|
Paducah And Louisville Railroad
The Paducah & Louisville Railway is a Class II railroad that operates freight service between Paducah and Louisville, Kentucky. The line is located entirely within the Commonwealth of Kentucky. The line was purchased from Illinois Central Gulf Railroad in August, 1986. The main route runs between Paducah and Louisville with branch lines from Paducah to Kevil and Mayfield, Kentucky and another from Cecilia to Elizabethtown, Kentucky. The PAL interchanges with Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) and Canadian National (CN), formerly Illinois Central Railroad, in Paducah. In Madisonville, the line interchanges with CSX Transportation (CSXT). In Louisville, the line interchanges with the Indiana Rail Road (INRD), CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Norfolk Southern (NS). Class III line connections are at Princeton with the Fredonia Valley Railroad (FVRR) and at Louisville with the Louisville and Indiana Railroad (LIRC). The line today carries over 200,000 carloads of traffic on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class III Railroad
In the United States, railroad carriers are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$504,803,294 for Class I carriers and US$40,384,263 for Class II carriers. (Smaller carriers were Class III by default.) There are seven Class I freight railroad companies in the United States including two Canadian carriers with subsidiary trackage in the United States: BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway (via its subsidiary Grand Trunk Corporation), Canadian Pacific Railway (via its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation), CSX Transportation, Kansas City Southern Railway, Norfolk Southern Railway, and Union Pacific Railroad. (Mexico's Ferromex and Kansas City Southern de México would qualify as Class I, but do not operate within the United States.) In addition, the national passenger railroad in the United States, Amtrak, would qualify as C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD GP7U
EMD may refer to: Finance and commerce * Emerging market debt * Earnest money deposit, in the United States, a security deposit, especially for real estate Medicine * Electromagnetic diaphragm * Electromechanical dissociation * Emergency medical dispatcher * Enamel matrix derivative * Esophageal motility disorder * Merck Group, known as EMD in Canada and the United States, a German pharmaceutical company Science and technology * Electrolytic manganese dioxide * Emerin * Empirical mode decomposition * Equilibrium mode distribution * ReadyBoost, disk-caching software Transport * East Midlands Parkway railway station, in England * Electro-Motive Diesel, an American locomotive manufacturer * Electronic Miscellaneous Document in the airline industry * Emerald Airport, in Queensland, Australia Other uses * Schneider Electric EMD a Armenian-Serbian electric company * EMD (band), a Swedish band * Earth mover's distance * European Marketing Distribution, a European purcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
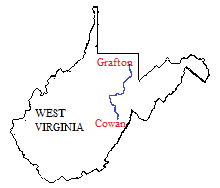
Appalachian And Ohio Railroad
The Appalachian and Ohio Railroad is a class III railroad operating in West Virginia. Originally the Cowen and Pickens Subdivisions of the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad, the railroad was a part of CSX until it was leased to Watco, which began operating the railroad on March 25, 2005. Watco only held the line for a short time before turning the lease from CSX over to Four Rivers Transportation, now P&L Transportation, on May 15, 2006.A & O Railroad Appalachian and Ohio Railroad, 2006. Accessed 2007-07-22. The railroad operates 158 miles of track between Grafton and Cowen. It has one active branch, a portion of the Pickens Subdivision t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evansville Western Railway
The Evansville Western Railway is a Class III common carrier shortline railroad operating in the southern Illinois and Indiana region. It is one of three regional railroad subsidiaries owned and operated by P&L Transportation. Overview Founded in August 2005, the railroad commenced its first operations on January 1, 2006, when P&L Transportation, formerly Four Rivers Transportation, the parent company of both the Evansville Western and Paducah & Louisville railroads, leased of mainline track, ties and track equipment between CSX's Howell Yard in Evansville, Indiana, and the end-of-track at Okawville, Illinois, from CSX Transportation. This line was once part of the Louisville & Nashville's former Saint Louis Subdivision route that previously terminated in the metro-area of East St. Louis, Illinois, before being embargoed and slightly shortened under CSX ownership during the fall of 1993. CSX Transportation retains title to the real estate comprising the right of way on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P&L Transportation
The Paducah & Louisville Railway is a Class II railroad that operates freight service between Paducah and Louisville, Kentucky. The line is located entirely within the Commonwealth of Kentucky. The line was purchased from Illinois Central Gulf Railroad in August, 1986. The main route runs between Paducah and Louisville with branch lines from Paducah to Kevil and Mayfield, Kentucky and another from Cecilia to Elizabethtown, Kentucky. The PAL interchanges with Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) and Canadian National (CN), formerly Illinois Central Railroad, in Paducah. In Madisonville, the line interchanges with CSX Transportation (CSXT). In Louisville, the line interchanges with the Indiana Rail Road (INRD), CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Norfolk Southern (NS). Class III line connections are at Princeton with the Fredonia Valley Railroad (FVRR) and at Louisville with the Louisville and Indiana Railroad (LIRC). The line today carries over 200,000 carloads of traffic on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Knox
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository, which is used to house a large portion of the United States' official gold reserves, and with which it is often conflated. The base covers parts of Bullitt, Hardin and Meade counties. It currently holds the Army Human Resources Center of Excellence, including the Army Human Resources Command. It is named in honor of Henry Knox, Chief of Artillery in the American Revolutionary War and the first United States Secretary of War. For 60 years, Fort Knox was the home of the U.S. Army Armor Center and the U.S. Army Armor School, and was used by both the Army and the Marine Corps to train crews on the American tanks of the day; the last was the M1 Abrams main battle tank. The history of the U.S. Army's Cavalry and Armored forces, and of General George S. Patton's career, is shown at the General George Patton Museum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class I Railroads
In the United States, railroad carriers are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$504,803,294 for Class I carriers and US$40,384,263 for Class II carriers. (Smaller carriers were Class III by default.) There are seven Class I freight railroad companies in the United States including two Canadian carriers with subsidiary trackage in the United States: BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway (via its subsidiary Grand Trunk Corporation), Canadian Pacific Railway (via its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation), CSX Transportation, Kansas City Southern Railway, Norfolk Southern Railway, and Union Pacific Railroad. (Mexico's Ferromex and Kansas City Southern de México would qualify as Class I, but do not operate within the United States.) In addition, the national passenger railroad in the United States, Amtrak, would qualify as C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class II Railroad
In the United States, railroad carriers are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$504,803,294 for Class I carriers and US$40,384,263 for Class II carriers. (Smaller carriers were Class III by default.) There are seven Class I freight railroad companies in the United States including two Canadian carriers with subsidiary trackage in the United States: BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway (via its subsidiary Grand Trunk Corporation), Canadian Pacific Railway (via its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation), CSX Transportation, Kansas City Southern Railway, Norfolk Southern Railway, and Union Pacific Railroad. (Mexico's Ferromex and Kansas City Southern de México would qualify as Class I, but do not operate within the United States.) In addition, the national passenger railroad in the United States, Amtrak, would qualify as C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Railroad
In the United States, a regional railroad is a railroad company that is not Class I, but still has a substantial amount of traffic or trackage (and is thus not a short line). The Association of American Railroads (AAR) has defined the lower bound as of track or $40 million in annual operating revenue. (The Class I threshold is $250 million, adjusted for inflation since 1991.) List of regional railroads The following railroads were classified as regional by the AAR in 2007.Association of American RailroadsAbout the Industry: Railroads and States accessed May 2009 References {{Reflist See also * Regional Railroad of the Year *Regional rail Regional rail, also known as local trains and stopping trains, are passenger rail services that operate between towns and cities. These trains operate with more stops over shorter distances than inter-city rail, but fewer stops and faster serv ..., Regionalbahn — terms for intercity passenger services with more stops than an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvert City, Kentucky
Calvert City is a home rule-class city in Marshall County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 2,566 at the 2010 census. History Calvert City was named for Potilla Willis Calvert. He built his home, Oak Hill, in 1860 and around a decade later gave a portion of his land to a new railroad, specifying that a station be built near his home.Rennick, Robert. ''Kentucky Place Names'', p. 46. University Press of Kentucky (Lexington), 1987. Accessed 24 July 2013. That station served as the starting point of the town, which was incorporated on March 18, 1871. The railroad station and post office long favored the shorter Calvert, but the Board on Geographic Names reversed its earlier decision in 1957 and switched to the longer form. By 1896, Calvert City was known as a sundown town, where African Americans were not allowed to reside. By 1908, the rest of Marshall County had also expelled its African American residents. During the Ohio River flood of 1937, Calvert City's busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
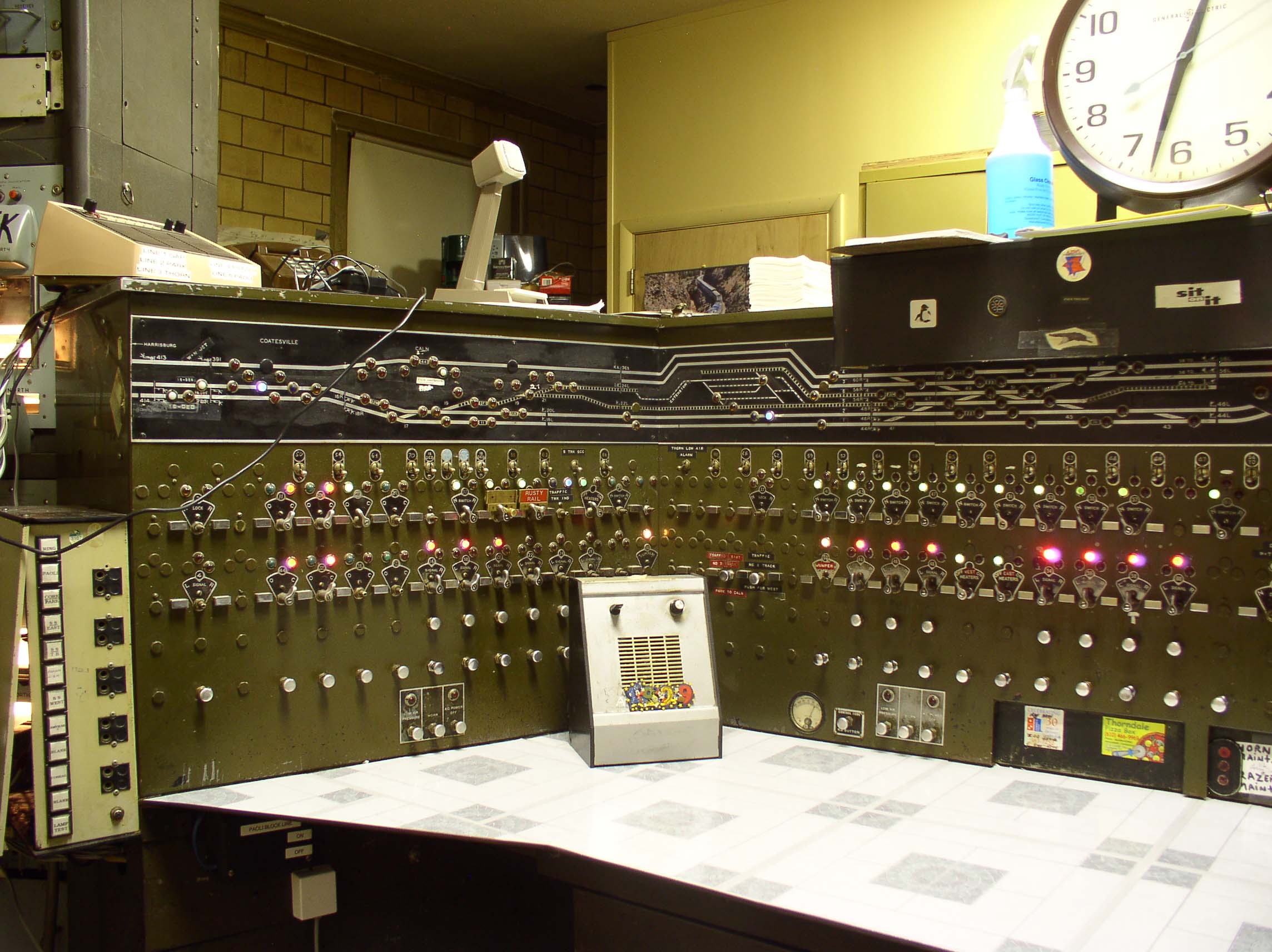
Centralized Traffic Control
Centralized traffic control (CTC) is a form of railway signalling that originated in North America. CTC consolidates train routing decisions that were previously carried out by local signal operators or the train crews themselves. The system consists of a centralized train dispatcher's office that controls railroad interlockings and traffic flows in portions of the rail system designated as CTC territory. One hallmark of CTC is a control panel with a graphical depiction of the railroad. On this panel, the dispatcher can keep track of trains' locations across the territory that the dispatcher controls. Larger railroads may have multiple dispatcher's offices and even multiple dispatchers for each operating division. These offices are usually located near the busiest yards or stations, and their operational qualities can be compared to air traffic towers. Background Key to the concept of CTC is the notion of ''traffic control'' as it applies to railroads. Trains moving in opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |