|
Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation
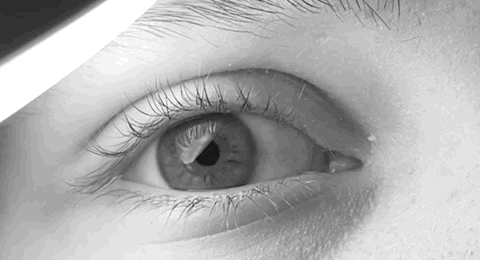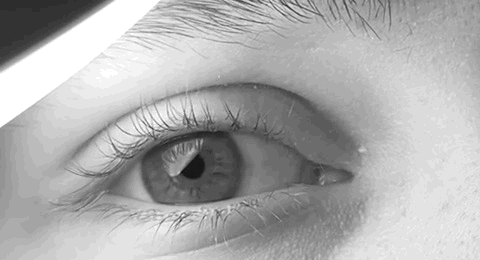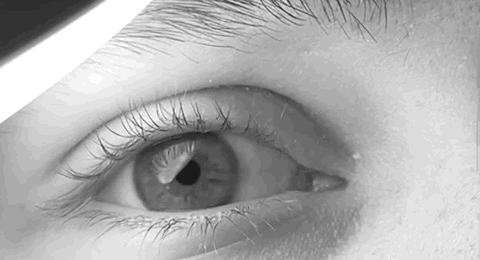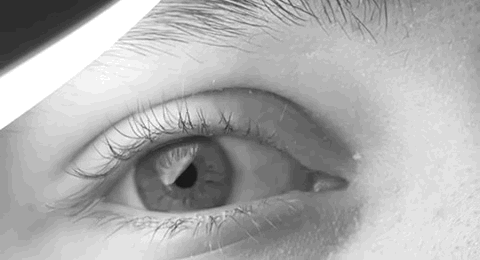
The paramedian pontine reticular formation, also known as PPRF or paraabducens nucleus, is part of the pontine reticular formation, a brain region without clearly defined borders in the center of the pons. It is involved in the coordination of eye movements, particularly horizontal gaze and saccades. Input, output, and function The PPRF is located anterior and lateral to the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). It receives input from the superior colliculus via the predorsal bundle and from the frontal eye fields via frontopontine fibers. The rostral PPRF probably coordinates vertical saccades; the caudal PPRF may be the generator of horizontal saccades. In particular, activity of the excitatory burst neurons (EBNs) in the PPRF generates the "pulse" movement that initiates a saccade. In the case of horizontal saccades the "pulse" information is conveyed via axonal fibres to the abducens nucleus, initiating lateral eye movements. The angular velocity of the eye during horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts. Neurons of the reticular formation, particularly those of the ascending reticular activating system, play a crucial role in maintaining behavioral arousal and consciousness. The overall functions of the reticular formation are modulatory and premotor, involving somatic motor control, cardiovascular control, pain modulation, sleep and consciousness, and habituation. The modulatory functions are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsoclonus
Opsoclonus refers to uncontrolled, irregular, and nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements without inter-saccadic intervals. It is also referred to as saccadomania or reflexive saccade. The movements of opsoclonus may have a very small amplitude, appearing as tiny deviations from primary position. Possible causes of opsoclonus include neuroblastoma and encephalitis in children, and breast, lung, or ovarian cancer in adults. Other considerations include multiple sclerosis, toxins, medication effects (e.g. Serotonin Syndrome), celiac disease, certain infections (West Nile virus, Lyme disease), non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and renal adenocarcinoma. It can also be caused by a lesion in the omnipause neurons which tonically inhibit initiation of saccadic eye movement (until signaled by the superior colliculus) by blocking paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) burst neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramedian Reticular Nucleus
The paramedian reticular nucleus (in Terminologia Anatomica, or paramedian medullary reticular group in NeuroNames) sends its connections to the spinal cord in a mostly ipsilateral manner, although there is some decussation. It projects to the vermis in the anterior lobe, the pyramis and the uvula. The paramedian nucleus also projects to the contralateral PRN, the gigantocellular nucleus, and the nucleus ambiguous. The paramedian reticular formation is adjacent to the abducens (VI)nucleus in the pons and adjacent to the oculomotor nucleus(III) in the midbrain. The paramedian nucleus receives afferents mostly from the fastigial nucleus in the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex; however, the projections from the spinal cord are very sparse. The descending afferent connections come mostly from the frontal and parietal lobes; however the pontine reticular formation also sends projections to the paramedian reticular nucleus. There are also very sparse innervations from the superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or Homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A subarachnoid hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts. Neurons of the reticular formation, particularly those of the ascending reticular activating system, play a crucial role in maintaining behavioral arousal and consciousness. The overall functions of the reticular formation are modulatory and premotor, involving somatic motor control, cardiovascular control, pain modulation, sleep and consciousness, and habituation. The modulatory functions are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoparesis
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease. Internal ophthalmoplegia means involvement limited to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. External ophthalmoplegia refers to involvement of only the extraocular muscles. Complete ophthalmoplegia indicates involvement of both. Causes Ophthalmoparesis can result from disorders of various parts of the eye and nervous system: * Infection around the eye. Ophthalmoplegia is an important finding in orbital cellulitis. * The orbit of the eye, including mechanical restrictions of eye movement, as in Graves' disease. * The muscle, as in progressive external ophthalmoplegia or Kearns–Sayre syndrome. * The neuromuscular junction, as in myasthenia gravis. * The relevant cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens), as in cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One And A Half Syndrome
The one and a half syndrome is a rare weakness in eye movement affecting both eyes, in which one cannot move laterally at all, and the other can move only in outward direction. More formally, it is characterized by "''a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other''". Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is abducted. Convergence is classically spared as cranial nerve III (oculomotor nerve) and its nucleus is spared bilaterally. Causes Causes of the one and a half syndrome include pontine haemorrhage, ischemia, tumors, infective mass lesions such as tuberculomas, demyelinating conditions like multiple sclerosis, Arteriovenous malformation, Basilar artery aneurysms and Trauma. Anatomy The syndrome usually results from single unilateral lesion of the paramedian pontine reticular formation and the ipsilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus. An alternative anatomical cause is a lesion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) is a disorder of conjugate lateral gaze in which the affected eye shows impairment of adduction. When an attempt is made to gaze contralaterally (relative to the affected eye), the affected eye adducts minimally, if at all. The contralateral eye abducts, however with nystagmus. Additionally, the divergence of the eyes leads to horizontal diplopia. That is if the right eye is affected the patient will "see double" when looking to the left, seeing two images side-by-side. Convergence is generally preserved. Causes The disorder is caused by injury or dysfunction in the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF), a heavily myelinated tract that allows conjugate eye movement by connecting the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF)-abducens nucleus complex of the contralateral side to the oculomotor nucleus of the ipsilateral side. In young patients with bilateral INO, multiple sclerosis is often the cause. In older patients with one-sided lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoparesis
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease. Internal ophthalmoplegia means involvement limited to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. External ophthalmoplegia refers to involvement of only the extraocular muscles. Complete ophthalmoplegia indicates involvement of both. Causes Ophthalmoparesis can result from disorders of various parts of the eye and nervous system: * Infection around the eye. Ophthalmoplegia is an important finding in orbital cellulitis. * The orbit of the eye, including mechanical restrictions of eye movement, as in Graves' disease. * The muscle, as in progressive external ophthalmoplegia or Kearns–Sayre syndrome. * The neuromuscular junction, as in myasthenia gravis. * The relevant cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens), as in cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologic Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |