|
Paranapanema Block
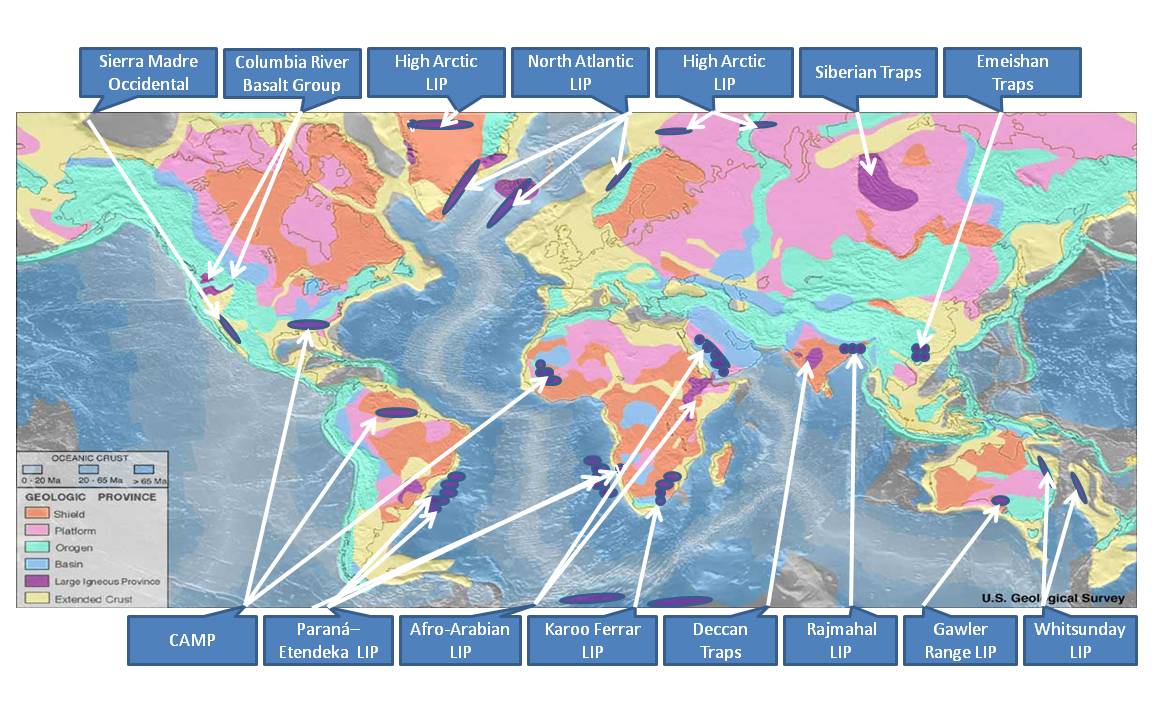
The Paranapanema block is a coherent block of lithosphere located in southeastern South America spanning roughly the same area as the Paraná Basin. The existence of a tectonically stable zone beneath the Paraná Basin was first suggested in 1975. Despite difficulties in accessing the buried Paranapanema block it is inferred it must be composed mostly of orthogneiss and that it existed before the Brasiliano orogeny. Description Paranapanema is a triangular block surrounded by structures of the Neoproterozoic Brasiliano orogeny. The northwestern edge faces the Paraguai Belt, probably the remains of an island arc from the Brazilides Ocean. On the northeast edge are the southern end of the Brasilia Belt and the Arenópolis magmatic arc. To the south and southeast are the Apiaí and São Roque belts. During the Carboniferous, Paranapanema was covered by sediments and during the Early Cretaceous, the Paraná-Etendeka large igneous province A large igneous province (LIP) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the uppermost mantle. The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plasticity (physics), pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná Basin
The Paraná Basin ( pt, Bacia do Paraná, es, Cuenca del Paraná) is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distributed in eastern Paraguay, northeastern Argentina and northern Uruguay. The shape of the depression is roughly Ellipse, elliptical and covers an area of about . The Paraná River, from which the Paraná Basin derived its name, flows along the central axis of the Paraná Basin and drains it. Description The Paraná Basin stretches from the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso in the north to northern Argentina and Uruguay in the south. The southern portion in Uruguay is locally known as Norte Basin.De Santa Ana et al., 2004, p.88Daners et al., 2006, p.148 Pioneer studies The first study on the Brazilian side of the Paraná Basin dates from 1841, when a Brazilian Empire, Brazilian Imperial Govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures and pressures than schist. Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct cleavage. Gneisses are common in the ancient crust of continental shields. Some of the oldest rocks on Earth are gneisses, such as the Acasta Gneiss. Description Orthogneiss from the Czech Republic In traditional English and North American usage, a gneiss is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock showing compositional banding (gneissic banding) but poorly developed schistosity and indistinct cleavage. In other words, it is a metamorphic rock composed of mineral grains easily seen with the unaided eye, which form obvious compositional layers, but which has only a weak tendency to fracture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasiliano Orogeny
Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle ( pt, Orogênese Brasiliana and ''Ciclo Brasiliano'') refers to a series of orogenies of Neoproterozoic age exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a regional name for the larger Pan-African/Brasiliano orogeny that extended not only in South America but across most of Gondwana. In a wide sense the Brasiliano orogeny includes also the Pampean orogeny. Almeida ''et al''. coined the term Brasiliano Orogenic Cycle in 1973. The orogeny led to the closure of several oceans and aulacogens including the Adamastor Ocean, the Goianides Ocean, the Puncoviscana Ocean and the Peri-Franciscano Ocean. Attempts to correlate the South American Brasiliano belts with the African Pan-African belts on the other side of the Atlantic has in many cases been problematic. Belts and belt provinces }) , Northeast Brazil, Southeast Brazil , São Francisco Craton , , The Araçuaí Belt is the west portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction, subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a Oceanic trench, deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of islands which contains older volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná And Etendeka Traps
The Paraná-Etendeka traps (or Paraná and Etendeka Plateau; or Paraná and Etendeka Province) comprise a large igneous province that includes both the main Paraná traps (in Paraná Basin, a South American geological basin) as well as the smaller severed portions of the flood basalts at the Etendeka traps (in northwest Namibia and southwest Angola). The original basalt flows occurred 138 to 128 million years ago. The province had a post-flow surface area of and an original volume projected to be in excess of 2.3 x 106 km³. Geodynamics The basalt samples at Paraná and Etendeka have an age of about 132 Ma, during the Valanginian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Indirectly, the rifting and extension are probably the origin of the Paraná and Etendeka traps and it could be the origin of the Gough and Tristan da Cunha Islands as well, as they are connected by the Walvis Ridge (Gough/Tristan hotspot). The seamounts of the Rio Grande Rise (25°S to 35°S) that go eastwards fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cratons
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots that extend as much as several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: A continental ''shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of South America
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Argentina
The geology of Argentina includes ancient Precambrian basement rock affected by the Grenville orogeny, sediment filled basins from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic as well as newly uplifted areas in the Andes. Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics The oldest rocks in Argentina date to the Precambrian. Strontium, oxygen and carbon isotope data from carbonate rocks in the Sierra de Pie de Palo are part of an ophiolite unit related to the Grenville orogeny, formed as cover rock in the Appalachian margin of the continent Laurentia around 720 million years ago. These Neoproterozoic age rocks are believed to have formed above much older Archean craton rock. Throughout the late Proterozoic, sections of Argentina were part of a metamorphic mobile belt adjacent to the Brazilian Shield. Regional metamorphism produced scheelite belts and wolframite in parts of San Luis and Cordoba Provinces. To the north, along the Bolivian border in the Altiplano, drilling has revealed Precambrian Hornblend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Brazil
The geology of Brazil includes very ancient craton basement rock from the Precambrian overlain by sedimentary rocks and intruded by igneous activity, as well as impacted by the rifting of the Atlantic Ocean. Geologic history, stratigraphy, and tectonics Much of the rock underlying Brazil formed during the Precambrian, including the São Francisco Craton which outcrops in Minas Gerais and Bahia. In the Mesoproterozoic, the Rio de la Plata Craton (beneath southern Brazil), the vast Amazonia Craton, and the small São Luis Craton and sections of the Congo Craton which form the basement rock of much of Brazil were joined with Africa. Earlier, during the Archean, the São Francisco Craton developed between 3.2 and 2.6 billion years ago and grew as microcontinents collided with it, forming a series of mobile belts. The rocks became a craton, a section of stable continental crust by the end of the Trans-amazonian orogeny 1.8 billion years ago. The Borborema Province is benea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |