|
Paleoloxodon Antiqus
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian '' Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to '' Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Taxonomy In 1924, circumscribed '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Natural Science
The National Museum of Natural Science () is a national museum in North District, Taichung, Taiwan. Overview The museum covers and is a six-venue complex housing: the Space Theater, Science Center, Life Science Hall, Human Cultures Hall, Global Environment Hall, and Botanical Garden. The Research and Collection Division of the museum is divided into departments for zoology, botany, geology and anthropology.Yang T. Y. AleckResearch and Collection of the National Museum of Natural Science in Taiwan ', Volume 24, pages 79–89, 2004. The architect and educator Han Pao-teh was appointed as the first director of the museum in 1987, a post he held until 1995. He was involved with helping to set up the museum before that from 1981. The current director is Chuan-Chin Chiao (()). History In 1980, the government announced plans to build the museum. On New Year's Day of 1986, the first phase of the museum opened, including the Science Center, Space Theater, administrative offices, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgenus
In biology, a subgenus (plural: subgenera) is a taxonomic rank directly below genus. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a subgeneric name can be used independently or included in a species name, in parentheses, placed between the generic name and the specific epithet: e.g. the tiger cowry of the Indo-Pacific, ''Cypraea'' (''Cypraea'') ''tigris'' Linnaeus, which belongs to the subgenus ''Cypraea'' of the genus ''Cypraea''. However, it is not mandatory, or even customary, when giving the name of a species, to include the subgeneric name. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICNafp), the subgenus is one of the possible subdivisions of a genus. There is no limit to the number of divisions that are permitted within a genus by adding the prefix "sub-" or in other ways as long as no confusion can result. Article 4 The secondary ranks of section and series are subordinate to subgenus. An example is ''Banksia'' subg. ''Isostylis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Xylophagou
''Palaeoloxodon cypriotes'', the Cyprus dwarf elephant, is an extinct species that inhabited the island of Cyprus during the Late Pleistocene. Remains comprise 44 molars, found in the north of the island, seven molars discovered in the south-east, a single measurable femur and a single tusk among very sparse additional bone and tusk fragments. The molars support derivation from the large straight-tusked elephant ''(Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), that inhabited Europe since 780,000 years ago. The species is presumably derived from the older, larger ''P. xylophagou'' from the late Middle Pleistocene which reached the island presumably during a Pleistocene glacial maximum when low sea levels allowed a low probability sea crossing between Cyprus and Asia Minor. During subsequent periods of isolation the population adapted within the evolutionary mechanisms of insular dwarfism, which the available sequence of molar fossils confirms to a certain extent. The fully developed ''Palaeoloxodon cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Creutzburgi
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to '' Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Taxonomy In 1924, circumscribed ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Chaniensis
''Palaeoloxodon chaniensis'' is an extinct species of pygmy straight-tusked elephant. The species is described from limited remains found in Stylos and in Vamos cave, Chania, west Crete. See also *Dwarf elephant Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example ... References Palaeoloxodon Pleistocene proboscideans Pleistocene species Pleistocene mammals of Europe Fossil taxa described in 2001 Prehistoric Crete Fauna of Crete {{paleo-proboscidean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Elephant
Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example of insular dwarfism, the phenomenon whereby large terrestrial vertebrates (usually mammals) that colonize islands evolve dwarf forms, a phenomenon attributed to adaptation to resource-poor environments and selection for early maturation and reproduction. Some modern populations of Asian elephants have also undergone size reduction on islands to a lesser degree, resulting in populations of pygmy elephants. Fossil remains of dwarf elephants have been found on the Mediterranean islands of Cyprus, Malta (at Għar Dalam), Crete (in Chania at Vamos, Stylos and in a now-underwater cave on the coast), Sicily, Sardinia, the Cyclades Islands and the Dodecanese Islands. Other islands where dwarf ''Stegodon'' have been found are Sulawesi, Flores, Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Huaihoensis
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to '' Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Taxonomy In 1924, circumscribed ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
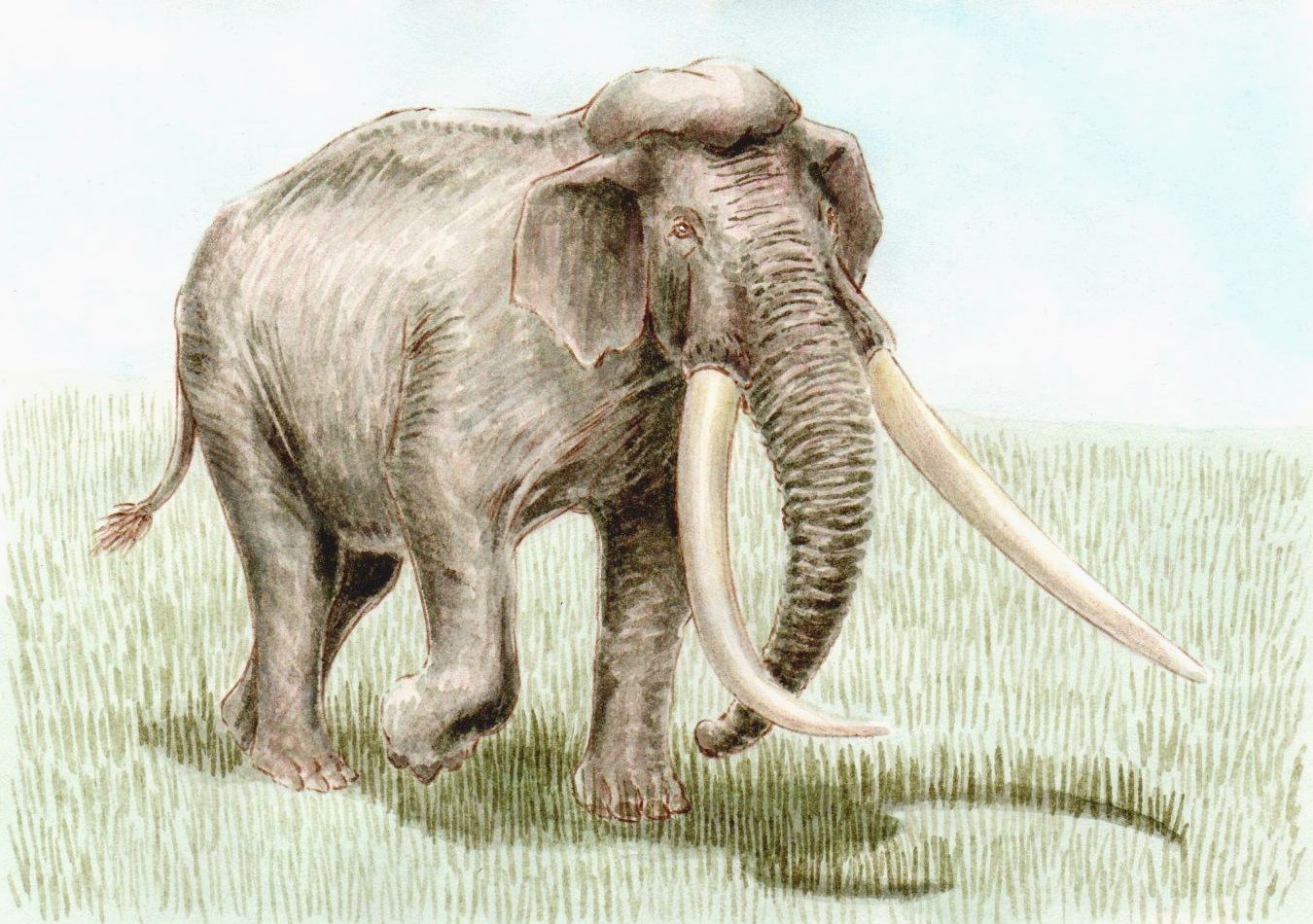
Palaeoloxodon Antiquus
The straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'') is an extinct species of elephant that inhabited Europe and Western Asia during the Middle and Late Pleistocene (781,000–30,000 years before present). Recovered individuals have reached up to in height, and an estimated in weight. The straight-tusked elephant probably lived in small herds, flourishing in interglacial periods, when its range would extend as far north as Great Britain. Isolated tusks are often found while partial or whole skeletons are rare, and there is evidence of predation by early humans. It is the ancestral species of most dwarf elephants that inhabited islands in the Mediterranean. Description ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'' was quite large, with individuals reaching in height. Like other members of ''Palaeoloxodon'', ''P. antiquus'' possesses a well developed parieto-occipital crest at the top of the cranium that anchored the splenius as well as possibly the rhomboid muscles to support the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Recki
''Palaeoloxodon recki'' is an extinct species of elephant native to Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene. At up to 14 feet (4.27 metres) in shoulder height, it was one of the largest elephant species to have ever lived. It is believed that ''P. recki'' ranged throughout Africa between 3.5 and 1 million years ago. ''P. recki'' was a successful grass-eating elephant until it became extinct, perhaps by competition with members of the genus '' Loxodonta'', the African elephants of today. Its descendant taxon, "''Elephas" jolensis'' persisted into the late Middle Pleistocene, c. 205-130 kya in Kenya, after which it was replaced by ''Loxodonta africana'' after a severe drought period. ''P. recki'' is believed to be the ancestral species from which the ''Palaeoloxodon ''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair. They lived from the Pliocene epoch (from around 5 million years ago) into the Holocene at about 4,000 years ago, and various species existed in Africa, Europe, Asia, and North America. They were members of the family Elephantidae, which also contains the two genera of modern elephants and their ancestors. Mammoths are more closely related to living Asian elephants than African elephants. The oldest representative of ''Mammuthus'', the South African mammoth (''M. subplanifrons''), appeared around 5 million years ago during the early Pliocene in what is now southern and eastern Africa. Descendant species of these mammoths moved north and continued to propagate into numerous subsequent spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Genome
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA. Structure Nuclear DNA is a nucleic acid, a polymeric biomolecule or biopolymer, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis Crick and James D. Watson (1953) using data collected by Rosalind Franklin. Each strand is a long polymer chain of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and an organic base. Nucleotides are distinguished by their bases: purines, large bases that include adenine and guanine; and pyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |