|
Packet Capture Appliance
A packet capture appliance is a standalone device that performs packet capture. Packet capture appliances may be deployed anywhere on a network, however, most commonly are placed at the entrances to the network (i.e. the internet connections) and in front of critical equipment, such as servers containing sensitive information. In general, packet capture appliances capture and record all network packets in full (both header and payload), however, some appliances may be configured to capture a subset of a network's traffic based on user-definable filters. For many applications, especially network forensics and incident response, it is critical to conduct full packet capture, though filtered packet capture may be used at times for specific, limited information gathering purposes. Deployment The network data that a packet capture appliance captures depends on where and how the appliance is installed on a network. There are two options for deploying packet capture appliances on a networ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
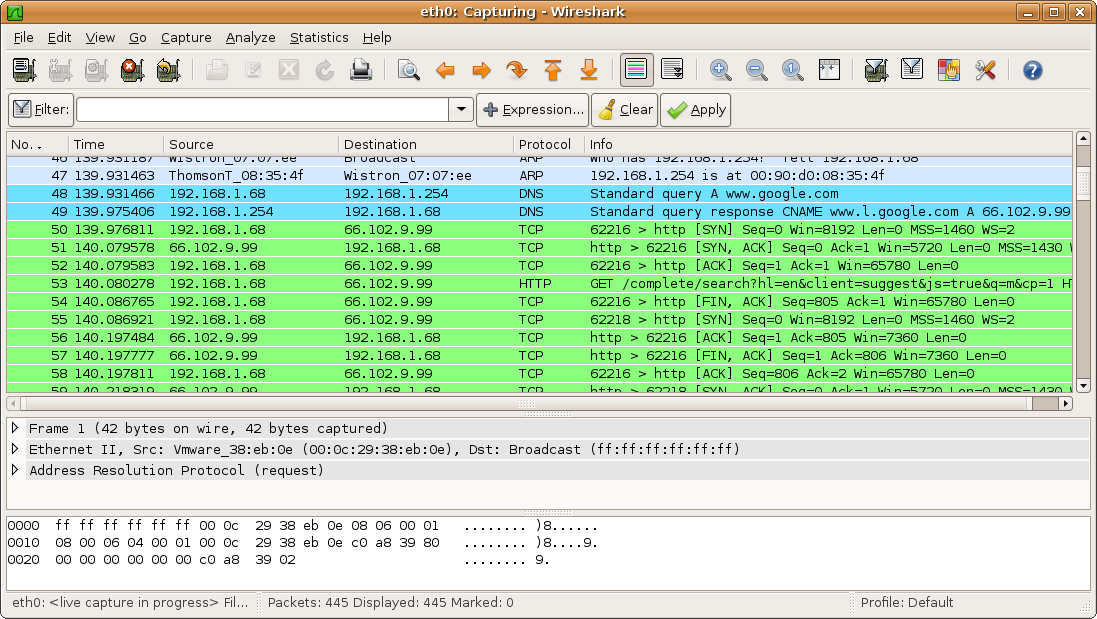
Packet Capture
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encrypt
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random A pseudorandom sequence of numbers is one that appears to be statistically random, despite having been produced by a completely deterministic and repeatable process. Background The generation of random numbers has many uses, such as for rando ... encryption Key (cryptography), key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Sniffer
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Capture
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion Detection
An intrusion detection system (IDS; also intrusion prevention system or IPS) is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. Any intrusion activity or violation is typically reported either to an administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event management (SIEM) system. A SIEM system combines outputs from multiple sources and uses alarm filtering techniques to distinguish malicious activity from false alarms. IDS types range in scope from single computers to large networks. The most common classifications are network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) and host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS). A system that monitors important operating system files is an example of an HIDS, while a system that analyzes incoming network traffic is an example of an NIDS. It is also possible to classify IDS by detection approach. The most well-known variants are signature-based detection (recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Network
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as either , but other representations such as ''true''/''false'', ''yes''/''no'', ''on''/''off'', or ''+''/''−'' are also commonly used. The relation between these values and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or program. It may be physically implemented with a two-state device. The symbol for the binary digit is either "bit" per recommendation by the IEC 80000-13:2008 standard, or the lowercase character "b", as recommended by the IEEE 1541-2002 standard. A contiguous group of binary digits is commonly called a ''bit string'', a bit vector, or a single-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) ''bit array''. A group of eight b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 GbE
10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GE, 10GbE, or 10 GigE) is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10 Gigabit Ethernet defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE. The 10 Gigabit Ethernet standard encompasses a number of different physical layer (PHY) standards. A networking device, such as a switch or a network interface controller may have different PHY types through pluggable PHY modules, such as those based on SFP+. Like previous versions of Ethernet, 10GbE can use either copper or fiber cabling. Maximum distance over copper cable is 100 meters but because of its bandwidth requirements, highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented physical and link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to 1000 Mbit/s. * The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z, and required optical fiber. 802.3z is commonly referred to as 1000BASE-X, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) is knowledge, skills and experience-based information concerning the occurrence and assessment of both cyber and physical threats and threat actors that is intended to help mitigate potential attacks and harmful events occurring in cyberspace. Cyber threat intelligence sources include open source intelligence, social media intelligence, human Intelligence, technical intelligence, device log files, forensically acquired data or intelligence from the internet traffic and data derived for the deep and dark web. In recent years, threat intelligence has become a crucial part of companies' cyber security strategy since it allows companies to be more proactive in their approach and determine which threats represent the greatest risks to a business. This puts companies on a more proactive front - actively trying to find their vulnerabilities and prevents hacks before they happen. This method is gaining importance in recent years since, as IBM estimates, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Forensics
Network forensics is a sub-branch of digital forensics relating to the monitoring and analysis of computer network traffic for the purposes of information gathering, legal evidence, or intrusion detection. Unlike other areas of digital forensics, network investigations deal with volatile and dynamic information. Network traffic is transmitted and then lost, so network forensics is often a pro-active investigation. Network forensics generally has two uses. The first, relating to security, involves monitoring a network for anomalous traffic and identifying intrusions. An attacker might be able to erase all log files on a compromised host; network-based evidence might therefore be the only evidence available for forensic analysis. The second form relates to law enforcement. In this case analysis of captured network traffic can include tasks such as reassembling transferred files, searching for keywords and parsing human communication such as emails or chat sessions. Two systems are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
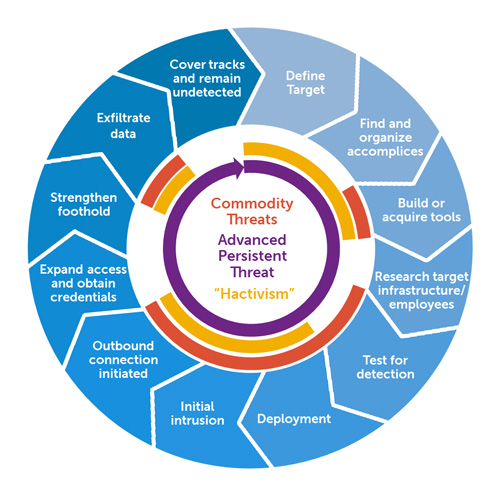
Advanced Persistent Threat
An advanced persistent threat (APT) is a stealthy threat actor, typically a nation state or state-sponsored group, which gains unauthorized access to a computer network and remains undetected for an extended period. In recent times, the term may also refer to non-state-sponsored groups conducting large-scale targeted intrusions for specific goals. Such threat actors' motivations are typically political or economic. Every major business sector has recorded instances of cyberattacks by advanced actors with specific goals, whether to steal, spy, or disrupt. These targeted sectors include government, defense, financial services, legal services, industrial, telecoms, consumer goods and many more. Some groups utilize traditional espionage vectors, including social engineering, human intelligence and infiltration to gain access to a physical location to enable network attacks. The purpose of these attacks is to install custom malware (malicious software). The median "dwell-time", the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAC Address
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Within the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model, MAC addresses are used in the medium access control protocol sublayer of the data link layer. As typically represented, MAC addresses are recognizable as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by hyphens, colons, or without a separator. MAC addresses are primarily assigned by device manufacturers, and are therefore often referred to as the burned-in address, or as an Ethernet hardware address, hardware address, or physical address. Each address can be stored in hardware, such as the card's read-only memory, or by a firmware mechanism. Many network interfaces, however, support changing their MAC address. The address typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |