Megacheirans were important components of several faunas, including the Burgess, Wheeler and Maotianshan Shales Lagerstatten. Homology of great appendages The homology between megacheiran great appendages and cephalic appendages of other arthropods had been discussed for decades. There is controversy over whether they are homologous to both dinocaridid (radiodonts and gilled lobopodians) frontal appendages, the frontalmost appendages of ''Isoxys'' and chelicerates' chelicerae. Based on neuroanatomical evidences, many studies support their homology to ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megacheira
Megacheira ("great hands") is an extinct class of predatory arthropods that possessed a pair of great appendages, hence the class name as well as the common name "great appendage arthropods". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. Most of them were found in marine environments throughout the world from the lower to middle Cambrian. Megacheirans were important components of several faunas, including the Burgess, Wheeler and Maotianshan Shales Lagerstatten. Homology of great appendages The homology between megacheiran great appendages and cephalic appendages of other arthropods had been discussed for decades. There is controversy over whether they are homologous to both dinocaridid (radiodonts and gilled lobopodians) frontal appendages, the frontalmost appendages of ''Isoxys'' and chelicerates' chelicerae. Based on neuroanatomical evidences, many studies support their homology to ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Appendage
Great appendages are claw-like appendages which attach to the heads of the "great appendage arthropods", a name usually refers to Megacheira, a class of extinct arthropod characterized by a pair of "short-great appendages" bearing in front of the animal's head. In general, megacheiran's great appendage have 6 segments, with the two proximal segments forming a peduncle and the four finger-like distal segments forming a claw, both connected by an elbow joint. Great appendages have been interpreted as raptorial limbs involved in predation, with those of some genera such as ''Yohoia'' being structurally comparable to the raptorial maxillipeds of mantis shrimp. The great appendages of leanchoilid megacheirans such as ''Leanchoilia'' and ''Yawunik'' have elongated flagella, suggesting a sensory role alongside predatory function. Radiodonta, Radiodont's frontal appendages have controversial relationships to those of the megacheirans. They have been suggested to be Homology (biology), ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnidens
''Omnidens amplus'', meaning "large all-tooth", is an extinct species of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian ''Pambdelurion'', indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, with which it may be synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of , ''Omnidens'' is suggested to have been the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. ''Omnidens'' fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales. Description ''Omnidens'' is only known from mouthparts. The preserved mouthparts would have formed a short muscular, potentially protrusible pharynx surrounded by circles of spiny sclerites, which were reminiscent of the scalids of priapulids, kinorhynchs, and loriciferans. The inside of the pharynx wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortiforceps
''Fortiforceps'' is an extinct genus of Cambrian megacheiran arthropod known from the Chengjiang biota of Yunnan, China. It was originally described by Hou and Bergström in 1997,X. Hou and J. Bergström. 1997Arthropods of the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, southwest China Fossils & Strata 45:1-116 and redescribed in 2020. It was relatively small, at or less in length. The head has a large pair of stalked eyes, a pair of frontal projections, as well as a pair of great appendages, like other megacheirans, along with two other cephalic appendages. The trunk has either 20 or 22 segments, depending on the specimen. These segments have pronounced blade-like spines on their upper-outer edge. Each of the trunk segments (aside from the last, typically 20th segment) are associated with pairs of biramous The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Stage 3
Cambrian Stage 3 is the still unnamed third stage of the Cambrian. It succeeds Cambrian Stage 2 and precedes Cambrian Stage 4, although neither its base nor top have been formally defined. The plan is for its lower boundary to correspond approximately to the first appearance of trilobites, about million years ago, though the globally asynchronous appearance of trilobites warrants the use of a separate, globally synchronous marker to define the base. The upper boundary and beginning of Cambrian Stage 4 is informally defined as the first appearance of the trilobite genera ''Olenellus'' or '' Redlichia'' around million years ago. Naming The International Commission on Stratigraphy has not officially named the 3rd stage of the Cambrian. The stage approximately corresponds to the "Atdabanian", which is used by geologists working in Siberia. Biostratigraphy The oldest trilobite known is ''Lemdadella'' which appears at the beginning of the '' Fallotaspis'' zone. The Cambrian radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Arthropods
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternite
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that vertrite numbers do not correspond to sternid numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendages
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body. In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs (pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs (gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In vertebrates, an appendage can refer to a locomotor part such as a tail, fins on a fish, limbs (legs, flippers or wings) on a tetrapod; exposed sex organ; defensive parts such as horns and antlers; or sensory organs such as auricles, proboscis ( trunk and snout) and barbels. Appendages may become ''uniramous'', as in insects and centipedes, where each appendage comprises a single series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yohoia
''Yohoia'' is an extinct genus of megacheiran arthropod from the Cambrian period that has been found as fossils in the Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia, Canada. It has been placed among the arachnomorpha, a group of arthropods that includes the chelicerates and possibly the trilobites. Fossils range in size from 7 to 23 mm. 711 specimens of ''Yohoia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 1.35% of the community. ''Yohoia'' is one of the "great appendage" arthropods. All taxa have a single pair of large pre-oral jointed limbs with branched spiny ends for grasping, impaling, or filtering food items. "Great appendage" arthropods have been seen as a polyphyletic group where the appendage has independently evolved, or as a Class Megacheira including ''Yohoia'' (with ''Leanchoilia'', ''Alalcomenaeus'', ''Oestokerkus'', ''Fortiforceps'', ''Jianfengia'', ''Yawunik'') defined as euarthropods, plus the radiodonts, defined as a sister group to arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |