|
Pame People
The north Pame, or Xi'iuy (alternate spelling: Xi'úi, Xi'ui, Xi'oi, or Xiyui), as they refer to themselves, the south Pame, or Ñáhu, Nyaxu (in Hidalgo), and the Pame in Querétaro or Re Nuye Eyyä, are an Indigenous people of central Mexico primarily living in the state of San Luis Potosí. When Spanish colonists arrived and conquered their traditional territory in the sixteenth century, which "extended from the modern state of Tamaulipas in the north to Hidalgo and the area around Mexico City in the south along the Sierra Madre," they renamed "the area ''Pamería'', and applied the name Pame to all of the peoples there." Estimates for population of the Pames at the time of contact with Spanish colonists in 1519 range between 40,000 and 70,000. In 1794, the population was estimated at around 25,000. Recent figures for the Pame have estimated the population to be approximately 10,000 people. The Pames, along with the Chichimeca-Jonaz of the Sierra Gorda in eastern Guanajuato, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí City. Located in Central Mexico, San Luis Potosí is bordered by seven other Mexican states: Nuevo León to the north; Tamaulipas to the north-east; Veracruz to the east; Hidalgo, Querétaro and Guanajuato to the south; and Zacatecas to north-west. In addition to the capital city, other major cities in the state include Ciudad Valles, Matehuala, Rioverde, and Tamazunchale. History In pre-Columbian times, the territory now occupied by the state of San Luis Potosí contained parts of the cultural areas of Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica. Its northern and western-central areas were inhabited by the Otomi and Chichimeca tribes. These indigenous groups were nomadic hunter-gatherers. Although many indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rioverde, San Luis Potosí
Rioverde is a city and its surrounding municipality located in the south-central part of the state of San Luis Potosí, Mexico. It is the fifth-most populated city in the state, behind San Luis Potosí, Soledad de Graciano Sánchez, Ciudad Valles, and Matehuala. It is the agricultural, economic, turistic and demographic most important core in the Zona Media, one of the four geographical divisions of the state. The city had a 2005 census population of 49,183, while the municipality, of which it serves as municipal seat, had a population of 85,945 and an area extent of 3,109.71 km² (1,200.07 sq mi). The population of its metropolitan area, which includes the largest municipality of Ciudad Fernández, was 126,997. The city is well known for its spring, called Media Luna. The city has been growing faster in the last four years. Rioverde lives up to its name in its rich surroundings and round the year pleasant weather. It is the birthplace of singer Ana Bárbara and composer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
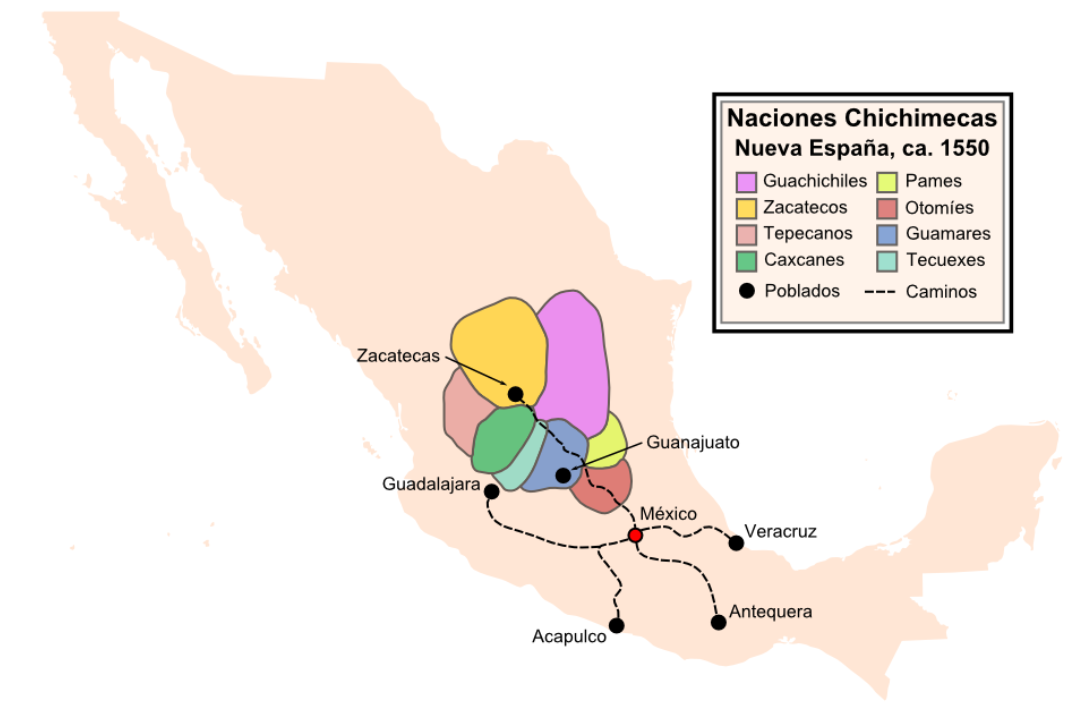
Chichimeca War
The Chichimeca War (1550–90) was a military conflict between the Spanish Empire and the Chichimeca Confederation established in the territories today known as the Central Mexican Plateau, called by the Conquistadores La Gran Chichimeca. The epicenter of the hostilities was the region now called the Bajío. The Chichimeca War is recorded as the longest and most expensive military campaign confronting the Spanish Empire and indigenous people in Mesoamerica. The forty-year conflict was settled through several peace treaties driven by the Spaniards which led to the pacification and, ultimately, the streamlined integration of the native populations into the New Spain society. The Chichimeca War (1550-1590) began eight years after the two-year Mixtón War. It can be considered a continuation of the rebellion as the fighting did not come to a halt in the intervening years. Unlike in the Mixtón rebellion, the Caxcanes were now allied with the Spanish. The war was fought in what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajío
El Bajío (the ''lowland'') is a cultural and geographical region within the central Mexican plateau which roughly spans from north-west of the Mexico City metropolitan area to the main silver mines in the northern-central part of the country. This includes (from south to north) the states of Querétaro, Guanajuato, parts of Jalisco (Centro, Los Altos de Jalisco), Aguascalientes and parts of Zacatecas, San Luis Potosí and Michoacán. Located at the border between Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica, El Bajío saw relatively few permanent settlements and big civilizations during Pre-Columbian history, being mostly inhabited by nomadic tribes known to the Aztecs as " The Chichimeca" peoples (''the barbarians''), another Nahua group from whom the Toltec and the Aztecs were probably descended. The tribes that inhabited El Bajío proved to be some of the hardest to conquer for the Spanish, but due to its strategic location in the Silver route, it also drew prominent attention from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, continued through the Middle Ages in Europe, and in the twenty-first century has spread around the globe. Historically, there are four stages of Christianization beginning with individual conversion, followed by the translation of Christian texts into local vernacular language, establishing education and building schools, and finally, social reform that sometimes emerged naturally and sometimes included politics, government, coercion and even force through colonialism. The first countries to make Christianity their state religion were Armenia, Georgia, Ethiopia and Eritrea. In the fourth to fifth centuries, multiple tribes of Germanic barbarians converted to either Arian or orthodox Christianity. The Frankish empire begins during this same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, State (polity), states, Realm, kingdoms, republics, Confederation, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Mission
A Christian mission is an organized effort for the propagation of the Christian faith. Missions involve sending individuals and groups across boundaries, most commonly geographical boundaries, to carry on evangelism or other activities, such as educational or hospital work. Sometimes individuals are sent and are called missionaries, and historically may have been based in mission stations. When groups are sent, they are often called mission teams and they do mission trips. There are a few different kinds of mission trips: short-term, long-term, relational and those that simply help people in need. Some people choose to dedicate their whole lives to mission. Missionaries preach the Christian faith (and sometimes to administer sacraments), and provide humanitarian aid. Christian doctrines (such as the "Doctrine of Love" professed by many missions) permit the provision of aid without requiring religious conversion. However, Christian missionaries are implicated in the genocide of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in Spanish East Indies, Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming the first empire known as " the empire on which the sun never sets", and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century. An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the dynastic union between Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the Catholic Monarchs, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purépecha
The Purépecha (endonym pua, P'urhepecha ) are a group of indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro. They are also known by the pejorative " Tarascan", an exonym, applied by outsiders and not one they use for themselves. The Purépecha occupied most of Michoacán but also some of the lower valleys of both Guanajuato and Jalisco. Celaya, Acambaro, Cerano, and Yurirapundaro. Now, the Purépecha live mostly in the highlands of central Michoacán, around Lakes Patzcuaro and Cuitzeo. History Prehispanic history It was one of the major empires of the Pre-Columbian era. The capital city was Tzintzuntzan. Purépecha architecture is noted for step pyramids in the shape of the letter "T". Pre-Columbian Purépecha artisans made feather mosaics that extensively used hummingbird feathers, which were highly regarded as luxury goods throughout the region. During the Pre-Colonial era, the Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otomi
The Otomi (; es, Otomí ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region. The Otomi are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguistically related to the rest of the Otomanguean-speaking peoples, whose ancestors have occupied the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt since several millennia before the Christian era. Currently, the Otomi inhabit a fragmented territory ranging from northern Guanajuato, to eastern Michoacán and southeastern Tlaxcala. However, most of them are concentrated in the states of Hidalgo, Mexico and Querétaro. According to the National Institute of Indigenous Peoples of Mexico, the Otomi ethnic group totaled 667,038 people in the Mexican Republic in 2015, making them the fifth largest indigenous people in the country. Of these, only a little more than half spoke Otomi. In this regard, it should be said that the Otomi language presents a high degree of inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_2007.jpg)
