|
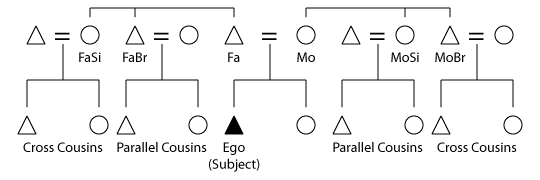
Parallel-cousin
In discussing consanguineal kinship in anthropology, a parallel cousin or ortho-cousin is a cousin from a parent's same-sex sibling, while a cross-cousin is from a parent's opposite-sex sibling. Thus, a parallel cousin is the child of the father's brother (paternal uncle's child) or of the mother's sister (maternal aunt's child), while a cross-cousin is the child of the mother's brother (maternal uncle's child) or of the father's sister (paternal aunt's child). Where there are unilineal descent groups in a society (i.e. matrilineal and/or patrilineal), one's parallel cousins on one or both sides will belong to one's own descent group, while cross-cousins will not (assuming descent group exogamy). Role The role of cross-cousins is especially important in some cultures. For example, marriage is promoted between them in the Iroquois system. Parallel cousins are occasionally the subject of promoted marriage, such as the preferential marriage of a male to his father's brother's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cousin Marriage
A cousin marriage is a marriage where the spouses are cousins (i.e. people with common grandparents or people who share other fairly recent ancestors). The practice was common in earlier times, and continues to be common in some societies today, though in some jurisdictions such marriages are prohibited. Worldwide, more than 10% of marriages are between first or second cousins. Cousin marriage is an important topic in anthropology and alliance theory. In some cultures and communities, cousin marriages are considered ideal and are actively encouraged and expected; in others, they are seen as incestuous and are subject to social stigma and taboo. Cousin marriage was historically practiced by indigenous cultures in Australia, North America, South America, and Polynesia. In some jurisdictions, cousin marriage is legally prohibited: for example, in mainland China, Taiwan, North Korea, South Korea, the Philippines and 24 of the 50 United States. The laws of many jurisdictions se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Korotayev
Andrey Vitalievich Korotayev (russian: link=yes, Андре́й Вита́льевич Корота́ев; born 17 February 1961) is a Russian anthropologist, economic historian, comparative political scientist, demographer and sociologist, with major contributions to world-systems theory, cross-cultural studies, Near Eastern history, Big History, and mathematical modelling of social and economic macrodynamics. He is currently the Head of the Laboratory for Monitoring of the Risks of Sociopolitical Destabilization at the HSE University in Moscow,http://www.hse.ru/org/hse/cfi/lab_mr/staff and a Senior Research Professor at the Center for Big History and System Forecasting of the Institute of Oriental Studies as well as in the Institute for African Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In addition, he is a senior research professor of the International Laboratory on Political Demography and Social Macrodynamics (PDSM) of the Russian Presidential Academy of National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incest
Incest ( ) is human sexual activity between family members or close relatives. This typically includes sexual activity between people in consanguinity (blood relations), and sometimes those related by affinity (marriage or stepfamily), adoption, or lineage. It is strictly forbidden and considered immoral in most societies, and can lead to an increased risk of genetic disorders in children. The incest taboo is one of the most widespread of all cultural taboos, both in present and in past societies. Most modern societies have laws regarding incest or social restrictions on closely consanguineous marriages. In societies where it is illegal, consensual adult incest is seen by some as a victimless crime. Some cultures extend the incest taboo to relatives with no consanguinity such as milk-siblings, step-siblings, and adoptive siblings, albeit sometimes with less intensity. Third-degree relatives (such as half-aunt, half-nephew, first cousin) on average have 12.5% common genetic heri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consanguinity
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor). Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood from marrying or having sexual relations with each other. The degree of consanguinity that gives rise to this prohibition varies from place to place. Such rules are also used to determine heirs of an estate according to statutes that govern intestate succession, which also vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. In some places and time periods, cousin marriage is allowed or even encouraged; in others, it is taboo, and considered to be incest. The degree of relative consanguinity can be illustrated with a ''consanguinity table'' in which each level of lineal consanguinity (''generation'' or ''meiosis'') appears as a row, and individuals with a collaterally consanguineous relationship share the same row. The Knot System is a numerical notati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskimo Kinship
Eskimo kinship or Inuit kinship is a category of kinship used to define family organization in anthropology. Identified by Lewis Henry Morgan in his 1871 work ''Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family'', the Eskimo system was one of six major kinship systems (Eskimo, Hawaiian, Iroquois, Crow, Omaha, and Sudanese). The system of English-language kinship terms falls into the Eskimo type. Joint family The joint family system places no distinction between patrilineal and matrilineal relatives; instead, it focuses on differences in kinship distance (the closer the relative is, the more distinctions are made). The system emphasizes the nuclear family, identifying directly only the mother, father, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. It uses both classificatory and descriptive terms, differentiating between gender, generation, lineal relatives (relatives in the direct line of descent), and collateral relatives (blood relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palomar College
Palomar College is a public community college in San Diego County, California. The main campus is in San Marcos and three centers and four education sites are located elsewhere throughout north San Diego County. The largest of these by student population is the education center located in Escondido. In 2018, education centers in Rancho Bernardo and Fallbrook opened. The Rancho Bernardo Education Center is located on 27 acres at 11111 Rancho Bernardo Road, and the Fallbrook Education Center is located on 81 acres at 35090 Horse Ranch Creek Road. Other education sites are located at Camp Pendleton and at Ramona High School. Academics Palomar College offers 250 associate's degrees and certificate programs, and also offers programs for students wishing to transfer to many different four-year universities, including institutions in the University of California and California State University systems. These programs are organized into five academic divisions: *Arts, Media, Busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahram
In Islam, a ''mahram'' is a family member with whom marriage would be considered permanently unlawful (''haram''). One's spouse is also a mahram. A woman does not need to wear hijab around her mahram, and an adult male mahram may escort a woman on a journey, although an escort may not be obligatory. Overview People with whom marriage is prohibited * permanent or blood ''mahrams'' include: ** all direct ancestors ** all direct descendants ** siblings ** siblings of parents, grandparents and further antecedents ** children and further descendants of siblings * in-law ''mahrams'' with whom one becomes ''mahram'' by marrying someone: ** all the ancestors of one's spouse ** all the descendants of one's spouse ** all who marry a direct ancestor ** all who marry a direct descendant (Note: A woman may marry her stepfather only if the stepfather has not consummated his marriage to her mother.) * ''Rada'' or "milk-suckling ''mahrams''" with whom one becomes ''mahram'' because of being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Coupled Cousins
This is a list of notable individuals who have been romantically or maritally coupled with a first cousin. Worldwide, more than 10% of marriages are between first or second cousins. Cousin marriage is an important topic in anthropology and alliance theory. Notable people A *John Adams II (1803–1834), American government functionary and businessman, and his first cousin, Mary Catherine Hellen *Ali ibn Husayn Zayn al-Abidin (c. 659 – c. 713), grandson of Ali ibn Abi Talib and his first cousin, Fatimah bint Hasan *Mark Antony and his first cousin, Antonia Hybrida Minor B *Josiah Bartlett (1729–1795), second signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, and his first cousin, Mary Bartlett *Ilsley Boone (1879–1968) and his first cousin, Ella Murray "Mae" Boone, founder of the American Sunbathing Association, which today is known as the American Association for Nude Recreation *James Boswell (1740–95) (biographer of Samuel Johnson) and his first cousin Margaret M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Anthropology
Cultural anthropology is a branch of anthropology focused on the study of cultural variation among humans. It is in contrast to social anthropology, which perceives cultural variation as a subset of a posited anthropological constant. The portmanteau term sociocultural anthropology includes both cultural and social anthropology traditions. Anthropologists have pointed out that through culture people can adapt to their environment in non-genetic ways, so people living in different environments will often have different cultures. Much of anthropological theory has originated in an appreciation of and interest in the tension between the local (particular cultures) and the global (a universal human nature, or the web of connections between people in distinct places/circumstances). Cultural anthropology has a rich methodology, including participant observation (often called fieldwork because it requires the anthropologist spending an extended period of time at the research locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography. The record of genealogical work may be presented as a "genealogy", a "family history", or a "family tree". In the narrow sense, a "genealogy" or a "family tree" traces the descendants of one person, whereas a "family history" traces the ancestors of one person, but the terms are often used interchangeably. A family history may include additional biographical information, family traditions, and the like. The pursuit of family history and origins tends to be shaped by several motives, including the desire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of Attachment theory, attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as Matrifocal family, matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), wikt:conjugal, conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or Extended family, extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that the study of kinship is the study of what humans do with these basic facts of lifemating, gestation, parenthood, socialization, siblingship etc. Human society is unique, he argues, in that we are "working with the same raw material as exists in the animal world, but ecan conceptualize and categorize it to serve social ends." These social ends include the socialization of children and the formation of basic economic, political and religious groups. Kinship can refer both to the patterns of social relationships themselves, or it can refer to the study of the patterns of social relationships in one or more human cultures (i.e. kinship studies). Over its history, anthropology has developed a number of related concepts and terms in the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)