|
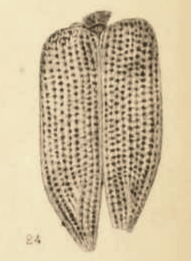
Palaeopsychops
''Palaeopsychops'' is an extinct genus of lacewing in the moth lacewings family Ithonidae. The genus is known from Early Eocene fossils found in Europe, and North America and is composed of ten species. The ten species can be informally separated into two species groups based on veination of the forewings, the "European" and "North American" groups. When first described, the genus was placed in the family Psychopsidae, but later was moved to Polystoechotidae, which itself is now considered a subgroup of the moth lacewings. Distribution & age The European species of ''Palaeopsychops'' are all known from the Early Eocene Fur Formation along the western Limfjord coast of Denmark. Most of the thick formation is diatomites with an interspersed sequence of approximately 179 ash layers. Argon–argon radiometric dating of ash layer "+19", which is slightly lower in the strata then the "insect beds", has determined a age. ''Palaeopsychops'' species have been recovered from three loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klondike Mountain Formation
The Klondike Mountain Formation is an Early Eocene (Ypresian) geological formation located in the northeast central area of Washington state. The formation, named for the type location designated in 1962, Klondike Mountain north of Republic, Washington, is composed of volcanic rocks in the upper unit and volcanics plus lacustrine (lakebed) sedimentation in which a lagerstätte with exceptionally well-preserved plant and insect fossils has been found, along with fossil epithermal hot springs. The formation is the youngest in a group of formations which belong to the Challis Sequence rocks. The formation unconformably overlies rocks of the Eocene Sanpoil Volcanics and much older Triassic and Permian formations. The formation is bounded on its edges by a series of high-angle strike slip faults, which have contained the Klondike Mountain Formation in a series of graben structures, such as the Republic Graben. Public access to a fossiliferous outcrop at the north end of Republic is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ithonidae
Ithonidae, commonly called moth lacewings and giant lacewings, is a small family of winged insects of the insect order Neuroptera. The family contains a total of ten living genera, and over a dozen extinct genera described from fossils. The modern Ithonids have a notably disjunct distribution, while the extinct genera had a more global range. The family is considered one of the most primitive living neuropteran families. The family has been expanded twice, first to include the genus '' Rapisma'', formerly placed in the monotypic family Rapismatidae, and then in 2010 to include the genera that had been placed into the family Polystoechotidae. Both Rapismatidae and Polystoechotidae have been shown to nest into Ithonidae ''sensu lato''. The larvae of ithonids are grub-like, subterranean and likely phytophagous (plant feeding). Description and ecology Ithonidae are typically medium to large-sized neuropterans. P. S. Welch conducted research in 1914 on "Polystoechotidae" larvae r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coldwater Beds
The Coldwater Beds are a geologic formation of the Okanagan Highlands in British Columbia, Canada. They preserve fossils dating back to the Ypresian stage of the Eocene period, or Wasatchian in the NALMA classification.Coldwater Beds at Fossilworks.org The formation comprises mudstones, shales and s deposited in a |
Neuroptera
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in the unranked taxon Neuropterida (once known as Planipennia) including: alderflies, fishflies, dobsonflies, and snakeflies. Adult Neuropterans have four membranous wings, all about the same size, with many veins. They have chewing mouthparts, and undergo complete metamorphosis. Neuropterans first appeared during the Permian period, and continued to diversify through the Mesozoic era. During this time, several unusually large forms evolved, especially in the extinct family Kalligrammatidae, often called "the butterflies of the Jurassic" for their large, patterned wings. Anatomy and biology Neuropterans are soft-bodied insects with relatively few specialized features. They have large lateral compound eyes, and may or may not also have oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Formation
The Fur Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian (Lower Eocene Epoch, c. 56.0-54.5 Ma) age which crops out in the Limfjord region of Denmark from Silstrup via Mors and Fur to Ertebølle, and can be seen in many cliffs and quarries in the area. The Diatomite Cliffs (''moler'' in Danish) is on the Danish list of tentative candidates for World Heritage and may become a world Heritage site. Geology The Fur Formation is a unit of diatomitic sediment approximately 60 meters thick consisting of diatoms and clay minerals with up to 180 layers of volcanic ash. In Danish literature the formation has informally been referred to as the ''moler'' (''Ler'' means clay). The diatomite comprises 2/3 opal tests of diatoms and 1/3 clay, interbedded with layers of volcanic ash and a few limestone horizons (‘cementstones’), and has exceptionally complete fossil preservation. It is known for its abundant fossil fish, insects, reptiles, birds and plants. The Fur Formation was deposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgai Sea
The Turgai Sea, also known as the Turgay Sea, Turgai Strait, Obik Sea, Ural Sea or West Siberian Sea, was a large shallow body of salt water (an epicontinental or epeiric sea) during the Mesozoic through Cenozoic Eras. It extended north of the present-day Caspian Sea to the "paleo-Arctic" region, and was in existence from the Middle Jurassic to Oligocene, approximately 160 to 29 million years ago. The Turgai Sea was not absolutely continuous throughout this entire era, though it was a persistent and predominating feature in its region; it "fragmented southern Europe and southwestern Asia into many large islands, and separated Europe from Asia." The division of the Eurasian landmass by the Turgai Sea had the effect of isolating animal populations. One of the better known groups are the ceratopsian dinosaurs during the Cretaceous Period, which were restricted to Asia and western North America that were connected for much of the era. The existence of the Turgai Sea also restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quilchena, British Columbia
Quilchena ( thp, q̓əłmíx) is an unincorporated community located on the south shore of Nicola Lake near the city of Merritt, British Columbia, Canada in that province's Nicola Country region. On the former main route between Merritt and Kamloops, it is now largely bypassed since the construction of the Coquihalla Highway Coquihalla may refer to: *British Columbia Highway 5, also known as Coquihalla highway * Coquihalla River * Coquihalla Pass * Okanagan—Coquihalla, a federal electoral district in British Columbia * Coquihalla Canyon Provincial Park *Coquihalla Ri .... A heritage hotel is the main landmark, lately transformed into a small golf resort. ReferencesBCGNIS listing "Quilchena (locality)" [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic, Washington
Republic is a city in Ferry County, Washington, United States. The population was 1,073 at the 2010 census, a 12.5% increase over the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Ferry County. It was the largest mining camp in the Republic Mining District, and home to the "Hot Air Line" railway. Geography Republic is located at (48.648159, −118.734947). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all of it land. Republic is located near the source of the Sanpoil River in a long graben valley bordered by the Okanagan Highlands to the west and the Kettle mountain range to the east. Curlew Lake, long (Elev: ), provides fishing and boating to summer visitors northeast of Republic. Swan Lake is small mountain lake to the south of Republic and also serves to be a popular lake for local residents and tourists to visit. Republic is surrounded by the Colville National Forest and to the south is the Colville Indian Reservation. History Republic Mining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferry County, Washington
Ferry County is a county located on the northern border of the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,178, making it the fourth-least populous county in Washington. The county seat and largest city is Republic. The county was created out of Stevens County in February 1899 and is named for Elisha P. Ferry, the state's first governor. History During the time of Washington Territory, the Territorial Legislature created Stevens County in 1863, containing all the land from the Columbia River to the Cascades north of the Wenatchee River from Walla Walla County. On January 20, 1864, the original Spokane County was dissolved and merged with the unorganized Stevens County. The western section of Stevens County was separated on February 18, 1899, and named Ferry County, in recognition of the Territory's last governor and the State's first governor, Elisha P. Ferry. The town of Republic is the county's seat of government, as well as the largest town. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the lower Eocene. Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. Stratigraphic definition The Ypresian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Belgium, Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The Ypresian is named after the Flanders, Flemish city of Ypres in Belgium (spelled ''Ieper'' in Dutch). The definitions of the original stage were totally different from the modern ones. The Ypresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsefly, British Columbia
Horsefly is an unincorporated community on the northwest shore of the Horsefly River, in the Cariboo region of central British Columbia. The location, via BC Highway 97, Likely Rd, and Horsefly Rd, is about northeast of Williams Lake, and by road south of Quesnel Lake. Mining Peter Dunlevey's party of prospectors is credited with the first discovery of gold in the Cariboo Gold Rush near the site of the present village. However, evidence indicates H.O. Bowe's party arrived weeks earlier to the Horsefly River in the summer of 1859. That year, at least four separate groups found gold. During the following years, small placer operations existed. In 1884, Thaddeus Harper obtained sizable mining leases, but his operations from 1886 to 1888 were unsuccessful. In 1891, R.T. Ward, who had bought or leased the Harper claims, found paying ground. Called the Horsefly Gold Mining Co., activities continued until 1902. From 1891, the Miocene Gravel Mining Co undertook underground hard-rock mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |