|
Pannonian Sea
The Pannonian Sea was a shallow ancient lake, where the Pannonian Basin in Central Europe is now. The Pannonian Sea existed from about 10 Ma (million years ago) until 1 Ma, during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, when marine sediments were deposited to a depth of in the Pannonian Basin. History The Pannonian Sea, for most of its history, was part of the Paratethys Sea, until about 10 million years ago, when a Miocene uplift of the Carpathian Mountains isolated the sea from the rest of Paratethys. During its first historical phase, the Pannonian Sea had a western connection with the Mediterranean Sea through the territories of the modern Ligurian Sea, Bavaria, and Vienna Basin. Through the Đerdap Strait, the Pannonian Sea was linked to the Paratethys in the Wallachian-Pontic Basin. The Pannonian Sea was also attached to the Aegean Sea through the modern Preševo Valley. The Pannonian Sea existed for about 9 million years. Throughout its diverse history the salinity of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
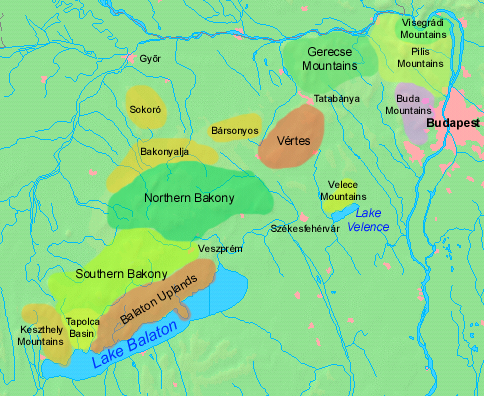
Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the largest inflow of water to the lake, and the canalised Sió is the only outflow. The mountainous region of the northern shore is known both for its historic character and as a major wine region, while the flat southern shore is known for its resort towns. Balatonfüred and Hévíz developed early as resorts for the wealthy, but it was not until the late 19th century when landowners, ruined by '' Phylloxera'' attacking their grape vines, began building summer homes to rent out to the burgeoning middle classes. Name In distinction to all other Hungarian endonyms for lakes, which universally bear the suffix ''-tó'' 'lake', Lake Balaton is referred to in Hungarian with a definite article; that is, ''a Balaton'' 'the Balaton'. It was called ''lacus Pelsodis'' or ''Pelso'' by the Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vršac Mountains
The Vršac Mountains ( sr, Вршачке планине / ''Vršačke planine'', ro, Munții Vârșeț), also known as Vršac Hill ( sr, Вршачки брег / ''Vršački breg'', ro, Dealurile Vârșețului), are located in the Banat region near the city of Vršac, Serbia and partially also in Romania. They represent an independent and distinct massif, 19 kilometers long and spreading on an area of 170 square kilometers, of which 122 belong to Serbia and 48 to Romania. Geography The Vršac mountains have a shape of an arch, where the basic mountain mass takes the central position, while the hills extend to the south and north. The mountains are built of Paleozoic rocks (which date back over 260 million years) which are surrounded by Neogene sediments (about 60 mya), including those of the ancient Pannonian sea (about 25 mya). Contrary to some literature data, the Vršac Mountains are not part of the Carpathians but are a Pannonian island mountain according to their geote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
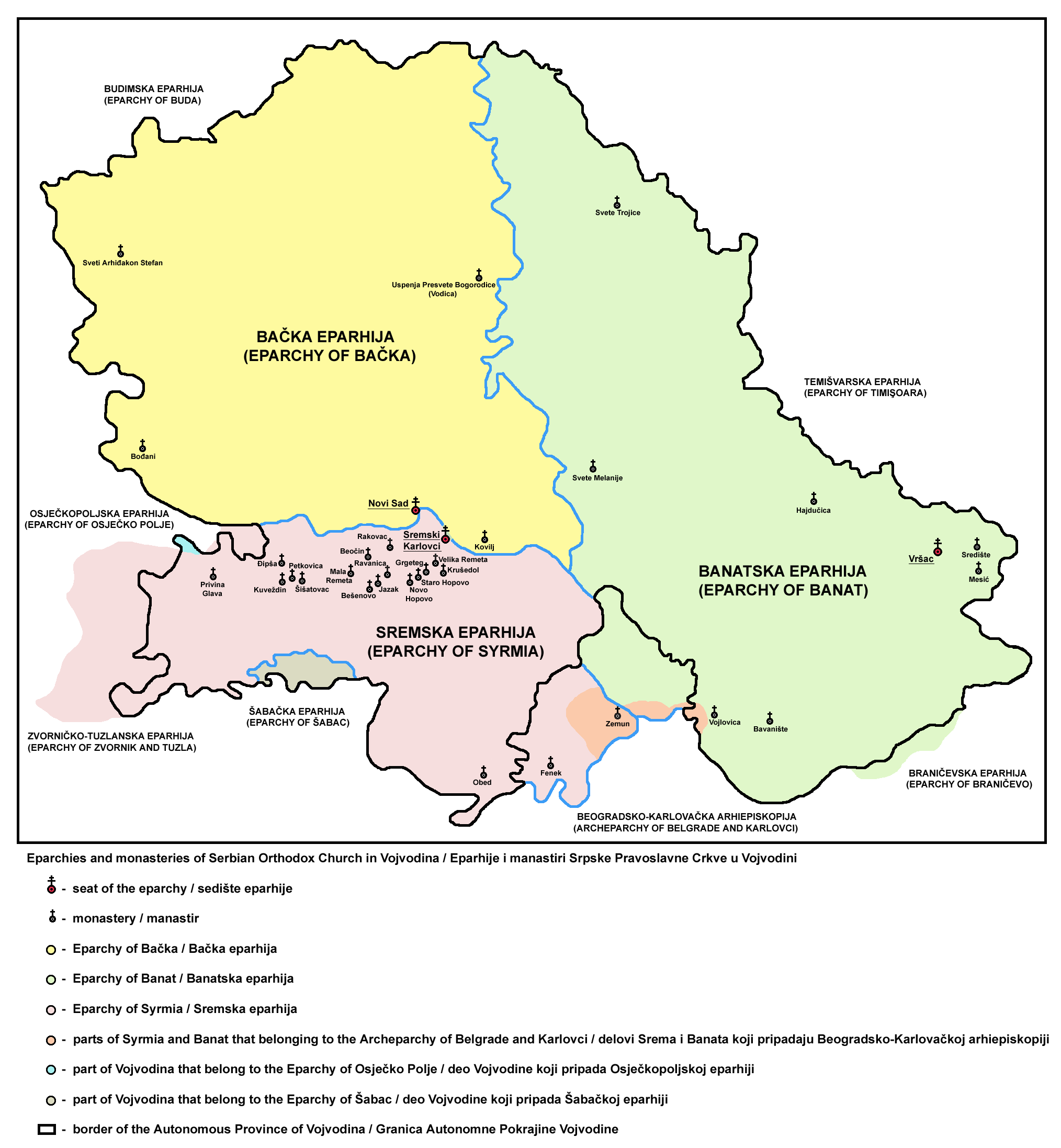
Fruška Gora
Fruška gora ( sr-Cyrl, Фрушка гора; hu, Tarcal-hegység) is a mountain in Syrmia, administratively part of Serbia with a part of its western side extending into eastern Croatia. The area under Serbian administration forms the country's oldest national park. Sometimes also referred to as the ''Jewel of Serbia'', due to its largely pristine landscape and protection effort, or the ''Serbian Mount Athos'', being the home of a large number of historical Serbian Orthodox monasteries. Name In Serbian, it is known as ''Fruška gora'' (, Фрушка гора), in Hungarian as ''Tarcal'' (also ''Almus-hegy'' or ''Árpatarló''), in German as ''Frankenwald'', and in Latin as ''Alma Mons''. In Medieval Greek, it was known as ''Frangochoria''. The mountain's name originates in the old Serbian word ''"Fruzi"'' derived from the singular form ''"Frug"''; and its adjective is ''Fruški'', used for naming the Frankish people. The name of ''"Fruška Gora"'' is ''"Frankish mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilj
Dilj is a low mountain in south-central Slavonia, located in eastern Croatia. Of all the mountains in Slavonia, Dilj is the lowest-lying, at 471 meters. It is located north of Slavonski Brod and south of Krndija. Dilj mountain contains a forest that spreads in an east–west direction of approximately 50 km, and a north–south direction of approximately 30 km. Forestation of the area includes a variety of plants, including Pannonian-Balkan forest oak. Areas not covered in forestation are mainly cultivated with Orchards, Vineyards and Dehesa A ''dehesa'' () is a multifunctional, agrosylvopastoral system (a type of agroforestry) and cultural landscape of southern and central Spain and southern Portugal; in Portugal, it is known as a ''montado''. Its name comes from the Latin 'defens ...s. References Mountains of Croatia Slavonia Slavonski Brod Hills of Croatia Pannonian island mountains {{Slavonia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krndija
Krndija is a mountain in Slavonia, Croatia, extending eastwards from Papuk. It is located south of Orahovica and Našice and north of Požega. The westernmost point of Krndija is the mountain pass that connects Orahovica with Kutjevo; the easternmost point is hard to determine, as it gradually passes into the lowland area near Đakovo and further east near Vinkovci Vinkovci () is a city in Slavonia, in the Vukovar-Syrmia County in eastern Croatia. The city's registered population was 28,247 in the 2021 census, the total population of the city was 31,057, making it the largest town of the county. Surrounde .... The highest peak Kapovac is located in the western part of Krndija, at . The peak of the central part of Krndija is at 263 meters of altitude. There are several theories about the origins of the name "Krndija". It's almost certainly not of Croatian origin. One is that it is related to the Greek word χορδή (itself without a widely accepted etymology), in the sense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psunj
Psunj is a mountain in the southwestern Slavonia region in eastern Croatia. It is the highest mountain of Slavonia, with the highest peak of Brezovo polje at 984 m.a.s.l. In the north it extends to Ravna gora and Papuk, while otherwise it is surrounded by lowlands. It is located north of Nova Gradiška and southeast of Pakrac. On Psunj, there is a 128.5 metres tall lattice tower used for FM- and TV-transmission, which was designed by Prof. Marjan Ivancic and built by Mostogradnja Mostogradnja (''Građevinsko preduzeće Mostogradnja a.d. Beograd'') is a Serbian bridge building company, with headquarters in Belgrade, Serbia. Its projects have included bridges and interchanges, as well as industrial and military structures i ... in 1962/1963. Originally this tower was completely free-standing. Today it is additionally guyed at its upper section. Psunj was called "Pisunus" in antiquity. There are several suggested etymologies for that. One is that it comes from the Indo-European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuk
Papuk is the largest mountain in the Slavonia region in eastern Croatia, near the city of Požega. It extends between Bilogora to the northwest, Krndija to the east, and Ravna gora and Psunj to the southwest. The highest peak is the eponymous peak at 953 m.a.A. The area of Papuk is designated a nature park (''park prirode''), a kind of protected area in Croatia. At the seventh European Geopark Network Open Conference, hosted by North West Highlands Geopark in September 2007, the Papuk Geopark became the first Croatian Geopark and 30th member of the European and UNESCO Global Geoparks Network. Geopark Papuk was awarded licence second time from UNESCO in 2011. Name There are several supposed etymologies of the name "Papuk", it's almost certainly not of Croatian origin. One is that it comes by assimilation from earlier "Bapuk", where "Ba" is the name of the Celtic tribe that inhabited the region, and "Puk" comes from the Indo-European root *peiH, meaning "big". However, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecsek
Mecsek (; hr, Meček; Serbian: ''Meček'' or Мечек; german: Metscheck) is a mountain range in southern Hungary. It is situated in the Baranya region, in the north of the city of Pécs. Etymology The Hungarian toponym "Mecsek" derives from the sobriquet version of the name Mihály (Michael). Originally applied only to the hills adjacent to Pécs, the name Mecsek was first mentioned in 16th century. Geography The mountains cover an area of approximately 500 km2. The highest peak in the mountain range is Zengő (literally translates to 'resonant'), which has an elevation of 682 metres (2238 feet). The Mecsek Hills consist of plateau-like block mountains of a broken, folded structure. Its basis is crystalline rock of Variscan origin surmounted by Triassic and Jurassic limestone and dolomite and Tertiary formations that form the main block. The mountains are divided by a structural fault running NW to SE. The eastern part consist mainly of high ridges of sedimentary r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Island Mountains
The Pannonian island mountains ( sr, / , hr, Panonske otočne planine) is a term for isolated mountains scattered across the Pannonian Plain, chiefly its western and southern parts, in Hungary, Serbia and Croatia. In prehistoric times, these mountains were islands of the ancient Pannonian Sea that disappeared about 600,000 years ago. The island mountains include: ;Croatia *Central Slavonian Mountains: **Dilj ** Krndija ** Papuk **Psunj ** Požeška Gora *Medvednica in western Croatia ;Hungary *Transdanubian Mountains of western Hungary: **Bakony **Buda Hills **Gerecse Gerecse is a mountain range in north-western Hungary, that belongs to the Transdanubian Mountains Geography The range lies in the Central Transdanubian region and connects Vértes Hills with Pilis Mountains in Komárom-Esztergom County, betw ... ** Pilis Mountains **Vértes Hills **Velence Mountains *Mecsek, in south Hungary *Kőszeg Mountains (Geschriebenstein), on Austria–Hungary border, Hungary– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)