|
Papillary Carcinomas Of The Breast
Papillary carcinomas of the breast (PCB), also termed malignant papillary carcinomas of the breast, are rare forms of the breast cancers. The World Health Organization (2019) classified papillary neoplasms (i.e. benign or cancerous tumors) of the breast into 5 types: intraductal papilloma, papillary ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (PDCIS), encapsulated papillary carcinoma (EPC), solid-papillary carcinoma (SPC), and invasive papillary carcinoma (IPC). The latter four carcinomas are considered here; intraductal papilloma is a benign neoplasm. The World Health Organization regarded solid papillary carcinoma as having two subtypes: ''in situ'' and invasive SPC. PCB develop from the epithelial cells that line the outer surfaces of Duct (anatomy), ducts leading from exocrine glands or Organ (biology), organs, blood vessels, or inner surfaces of the cavities in many internal organs. PCB are carcinomas derived from the epithelial cells of mammary gland ducts. They are a clinically, histolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokeratin 5/6 Antibodies
Cytokeratin 5/6 antibodies are antibodies that target both cytokeratin 5 and cytokeratin 6. Topic Completed: 3 June 2019. Revised: 8 December 2019 These are used in immunohistochemistry, often called CK 5/6 staining, including the following applications: *Identifying basal cells or myoepithelial cells in the breast and prostate. *For breast pathology, also in distinguishing usual ductal hyperplasia (UDH) and papillary lesions (having a mosaic-like pattern) from ductal carcinoma in situ, which is usually negative. Cyclin D1 and CK5/6 staining could be used in concert to distinguish between the diagnosis of papilloma (Cyclin D1 37.00%, CK 5/6 negative). *In the lung, distinguishing epithelioid mesothelioma (CK5/6 positive in 83%) from lung adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma of the lung is the most common type of lung cancer, and like other forms of lung cancer, it is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. It is classified as one of several non-small cell lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being detected through screening mammography. It has been diagnosed in a significant percentage of men (see male breast cancer). In DCIS, abnormal cells are found in the lining of one or more milk ducts in the breast. ''In situ'' means "in place" and refers to the fact that the abnormal cells have not moved out of the mammary duct and into any of the surrounding tissues in the breast ("pre-cancerous" refers to the fact that it has not yet become an invasive cancer). In some cases, DCIS may become invasive and spread to other tissues, but there is no way of determining which lesions will remain stable without treatment, and which will go on to become invasive. DCIS encompasses a wide spectrum of diseases ranging from low-grade lesions that are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (10 November 2018) Gynecomastia can cause significant psychological distress or unease. Gynecomastia can be normal in newborn babies due to exposure to estrogen from the mother, in adolescents going through puberty, in older men over age 50, and/or in obese men. Most occurrences of gynecomastia do not require diagnostic tests. Gynecomastia may be caused by abnormal hormone changes, any condition that leads to an increase in the ratio of estrogens/androgens such as liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid disease and some non-breast tumors. Alcohol and some drugs can also cause breast enlargement. Other causes may include Klinefelter syndrome, metabolic dysfunction, or a natural decline in testosterone production. This may occur even if the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcalcification
Microcalcifications are tiny deposits of calcium salts that are too small to be felt but can be detected by imaging. They can be scattered throughout the mammary gland, or occur in clusters. Microcalcifications can be an early sign of breast cancer. Based on morphology, it is possible to classify by radiography how likely microcalcifications are to indicate cancer. Microcalcifications are made up of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are whi .... The mechanism of their formation is not known. Microcalcification was first described in 1913 by surgeon Albert Salomon. References Medical signs {{Med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
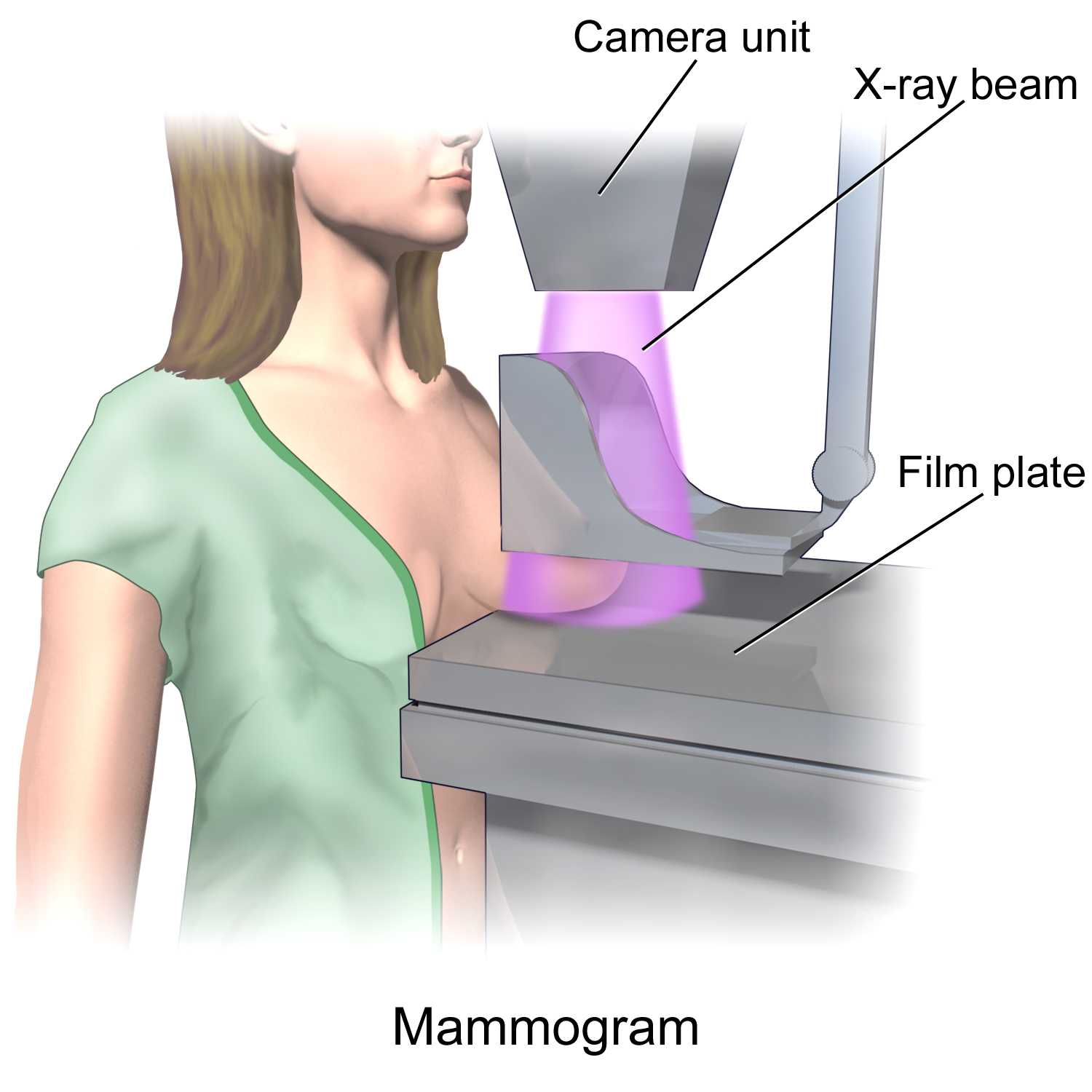
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen on mammogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins (glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most gel-like secretions, serving functions from lubrication to cell signalling to forming chemical barriers. They often take an inhibitory role. Some mucins are associated with controlling mineralization, including nacre formation in mollusks, calcification in echinoderms and bone formation in vertebrates. They bind to pathogens as part of the immune system. Overexpression of the mucin proteins, especially MUC1, is associated with many types of cancer. Although some mucins are membrane-bound due to the presence of a hydrophobic membrane-spanning domain that favors retention in the plasma membrane, most mucins are secreted as principal components of mucus by mucous membranes or are secreted to become a component of saliva. Genes Human muci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signet Ring Cells
In histology, a signet ring cell is a cell with a large vacuole. The malignant type is seen predominantly in carcinomas. Signet ring cells are most frequently associated with stomach cancer, but can arise from any number of tissues including the prostate, bladder, gallbladder, breast, colon, ovarian stroma and testis. Types The NCI Thesaurus identifies the following types of signet ring cell * Castration cell, a non-malignant cell arising in the anterior pituitary gland under certain abnormal hormonal conditions. * Neoplastic thyroid gland follicular signet ring cell * Signet ring adenocarcinoma cell * Signet ring melanoma cell * Signet ring stromal cell Appearance The name of the cell comes from its appearance; signet ring cells resemble signet rings. They contain a large amount of mucin, which pushes the nucleus to the cell periphery. The pool of mucin in a signet ring cell mimics the appearance of a finger hole and the nucleus mimics the appearance of the face of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
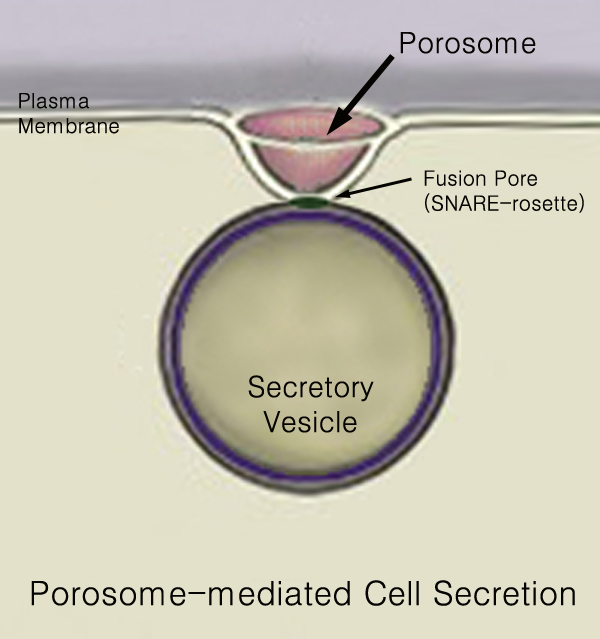
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)