|
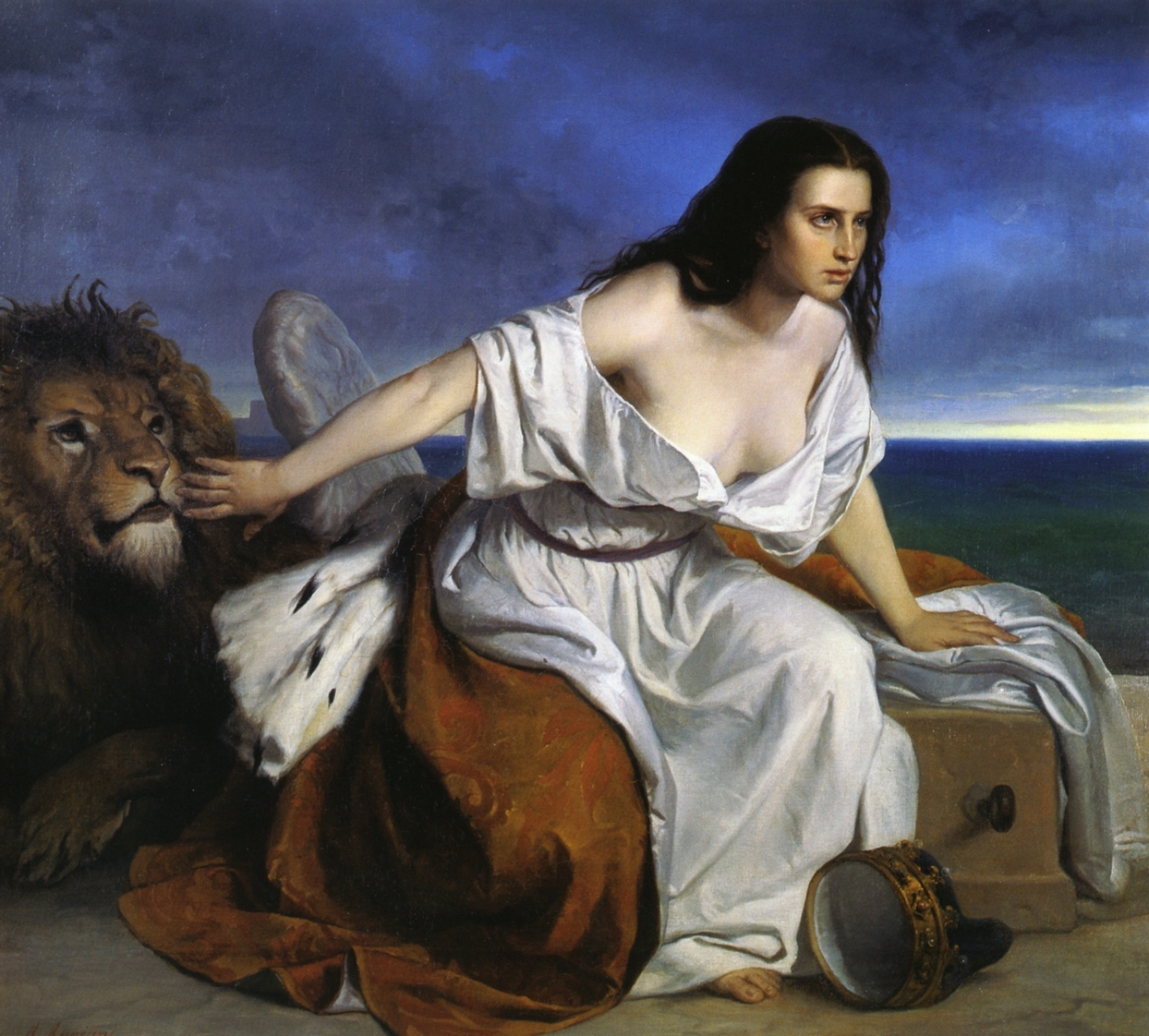
Palace Of St. Sebastian
The Palazzo San Sebastiano is a 16th-century palace in Mantua. Built by the Gonzaga family, since 19 March 2005 it has housed Mantua's city museum (''Museo della Città di Palazzo San Sebastiano''). History The building was constructed between 1506 and 1508 by Francesco II Gonzaga and became his favourite residence until his death in 1519. It was designed by Gerolamo Arcari and Bernardino Ghisolfo, who also commissioned artists such as Lorenzo Leonbruno, Matteo Costa and Lorenzo Costa the Elder to decorate the interior. The Palazzo's main hall was also the original setting for Mantegna's ''Triumphs of Caesar'', now at Hampton Court near London. After 1519 the Palazzo lost its prime position among the Gonzaga palaces, with its most valuable furniture and paintings moved elsewhere, and it was used by the Gonzaga di Novellara, Gazzuolo and Castiglione delle Stiviere branches of the family. It was in this Palazzo that Aloysius Gonzaga (a future saint) ceded his inheritance to his yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna (, , ; September 13, 1506) was an Italian painter, a student of Roman archeology, and son-in-law of Jacopo Bellini. Like other artists of the time, Mantegna experimented with perspective, e.g. by lowering the horizon in order to create a sense of greater monumentality. His flinty, metallic landscapes and somewhat stony figures give evidence of a fundamentally sculptural approach to painting. He also led a workshop that was the leading producer of prints in Venice before 1500. Biography Youth and education Mantegna was born in Isola di Carturo, Venetian Republic close to Padua (now Italy), second son of a carpenter, Biagio. At the age of 11, he became the apprentice of Paduan painter Francesco Squarcione. Squarcione, whose original profession was tailoring, appears to have had a remarkable enthusiasm for ancient art, and a faculty for acting. Like his famous compatriot Petrarca, Squarcione was an ancient Rome enthusiast: he traveled in Italy, and perhaps a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Mantua
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
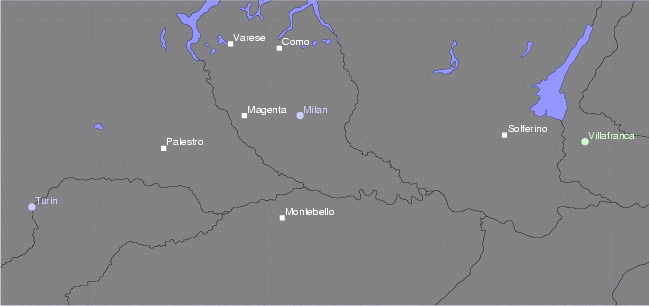
Second Italian War Of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the Second French Empire and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification. A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice. The two states signed a military alliance in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April. On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May. The Austrian invasion wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in European history to date. The revolutions were essentially Democracy, democratic and Liberalism, liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old Monarchy, monarchical structures and creating independent nation-states, as envisioned by romantic nationalism. The revolutions spread across Europe after an initial revolution began in French Revolution of 1848, France in February. Over 50 countries were affected, but with no significant coordination or cooperation among their respective revolutionaries. Some of the major contributing factors were widespread dissatisfaction with political leadership, demands for more participation (decision making), participation in government and democracy, demands for freedom of the press, other demands made by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (1861-1946)
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and form the modern Italian Republic. The state resulted from a decades-long process, the ''Risorgimento'', of consolidating the different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state. That process was influenced by the Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia, which can be considered Italy's legal predecessor state. Italy declared war on Austria in alliance with Prussia in 1866 and received the region of Veneto following their victory. Italian troops entered Rome in 1870, ending more than one thousand years of Papal temporal power. Italy entered into a Triple Alliance with the German Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1882, following strong disagreements with France about their respective colonial expansions. Although relations with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Italian War Of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence ( it, Terza Guerra d'Indipendenza Italiana) was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in Austria conceding the region of Venetia (present-day Veneto, Friuli and the city of Mantua, the last remnant of the ''Quadrilatero'') to France, which were later annexed by Italy after a plebiscite. Italy's acquisition of this wealthy and populous territory represented a major step in the Unification of Italy. Background Victor Emmanuel II of Savoy had been proclaimed King of Italy on 17 March 1861 but did not control Venetia or the much-reduced Papal States. The situation of the , a later Italian term for part of the country under foreign domination that literally meaning ''unredeemed'', was an unceasing source of tension in the domestic politics of the new kingdom and a cornerstone of its foreign policy. The first attempt to seize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state in 1861, the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1871 after the Capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. Some of the states that had been targeted for unification ('' terre irredente'') did not join the Kingdom of Italy until 1918 after Italy defeated Austria-Hungary in the First World War. For this reason, historians sometimes describe the unification period as continuing past 1871, including activities during the late 19th century and the First World War (1915–1918), and reaching completion only with the Armistice of Villa G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfiore Martyrs
The Belfiore martyrs were a group of pro-independence fighters condemned to death by hanging between 1852 and 1853 during the Italian Risorgimento. They included Tito Speri and the priest Enrico Tazzoli and are named after the site where the sentence was carried out, in the valley of Belfiore at the south entrance to Mantua. The hanging was the first in a long series of death sentences imposed by Josef Radetzky, governor general of Lombardy–Venetia. As a whole these sentences marked the culmination of Austrian repression after the First Italian War of Independence and marked the failure of all re-pacification policies. Mantua The city of Mantua had formed part of the lands of the Austrian House of Habsburg since 1707. It was the capital of a small but quite rich dukedom, as well as being of some military importance, both for the quality of its fortifications but also for its geographic position, allowing it to control the route between the Veneto and Lombardy and a large num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bust Of Francesco II Gonzaga
{{Disambiguation ...
Bust commonly refers to: * A woman's breasts * Bust (sculpture), of head and shoulders * An arrest Bust may also refer to: Places * Bust, Bas-Rhin, a city in France *Lashkargah, Afghanistan, known as Bust historically Media * ''Bust'' (magazine) of feminist pop culture *''Bust'', a British television series (1987–1988) *"Bust", a 2015 song by rapper Waka Flocka Flame Other uses *Bust, in blackjack *Boom and bust economic cycle *Draft bust in sports, referring to an highly touted athlete that does not meet expectations See also * Busted (other) * Crimebuster (other) *Gangbuster (other) ''Gang Busters'' was an American radio series. Gangbuster(s) or Gang Busters might also refer to: * ''Gang Busters'' (serial), a movie serial based on the radio series * ''Gang Busters'', a 1955 crime film * "Gang Busters" (Tiny Toons episode), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Cristoforo Romano
Giovanni Cristoforo (or Giancristoforo) Romano (1456–1512) was an Italian Renaissance sculptor and medallist. Born in Rome to Isaia da Pisa, he was probably a pupil of Andrea Bregno. His first known works are in the Ducal Palace of Urbino, dating from before 1482. Later he worked as medallist for the courts of Ferrara and Mantua, where he was a favourite of duchess Isabella d'Este. In 1491 he moved to Milan called by Isabella's brother-in-law Ludovico Sforza, who commissioned him the tomb of Gian Galeazzo Visconti at the Certosa di Pavia, which he executed in collaboration with Benedetto Briosco. After the fall of the Sforza (1499) he returned to work for Isabella d'Este, for which he executed some fine medals and the precious marble portal of her study in the Ducal Palace of Mantua. Later, he sojourned in Rome (called by Pope Julius II), Naples, Cremona, and again Milan and Urbino. The tripartite marble altar-piece in the Costa Chapel in Santa Maria del Popolo was probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Da Pavia
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular male baby names in the United States since the late 19th century and has been among the top 200 since the mid 20th century. In the English language it is translated as Anthony, and has some female derivatives: Antonia, Antónia, Antonieta, Antonietta, and Antonella'. It also has some male derivatives, such as Anthonio, Antón, Antò, Antonis, Antoñito, Antonino, Antonello, Tonio, Tono, Toño, Toñín, Tonino, Nantonio, Ninni, Totò, Tó, Tonini, Tony, Toni, Toninho, Toñito, and Tõnis. The Portuguese equivalent is António ( Portuguese orthography) or Antônio (Brazilian Portuguese). In old Portuguese the form Antão was also used, not just to differentiate between older and younger but also between more and less important. In Galici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |