|
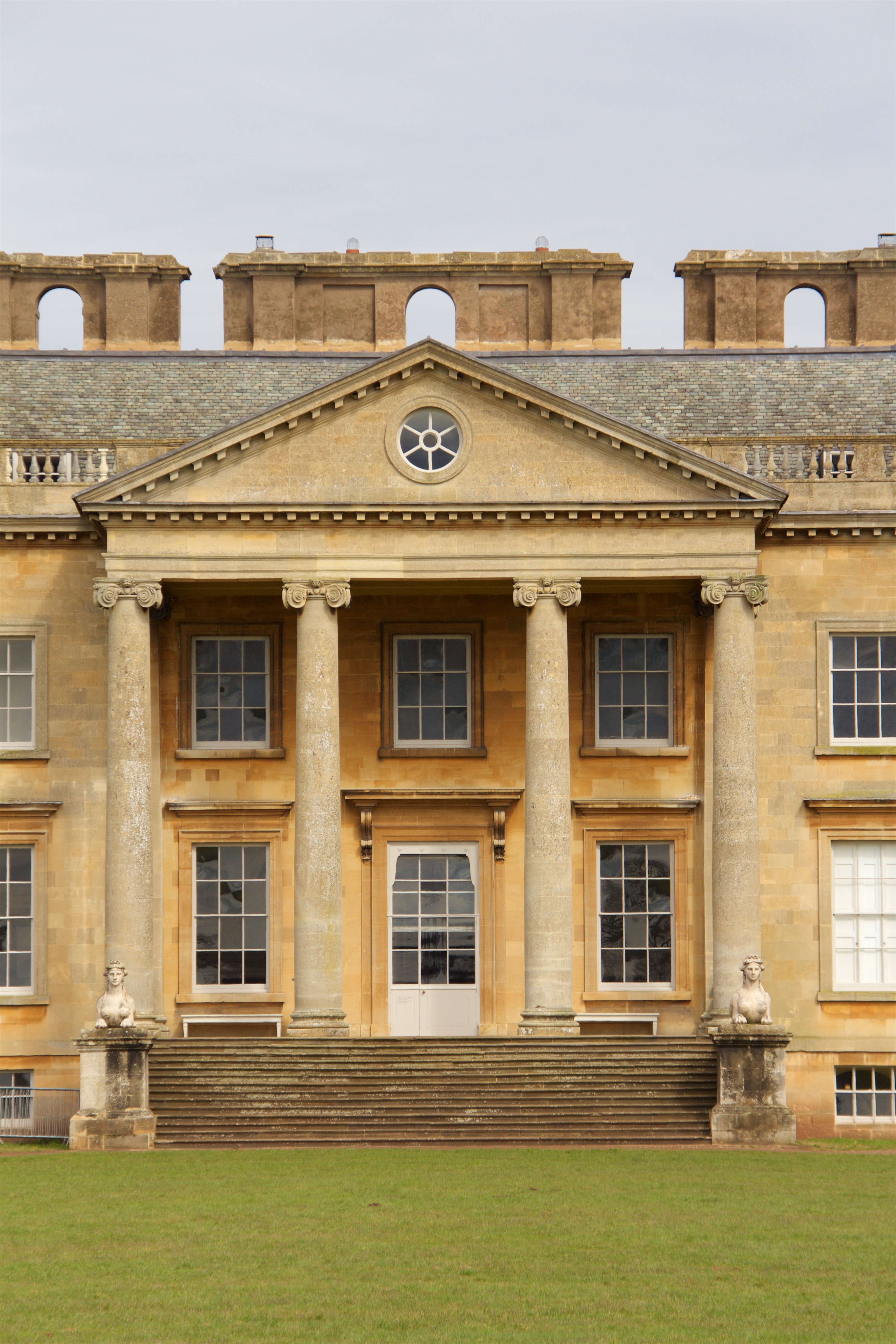
Palazzo Saporiti
The Palazzo Saporiti, also known as Palazzo Rocca-Saporiti, is a historic Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical mansion in the centre of the north Italian city of Milan. History The mansion was commissioned in 1800 by Gaetano Belloni who managed the gaming room at La Scala. However, as a result of the prohibition of gambling in the Napoleonic era, he was forced to sell the residence to the Marquis Rocca Saporiti from Genoa. The mansion was built as part of a redevelopment project in the vicinity of the Porta Venezia, Porta Orientale on land which had belonged to the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, Capuchin Friars until their order was dissolved by the Austrian administration."Palazzo Rocca Saporti" ''Fondo per l'Ambiente Italiano''. Retrieved 13 September 2012. Completed in 1812, the project was said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9039 - Milano, Corso Venezia - Giovanni Perego, Palazzo Saporiti (1812) - Foto Giovanni Dall'Orto 22-Apr-2007
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the Brahmi numerals, beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an Ascender (typography), ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugnato
Two different styles of rustication in the Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence; smooth-faced above and rough-faced below.">Florence.html" ;"title="Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence">Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence; smooth-faced above and rough-faced below. Rustication is a range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar. The visible face of each individual block is cut back around the edges to make its size and placing very clear. In addition the central part of the face of each block may be given a deliberately rough or patterned surface. Rusticated masonry is usually "dressed", or squared off neatly, on all sides of the stones except the face that will be visible when the stone is put in place. This is given wide joints that emphasize the edges of each block, by angling the edges ("channel-jointed"), or dropping them back a little. The main part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In 1812
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture In Milan
Neoclassical architecture in Milan encompasses the main artistic movement from about 1750 to 1850 in this northern Italian city. From the final years of the reign of Maria Theresa of Austria, through the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy and the European Restoration, Milan was in the forefront of a strong cultural and economic renaissance in which Neoclassicism was the dominant style, creating in Milan some of the most influential works in this style in Italy and across Europe. Notable developments include construction of the Teatro alla Scala, the restyled Royal Palace of Milan, Royal Palace, and the Brera institutions including the Brera Academy, Academy of Fine Arts, the Braidense Library and the Brera Astronomical Observatory.Pisaroni, 18 Neoclassicism also led to the development of monumental city gates, new squares and boulevards as well as public gardens and private mansions.TCI rosso, 40 Latterly two churches, San Tomaso in Terramara and San Carlo al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazioso Rusca
Grazioso Rusca (1757 – 18 June 1829) was a Swiss sculptor who was also active in northern Italy. Biography Originally from Rancate in the Swiss canton of Ticino, he was trained as a stonemason by architects including Simone Cantoni. He worked at the Veneranda Fabbrica del Duomo di Milano in Milan where he created reliefs for the cathedral's facade. In the 1880s, he worked with Austrian architect Leopold Pollack at the College of Pavia, creating two large statues representing Philosophy and Theology. From 1796 to 1797, his decorations for the Palazzo Belgioioso included bas-reliefs depicting Napoleon as Hercules helping Italy. In Bergamo's Cappella Colleoni, he sculpted the two angels supporting Pollack's altar table. Again working with Pollack in Bergamo, he decorated the high altar at Santa Maria Maggiore and created the bas-reliefs of Apollo and the muses at the Palazzo Agosti. In 1805, he replaced Carlo Maria Giudici at the Fabbrica del Duomo, earning him a position of gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeo Marchesi
Pompeo Marchesi (; 7 August 1783, in Saltrio, near Milan – 6 February 1858, in Milan) was a Lombard sculptor of the neoclassical school. Biography He first studied at the Brera Academy of Fine Arts in Milan. In 1804 he won a scholarship to study in Rome under Canova, from whom he received much encouragement. The greater part of his life was spent in Milan, where for many years he was professor of sculpture at the Academy. He executed a large number of groups in marble and portrait busts. One of his earliest works was a larger than life statue of St. Ambrose, patron of the city, for the Duomo of Milan. For the Arco della Pace (commemorative arch now in the Parco Sempione), completed in 1838, he made various reliefs including of Terpsichore and Venus Urania, and of the rivers Adige and Tagliamento. He decorated the façade of the Castello with twelve figures of great Italian captains, and that of the Palazzo Saporiti with reliefs in modern classic style. One of his best-kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dii Consentes
The ''Dii Consentes'', also known as ''Di'' or ''Dei Consentes'' (once ''Dii Complices''), is an ancient list of twelve major deities, six gods and six goddesses, in the pantheon of Ancient Rome. Their gilt statues stood in the Roman Forum, and later apparently in the Porticus Deorum Consentium. The gods were listed by the poet Ennius in the late 3rd century BCE in a paraphrase of an unknown Greek poet: :Juno, Vesta, Minerva, Ceres, Diana, Venus :Mars, Mercurius, Iovis, Neptunus, Vulcanus, Apollo Livy arranges them in six male-female pairs: Jupiter-Juno, Neptune-Minerva, Mars-Venus, Apollo-Diana, Vulcan-Vesta and Mercury-Ceres. Three of the ''Dii Consentes'' formed the Capitoline Triad: Jupiter, Juno and Minerva. Precursor lists The grouping of twelve deities has origins older than the Greek or Roman sources. Hittite The Greek grouping may have Hittite origins via Lycia, in Anatolia. A group of twelve Hittite gods is known both from cuneiform texts and from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balustrade
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its construction are wood, stone, and less frequently metal and ceramic. A group of balusters supporting a handrail, coping, or ornamental detail are known as a balustrade. The term baluster shaft is used to describe forms such as a candlestick, upright furniture support, and the stem of a brass chandelier. The term banister (also bannister) refers to a baluster or to the system of balusters and handrail of a stairway. It may be used to include its supporting structures, such as a supporting newel post. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', "baluster" is derived through the french: balustre, from it, balaustro, from ''balaustra'', "pomegranate flower" rom a resemblance to the swelling form of the half-open flower (''illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
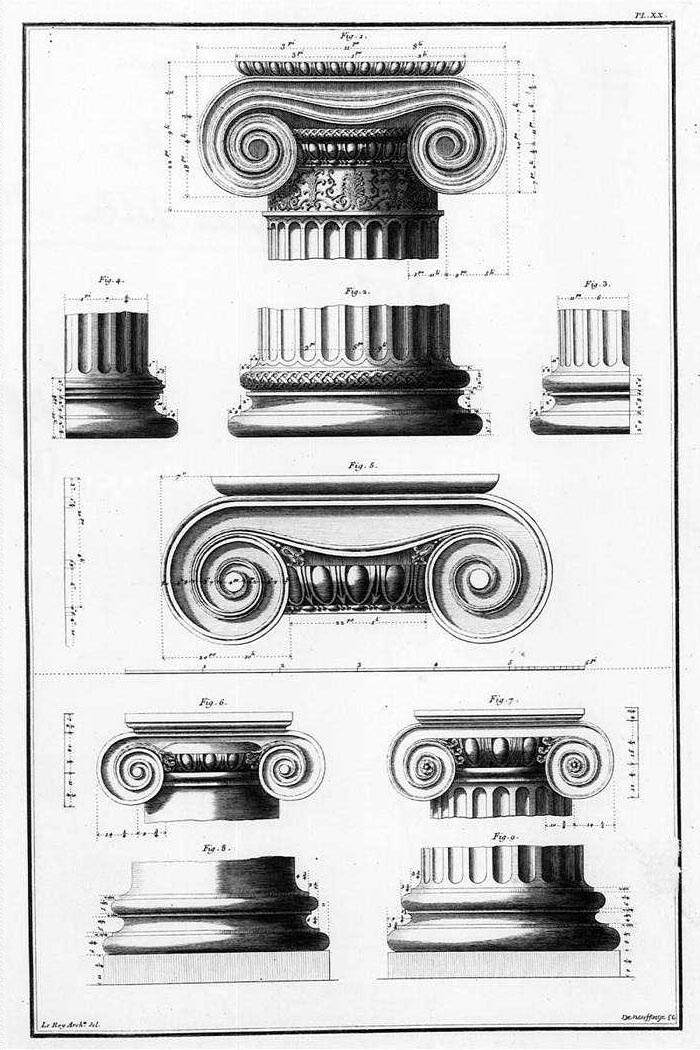
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of the most influential individuals in the history of architecture. While he designed churches and palaces, he was best known for country houses and villas. His teachings, summarized in the architectural treatise, ''The Four Books of Architecture'', gained him wide recognition. The city of Vicenza, with its 23 buildings designed by Palladio, and 24 Palladian villas of the Veneto are listed by UNESCO as part of a World Heritage Site named City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto. The churches of Palladio are to be found within the "Venice and its Lagoon" UNESCO World Heritage Site. Biography and major works Palladio was born on 30 November 1508 in Padua and was given the name Andrea di Pietro della Gondola. His father, Pietro, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)