|
Pallada Guyot
Pako Guyot is a guyot in the Pacific Ocean. Name The guyot is also known as Caiwei or Pallada after the . Geomorphology Pako Guyot reaches a depth of . It has dimensions of and features a summit plateau wide at a depth of with a shape corresponding to an irregular rectangle-triangle. With an area of , Pako Guyot is the third-largest guyot on Earth, only behind Koko Seamount and Suiko Seamount. The summit plateau is covered by sediments thick including foraminiferal ooze, while the flanks feature small-scale features such as depressions, ridges and trenches. Former reefs occur on the seamount and during the Cretaceous and Eocene left mudstones and limestones on the seamount. Later, pelagic limestones were emplaced on them. A large area on the northwestern corner of Pako Guyot's summit plateau is free of sediments. Geology The guyot is part of the Magellan Seamounts. The seamount was volcanically active during the Cretaceous-Paleogene 91.3 million years ago and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronesia And Marshall Islands Bathymetry, Pako (Pallada) Guyot
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples. The region has a tropical marine climate and is part of the Oceanian realm. It includes four main archipelagos—the Caroline Islands, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands—as well as numerous islands that are not part of any archipelago. Political control of areas within Micronesia varies depending on the island, and is distributed among six sovereign nations. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau and some are part of the Federated States of Micronesia (often shortened to "FSM" or "Micronesia"—not to be confused with the identical name for the overall region). The Gilbert Islands (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioah Guyot
Ioah Guyot is a seamount in the Pacific Ocean, close to the Marshall Islands. Part of the Magellan Seamounts, it is a shield volcano that has erupted alkali basalt and hawaiite 87 million years ago, but may have continued erupting into the Miocene. During the Cretaceous, reefs developed on the guyot. Geography and geomorphology The guyot belongs to the Magellan Seamounts which stretch from the Mariana Trench to Ita Mai Tai seamount. It is also known as Fedorov and Ioan/ IOAN, which stands for "Institute of Oceanology of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR". Ita Mai Tai guyot lies south-southeast of Ioah and Pallada guyot north-northwest, other seamounts in the area east of Ioah are Changpogo, Gramberg, Zatonskii and Arirang. There are about 1000 seamounts in the central western Pacific. Ioah Guyot is a shield volcano with an arcuate shape; the two halves that make it up have dimensions of and . The guyot rises from the seafloor to – depth, forming a summit plateau with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squat Lobster
Squat lobsters are dorsoventrally flattened crustaceans with long tails held curled beneath the cephalothorax. They are found in the two superfamilies Galatheoidea and Chirostyloidea, which form part of the decapod infraorder Anomura, alongside groups including the hermit crabs and mole crabs. They are distributed worldwide in the oceans, and occur from near the surface to deep sea hydrothermal vents, with one species occupying caves above sea level. More than 900 species have been described, in around 60 genera. Some species form dense aggregations, either on the sea floor or in the water column, and a small number are commercially fished. Description The two main groups of squat lobsters share most features of their morphology. They resemble true lobsters in some ways, but are somewhat flattened dorsoventrally, and are typically smaller. Squat lobsters vary in carapace length (measured from the eye socket to the rear edge), from in the case of ''Munidopsis aries'', down to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form planulae, a mobile early form of the coral polyp which, when m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
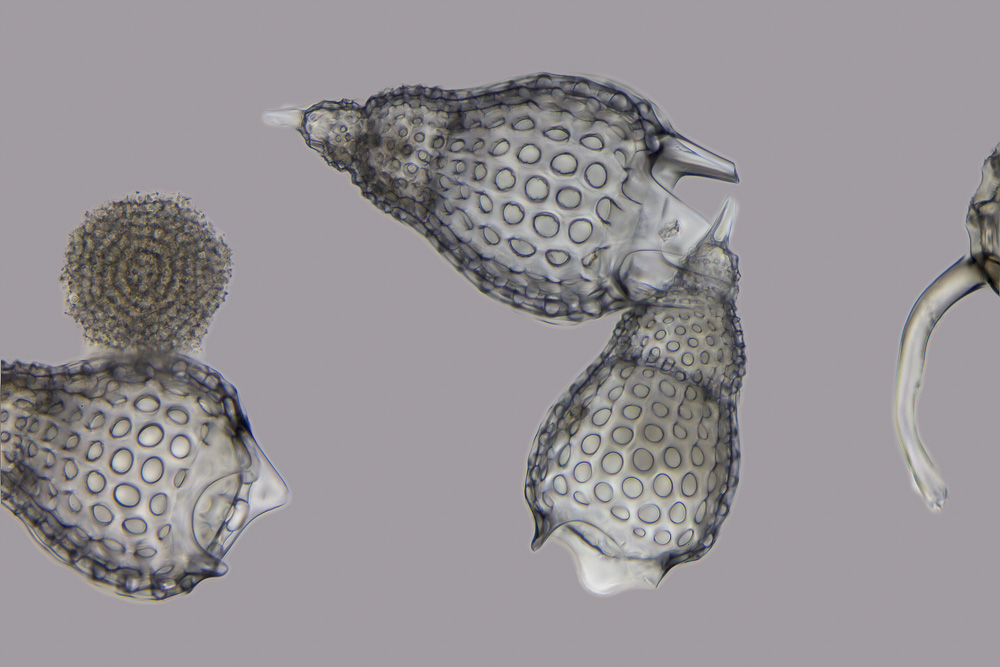
Radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while the ectoplasm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rarotonga Hotspot
The Rarotonga hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the southern Pacific Ocean. The hotspot was responsible for the formation of Rarotonga and some volcanics of Aitutaki. In addition to these volcanoes in the Cook Islands, the composition of volcanic rocks in Samoa and in the Lau Basin may have been influenced by the Rarotonga hotspot, and some atolls and seamounts in the Marshall Islands may have formed on the hotspot as well. Geology Oceanic plateaus and linear volcanic chains dot the floor of the Pacific Ocean. Their formation has been explained with mantle plumes which rise from the core-mantle boundary and spread out when they rise, forming a large "head" that causes intense volcanic activity once it hits the crust. This volcanism is responsible for the formation of the oceanic plateaus. Later, the remnant "tail" of the plume is still rising and induces the formation of volcano chains as the crust moves over the plume tail, thus forming the linear chains. A number of hotsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
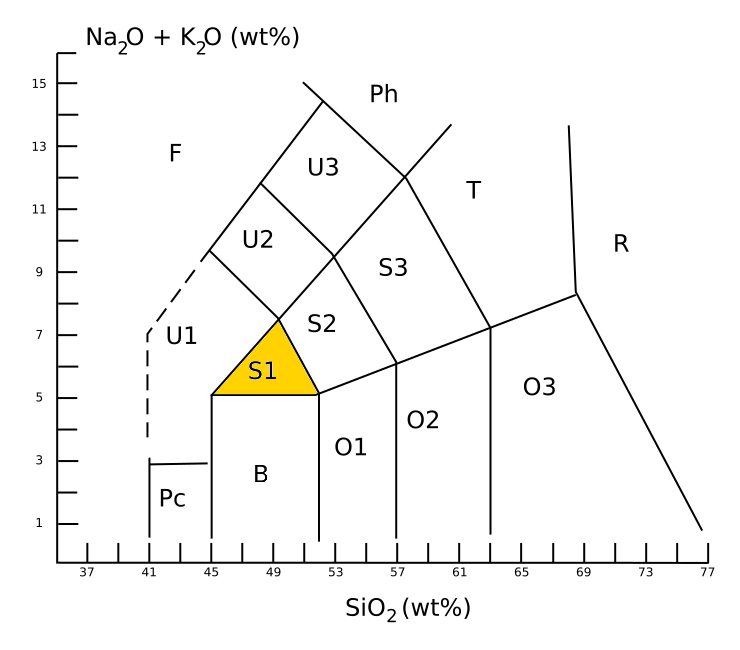
Trachybasalt
Trachybasalt is a volcanic rock with a composition between trachyte and basalt. It resembles basalt but has a high content of alkali metal oxides. Minerals in trachybasalt include alkali feldspar, calcic plagioclase, olivine, clinopyroxene and likely very small amounts of leucite or analcime. Description An aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock is classified as trachybasalt when it has a silica content of about 49% and a total alkali metal oxide content of about 6%. This places trachybasalt in the S1 field of the TAS classification, TAS diagram. Trachybasalt is further divided into sodium-rich ''hawaiite'' and potassium-rich ''potassic trachybasalt'', with wt% > + 2 for hawaiite. The intrusive equivalent of trachybasalt is monzonite. Trachybasalt is not defined on the QAPF diagram, which classifies crystalline igneous rock by its relative content of feldspars and quartz. However, the U.S. Geological Survey defines trachybasalt as a mafic volcanic rock (composed of over 35% maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiitic
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii. It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Hawaii, which happens to be when the alkaline metals are most present. In gemology, hawaiite is a colloquial term for Hawaii-originated peridot, which is a gem-quality form of the mineral olivine. Description Hawaiite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock produced by rapid cooling of lava moderately poor in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides (potassium oxide plus sodium oxide). It is often impractical to determine the mineral composition of such a fine-grained rock, and so hawaiite is defined chemically. Under the TAS classification, hawaiite is sodic trachybasalt, with a silica content close to 49 wt%, a total alkali metal oxide content close to 6%, and wt% > wt% + 2. This places hawaiite in the S1 field of the TAS dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Guyot.png)