|
Panda3D
Panda3D is a game engine that includes graphics, audio, I/O, collision detection, and other abilities relevant to the creation of 3D games. Panda3D is free, open-source software under the revised BSD license. Panda3D's intended game-development language is Python. The engine itself is written in C++ and utilizes an automatic wrapper-generator to expose the complete functionality of the engine in a Python interface. This approach gives a developer the advantages of Python development, such as rapid development and advanced memory management, but keeps the performance of a compiled language in the engine core. For instance, the engine is integrated with Python's garbage collector, and engine structures are automatically managed. The manual and the sample programs use Python by default, with C++ available as an alternative. Both languages are fully supported. Python is the most commonly used language by developers, but C++ is also common. The users of Panda3D include the develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Game Engine
A game engine is a software framework primarily designed for the development of video games which generally includes relevant libraries and support programs such as a level editor. The "engine" terminology is akin to the term " software engine" used more widely in the software industry. ''Game engine'' can also refer to the development software supporting this framework, typically a suite of tools and features for developing games. Developers can use game engines to construct games for video game consoles and other types of computers. The core functionality typically provided by a game engine may include a rendering engine ("renderer") for 2D or 3D graphics, a physics engine or collision detection (and collision response), sound, scripting, animation, artificial intelligence, networking, streaming, memory management, threading, localization support, scene graph, and video support for cinematics. Game engine implementers often economize on the process of game developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cg (programming Language)
Cg (short for C for Graphics) and High-Level Shader Language (HLSL) are two names given to a high-level shading language developed by Nvidia and Microsoft for programming shaders. Cg/HLSL is based on the C programming language and although they share the same core syntax, some features of C were modified and new data types were added to make Cg/HLSL more suitable for programming graphics processing units. Two main branches of the Cg/HLSL language exist: the Nvidia Cg compiler (cgc) which outputs DirectX or OpenGL and the Microsoft HLSL which outputs DirectX shaders in bytecode format. Nvidia's cgc was deprecated in 2012, with no additional development or support available. HLSL shaders can enable many special effects in both 2D and 3D computer graphics. The Cg/HLSL language originally only included support for vertex shaders and pixel shaders, but other types of shaders were introduced gradually as well: * DirectX 10 (Shader Model 4) and Cg 2.0 introduced geometry shade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Game Engine
A game engine is a software framework primarily designed for the development of video games which generally includes relevant libraries and support programs such as a level editor. The "engine" terminology is akin to the term " software engine" used more widely in the software industry. ''Game engine'' can also refer to the development software supporting this framework, typically a suite of tools and features for developing games. Developers can use game engines to construct games for video game consoles and other types of computers. The core functionality typically provided by a game engine may include a rendering engine ("renderer") for 2D or 3D graphics, a physics engine or collision detection (and collision response), sound, scripting, animation, artificial intelligence, networking, streaming, memory management, threading, localization support, scene graph, and video support for cinematics. Game engine implementers often economize on the process of game developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
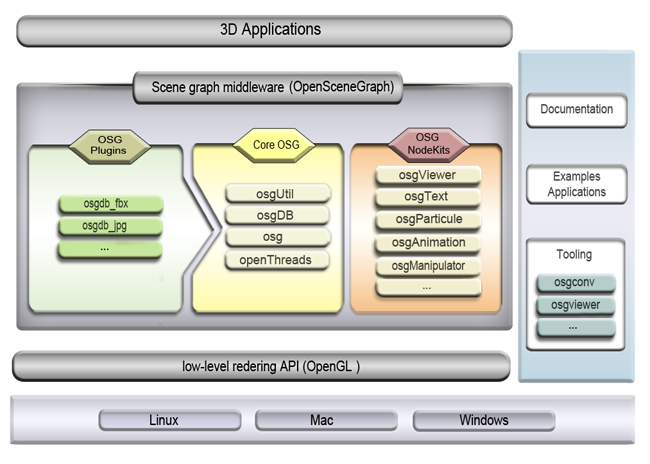
Scene Graph
A scene graph is a general data structure commonly used by vector-based graphics editing applications and modern computer games, which arranges the logical and often spatial representation of a graphical scene. It is a collection of nodes in a graph or tree structure. A tree node may have many children but only a single parent, with the effect of a parent applied to all its child nodes; an operation performed on a group automatically propagates its effect to all of its members. In many programs, associating a geometrical transformation matrix (see also transformation and matrix) at each group level and concatenating such matrices together is an efficient and natural way to process such operations. A common feature, for instance, is the ability to group related shapes and objects into a compound object that can then be manipulated as easily as a single object. Scene graphs in graphics editing tools In vector-based graphics editing, each leaf node in a scene graph represents some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Software License
A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder (usually the author) of a piece of software can remove these restrictions by accompanying the software with a software license which grants the recipient these rights. Software using such a license is free software (or free and open-source software) as conferred by the copyright holder. Free-software licenses are applied to software in source code and also binary object-code form, as the copyright law recognizes both forms. Comparison Free-software licenses provide risk mitigation against different legal threats or behaviors that are seen as potentially harmful by developers: History Pre-1980s In the early times of software, sharing of software and source code was common in certain communities, for instance academic institutions. Before the US Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Open Dynamics Engine
The Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) is a physics engine written in C/C++. Its two main components are a rigid body dynamics simulation engine and a collision detection engine. It is free software licensed both under the BSD license and the LGPL. ODE was started in 2001 and has already been used in many applications and games, such as '' Assetto Corsa'', '' BloodRayne 2'', '' Call of Juarez'', ''S.T.A.L.K.E.R.'', '' Titan Quest'', '' World of Goo'', '' X-Moto'' and ''OpenSimulator''. Overview The Open Dynamics Engine is used for simulating the dynamic interactions between bodies in space. It is not tied to any particular graphics package although it includes a basic one called ''drawstuff''. It supports several geometries: box, sphere, capsule (cylinder capped with hemispheres), triangle mesh, cylinder and heightmap. Simulation Higher level environments that allow non-programmers access to ODE include Player Project, Webots, Opensimulator, anyKode Marilou and CoppeliaSim. ODE is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miles Sound System
Miles Sound System (MSS), formerly known as Audio Interface Library (AIL), is a sound software system primarily for video games and used mostly as an alternative for low-end audio chipsets. It uses little CPU time while providing adequate audio output. It was originally a middleware driver library for soundcards to use in DOS applications when no viable alternative was available. Epic Games Tools (formerly RAD Game Tools) acquired the technology from Miles Design in 1995. The 1992 AIL version 2 for DOS has been released by John Miles as open-source (public domain without restrictions) in 2000. The package can be found on his personal site (''KE5FX.com'') and contains source code for both real-mode and protected-mode programs. Reception The Miles Sound System was used in its history by over 7,000 video games across 18 platforms, with customers including Sony, Capcom, Epic, and Microsoft. ''Computer Gaming World'' stated in 1994 that "Many of the game publishers have decid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenAL
OpenAL (Open Audio Library) is a cross-platform audio application programming interface (API). It is designed for efficient rendering of multichannel three-dimensional positional audio. Its API style and conventions deliberately resemble those of OpenGL. OpenAL is an environmental 3D audio library, which can add realism to a game by simulating attenuation (degradation of sound over distance), the Doppler effect (change in frequency as a result of motion), and material densities. OpenAL aimed to originally be an open standard and open-source replacement for proprietary (and generally incompatible with one another) 3D audio APIs such as DirectSound and Core Audio, though in practice has largely been implemented on various platforms as a wrapper around said proprietary APIs or as a proprietary and vendor-specific fork. While the reference implementation later became proprietary and unmaintained, there are open source implementations such as OpenAL Soft available. History OpenA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
FMOD
FMOD is a proprietary sound effects engine and authoring tool for video games and applications developed by Firelight Technologies. It is able to play and mix sounds of diverse formats on many operating systems. Features The FMOD sound system is supplied as a programmer's API and authoring tool, similar to a digital audio workstation. FMOD consists of the following technologies: * FMOD Studio - An audio creation tool for games, designed like a digital audio workstation. Succeeds ''FMOD Designer''. * FMOD Studio run-time API - A programmer API to interface with FMOD Studio. * FMOD Studio low-level API - A programmer API that stands alone, with a simple interface for playing sound files, adding special effects and performing 3D sound. Legacy products include: * FMOD Ex - The sound playback and mixing engine. * FMOD Designer 2010 - An audio designer tool used for authoring complex sound events and music for playback. * FMOD Event Player - An auditioning tool in conjunction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Normal Mapping
In 3D computer graphics, normal mapping, or Dot3 bump mapping, is a texture mapping technique used for faking the lighting of bumps and dents – an implementation of bump mapping. It is used to add details without using more polygonal modeling, polygons. A common use of this technique is to greatly enhance the appearance and details of a low poly, low polygon model by generating a normal map from a high polygon model or Heightmap, height map. Normal maps are commonly stored as regular RGB images where the RGB components correspond to the X, Y, and Z coordinates, respectively, of the surface normal. History In 1978 Jim Blinn described how the normals of a surface could be perturbed to make geometrically flat faces have a detailed appearance. The idea of taking geometric details from a high polygon model was introduced in "Fitting Smooth Surfaces to Dense Polygon Meshes" by Krishnamurthy and Levoy, Proc. SIGGRAPH 1996, where this approach was used for creating displacement mappi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distance Fog
Distance fog is a technique used in 3D computer graphics to enhance the perception of distance by shading distant objects differently. Because many of the shapes in graphical environments are relatively simple, and complex shadows are difficult to render, many graphics engines employ a " fog" gradient so objects further from the camera are progressively more obscured by haze and by aerial perspective. This technique simulates the effect of light scattering, which causes more distant objects to appear lower in contrast, especially in outdoor environments. Visibility in a natural haze declines exponentially, not linearly, with distance due to scattering. The colour of the light being scattered into the viewing path affects the colour of the haze; blue under blue skies, reddish near sunset, as with alpenglow. These more subtle details are represented in some graphics. "Fogging" is another use of distance fog in mid-to-late 1990s games, when processing power was not enou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |