|
Paix
''Paix'' is the fourth studio album by French singer Catherine Ribeiro and her third with the band Alpes. It was originally released in 1972 by Philips Records. The album integrates the group's original folk-oriented sound within the progressive style of their preceding records, with complex instrumentation, longform compositions, and psychedelic soundscapes. It has been described as containing Ribeiro's most experimental work and is generally considered by critics to be the best album in Alpes' catalogue. ''Paix'' was met with relative critical and commercial success upon release. As with Ribeiro's other albums, it became recognized as a cult album due to Ribeiro's distinct voice and lyrics, as well as its relative scarcity. In 2018, the album was issued for the first time in the United States, where it was well-received by critics and lauded among followers of niche folk scenes. Background Catherine Ribeiro's second album with Alpes, ''Âme debout'' (1971), showe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Ribeiro
Catherine Ribeiro (born 22 September 1941) is a French singer. Ribeiro is an experimental folk and avant-garde performer whose work has attained a cult following. With her band Catherine Ribeiro + Alpes, she released several albums in the late 1960s and early 1970s, including ''Catherine Ribeiro & 2Bis'' in 1969, ''No.2'' in 1970, and ''Paix'' in 1972. Since the late 1970s, Ribeiro has also released music as a solo artist. Public figures who have expressed appreciation for her work include the musicians Kim Gordon and Julian Cope, as well as the French mathematician Cédric Villani. Discography Studio albums With Alpes * ''Catherine Ribeiro + 2bis'' (1969) * ''N°2'' (also known as ''Catherine Ribeiro + Alpes'') (1970) * ''Âme debout'' (1971) * ''Paix'' (1972) * ''Le Rat débile et l'Homme des champs'' (1974) * ''Libertés ?'' (1975) * ''Le Temps de l'autre'' (1977) * ''Passions'' (1979) * ''La Déboussole'' (1980) Solo * ''Le Blues de Piaf'' (1977) * ''Jacqueries'' (1978 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Ribeiro + Alpes
Catherine Ribeiro + Alpes were a French band formed in 1968. It consisted of singer Catherine Ribeiro and composer Patrice Moullet. The other members changed through every record. The two used to be in the band Catherine Ribeiro + 2Bis, but decided to change the name after their first record. While their style was mostly folk and psychedelic rock in their first years, they also included elements of avant-garde into their music. Their lyrics often dealt with political and social issues, and they were all written by Catherine Ribeiro, who is also notable for her very special singing style, chaotic and expressive. They disbanded in 1981. Discography Catherine Ribeiro + 2Bis *''Catherine Ribeiro + 2Bis'' (1969) Catherine Ribeiro + Alpes *''N°2'' (1970) *''Ame Debout'' (1971) *''Paix ''Paix'' is the fourth studio album by French singer Catherine Ribeiro and her third with the band Alpes. It was originally released in 1972 by Philips Records. The album integrates the group's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Music
Progressive music is music that attempts to expand existing stylistic boundaries associated with specific genres of music. The word comes from the basic concept of "progress", which refers to advancements through accumulation, and is often deployed in the context of distinct genres, with progressive rock being the most notable example. Music that is deemed "progressive" usually synthesizes influences from various cultural domains, such as European art music, Celtic folk, West Indian, or African. It is rooted in the idea of a cultural alternative and may also be associated with auteur-stars and concept albums, considered traditional structures of the music industry. As an art theory, the progressive approach falls between formalism and eclecticism. "Formalism" refers to a preoccupation with established external compositional systems, structural unity, and the autonomy of individual art works. Like formalism, "eclecticism" connotes a predilection toward style synthesis or inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber Pop
Chamber pop (or Chamber rock; also called baroque pop and sometimes conflated with orchestral pop or symphonic pop) is a music genre that combines rock music with the intricate use of string section, strings, horn section, horns, piano, and vocal harmony, vocal harmonies, and other components drawn from the orchestral and lounge music, lounge pop of the 1960s, with an emphasis on melody and texture (music), texture. During chamber pop's initial emergence in the 1960s, producers such as Burt Bacharach, Lee Hazlewood, and the Beach Boys' Brian Wilson served as formative artists of the genre. Wilson's productions of the Beach Boys' albums ''Pet Sounds'' and ''Smile (The Beach Boys album), Smile'' are cited as particularly influential to the genre. From the early 1970s to early 1990s, most chamber pop acts saw little to no mainstream success. The genre's decline was attributed to costly touring and recording logistics and a reluctance among record labels to finance instruments like s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avant-garde Music
Avant-garde music is music that is considered to be at the forefront of innovation in its field, with the term "avant-garde" implying a critique of existing aesthetic conventions, rejection of the status quo in favor of unique or original elements, and the idea of deliberately challenging or alienating audiences. Avant-garde music may be distinguished from experimental music by the way it adopts an extreme position within a certain tradition, whereas experimental music lies outside tradition. Distinctions Avant-garde music may be distinguished from experimental music by the way it adopts an extreme position within a certain tradition, whereas experimental music lies outside tradition. In a historical sense, some musicologists use the term "avant-garde music" for the radical compositions that succeeded the death of Anton Webern in 1945,Paul Du Noyer (ed.), "Contemporary", in the ''Illustrated Encyclopedia of Music: From Rock, Pop, Jazz, Blues and Hip Hop to Classical, Folk, Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Music
Progressive music is music that attempts to expand existing stylistic boundaries associated with specific genres of music. The word comes from the basic concept of "progress", which refers to advancements through accumulation, and is often deployed in the context of distinct genres, with progressive rock being the most notable example. Music that is deemed "progressive" usually synthesizes influences from various cultural domains, such as European art music, Celtic folk, West Indian, or African. It is rooted in the idea of a cultural alternative and may also be associated with auteur-stars and concept albums, considered traditional structures of the music industry. As an art theory, the progressive approach falls between formalism and eclecticism. "Formalism" refers to a preoccupation with established external compositional systems, structural unity, and the autonomy of individual art works. Like formalism, "eclecticism" connotes a predilection toward style synthesis or inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Music
Rock music is a broad genre of popular music that originated as " rock and roll" in the United States in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of different styles in the mid-1960s and later, particularly in the United States and United Kingdom.W. E. Studwell and D. F. Lonergan, ''The Classic Rock and Roll Reader: Rock Music from its Beginnings to the mid-1970s'' (Abingdon: Routledge, 1999), p.xi It has its roots in 1940s and 1950s rock and roll, a style that drew directly from the blues and rhythm and blues genres of African-American music and from country music. Rock also drew strongly from a number of other genres such as electric blues and folk, and incorporated influences from jazz, classical, and other musical styles. For instrumentation, rock has centered on the electric guitar, usually as part of a rock group with electric bass guitar, drums, and one or more singers. Usually, rock is song-based music with a time signature using a verse–chorus form, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
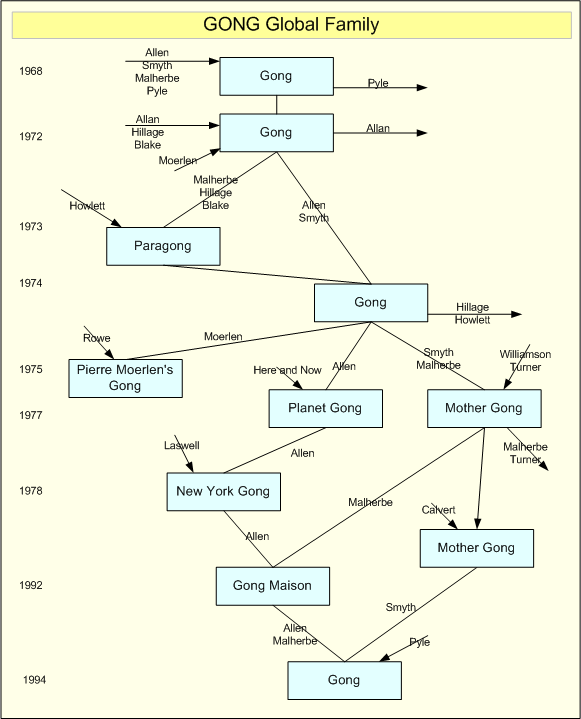
Gong (band)
Gong are a progressive rock band that incorporates elements of jazz and space rock into their musical style. The group was formed in Paris in 1967 by Australian musician Daevid Allen and English vocalist Gilli Smyth. Band members have included Didier Malherbe, Pip Pyle, Steve Hillage, Mike Howlett, Pierre Moerlen, Bill Laswell and Theo Travis. Others who have played on stage with Gong include Don Cherry, Chris Cutler, Bill Bruford, Brian Davison, Dave Stewart and Tatsuya Yoshida. Gong's 1970 debut album, ''Magick Brother'', featured a psychedelic pop sound. By the following year, the second album, ''Camembert Electrique'', featured the more psychedelic rock/space rock sound with which they would be most associated. Between 1973 and 1974, Gong released their best known work, the allegorical ''Radio Gnome Invisible'' trilogy, describing the adventures of Zero the Hero, the Good Witch Yoni and the Pot Head Pixies from the Planet Gong. In 1975, Allen and Smyth left the band, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gong Band Members ...
This is a list of the members of the international psychedelic rock ensemble Gong. Members Current members Former members Additional personnel Timeline Line-ups References Gongat ''Calyx, The Canterbury Music Website'', by Aymeric Leroy - includes detailed chronology {{gong Gong A gongFrom Indonesian and ms, gong; jv, ꦒꦺꦴꦁ ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ja, , dora; km, គង ; th, ฆ้อง ; vi, cồng chiêng; as, কাঁহ is a percussion instrument originating in East Asia and Southeast Asia. Gongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Music
Experimental music is a general label for any music or music genre that pushes existing boundaries and genre definitions. Experimental compositional practice is defined broadly by exploratory sensibilities radically opposed to, and questioning of, institutionalized compositional, performing, and aesthetic conventions in music. Elements of experimental music include Indeterminacy in music, indeterminate music, in which the composer introduces the elements of chance or unpredictability with regard to either the composition or its performance. Artists may also approach a hybrid of disparate styles or incorporate unorthodox and unique elements. The practice became prominent in the mid-20th century, particularly in Europe and North America. John Cage was one of the earliest composers to use the term and one of experimental music's primary innovators, utilizing Indeterminacy (music), indeterminacy techniques and seeking unknown outcomes. In France, as early as 1953, Pierre Schaeffer had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballad
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads derive from the medieval French ''chanson balladée'' or ''ballade'', which were originally "dance songs". Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and song of Britain and Ireland from the Late Middle Ages until the 19th century. They were widely used across Europe, and later in Australia, North Africa, North America and South America. Ballads are often 13 lines with an ABABBCBC form, consisting of couplets (two lines) of rhymed verse, each of 14 syllables. Another common form is ABAB or ABCB repeated, in alternating eight and six syllable lines. Many ballads were written and sold as single sheet broadsides. The form was often used by poets and composers from the 18th century onwards to produce lyrical ballads. In the later 19th century, the term took on the meaning of a slow form of popular love song and is often used for any love song, particularly the sentimental ballad of pop or roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult Following
A cult following refers to a group of fans who are highly dedicated to some person, idea, object, movement, or work, often an artist, in particular a performing artist, or an artwork in some medium. The lattermost is often called a cult classic. A film, book, musical artist, television series, or video game, among other things, is said to have a cult following when it has a small but very passionate fanbase. A common component of cult followings is the emotional attachment the fans have to the object of the cult following, often identifying themselves and other fans as members of a community. Cult followings are also commonly associated with niche markets. Cult media are often associated with underground culture, and are considered too eccentric or anti-establishment to be appreciated by the general public or to be widely commercially successful. Many cult fans express their devotion with a level of irony when describing entertainment that falls under this realm, in that something ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(LOC)_(5354790936)_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg)