|
Paata Burchuladze Prize
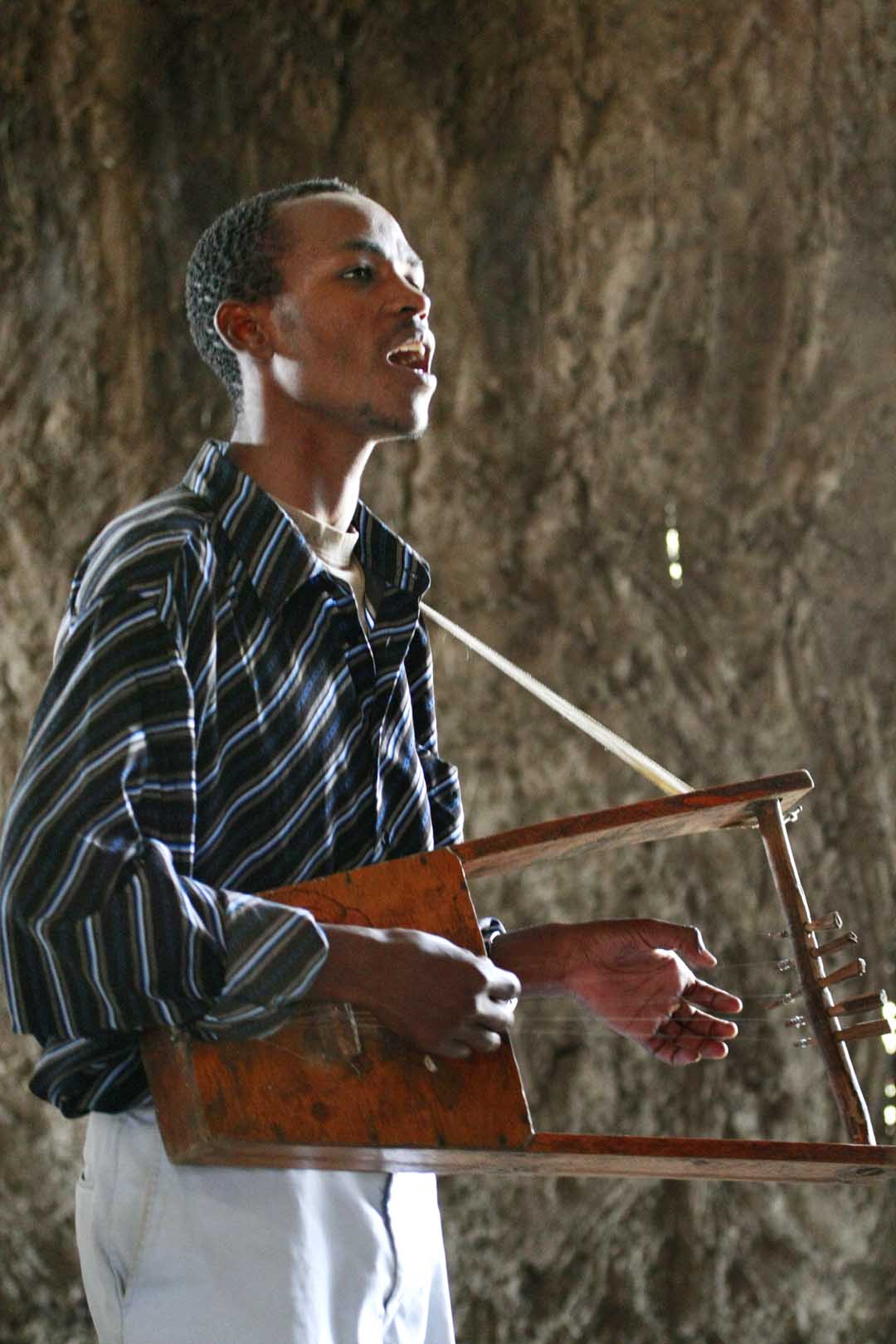
The pluriarc, also called paata, mapu, luku, kissanga, and bow lute is a stringed musical instrument of West Africa West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ..., classified as a type of lute. It has a hollow body and several curved, pliable necks made of reeds. The strings stretch from the necks to the bridge, which stands approximately above the body. The body may be round, rectangular, or triangular, and is usually made of light wood. The top of the body can either be a separate board, bound or nailed to the lower part, or made from the same piece of wood as the rest. A hole may exist on the underside that can be opened or closed to change the timbre. It is played by plucking the strings, which are usually open but sometimes contain a stop. The strings may be plucked with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordophone
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baroque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted. More specifically, the term "lute" can refer to an instrument from the family of European lutes. The term also refers generally to any string instrument having the strings running in a plane parallel to the sound table (in the Hornbostel–Sachs system). The strings are attached to pegs or posts at the end of the neck, which have some type of turning mechanism to enable the player to tighten the tension on the string or loosen the tension before playing (which respectively raise or lower the pitch of a string), so that each string is tuned to a specific pitch (or note). The lute is plucked or strummed with one hand while the other hand "frets" (presses down) the strings on the neck's fingerboard. By pressing the strings on different places of the fingerboard, the player can sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or concerts. Its most common form is triangular in shape and made of wood. Some have multiple rows of strings and pedal attachments. Ancient depictions of harps were recorded in Current-day Iraq (Mesopotamia), Iran (Persia), and Egypt, and later in India and China. By medieval times harps had spread across Europe. Harps were found across the Americas where it was a popular folk tradition in some areas. Distinct designs also emerged from the African continent. Harps have symbolic political traditions and are often used in logos, including in Ireland. History Harps have been known since antiquity in Asia, Africa, and Europe, dating back at least as early as 3000 BCE. The instrument had great popularity in Europe during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Bow
The musical bow (bowstring or string bow, a subset of bar zithers) is a simple string instrument used by a number of South African peoples, which is also found in the Americas via slave trade. It consists of a flexible, usually wooden, stick 1.5 to 10 feet (0.5 to 3 m) long, and strung end to end with a taut cord, usually metal. It can be played with the hands or a wooden stick or branch. It is uncertain if the musical bow developed from the hunting bow, though the San or Bushmen people of the Kalahari Desert do convert their hunting bows to musical use. Types of bow include mouth-resonated string bow, earth-resonated string bow, and gourd-resonated string bow. History There is speculation that the hunting bow may have been used as a musical instrument from as early as circa 13,000 B.C. Henri Breuil surveyed the Trois Frères in France caves and made an engraving that attempted to reproduce a c. 13,000 B.C. cave painting into a black-and-white lithograph engraving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masenqo
The Masenqo ( am, ማሲንቆ; Tigrinya: ጭራ-ዋጣ (ዋጣ) is a single-stringed bowed lute commonly found in the musical traditions of Ethiopia. As with the krar, this instrument is used by Ethiopian minstrels called ''azmaris'' ("singer" in Amharic) . Although it functions in a purely accompaniment capacity in songs, the masenqo requires considerable virtuosity, as azmaris accompany themselves while singing. Construction and design The square or diamond-shaped resonator is made of four small wooden boards glued together, then covered with a stretched parchment or rawhide. The single string is typically made of horse hair, and passes over a bridge. The instrument is tuned by means of a large tuning peg to fit the range of the singer's voice. It may be bowed by either the right or left hand, and the non-bow hand sits lightly on top of the upper part of the string. See also * Music of Ethiopia * Music of Eritrea The music of Eritrea, is a diverse mix of traditional an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gusle
The gusle ( sr-cyrl, гусле) or lahuta ( sq, lahutë) is a single-stringed musical instrument (and musical style) traditionally used in the Dinarides region of Southeastern Europe (in the Balkans). The instrument is always accompanied by singing; musical folklore, specifically epic poetry. The gusle player holds the instrument vertically between his knees, with the left hand fingers on the strings. The strings are never pressed to the neck, giving a harmonic and unique sound. Singing to the accompaniment of the Gusle as a part of Serbia's intangible cultural heritage was inscribed in 2018 on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity of UNESCO. Origin There is no consensus about the origin of the instrument. 6th-century Byzantine Greek historian Theophylact Simocatta ( 630) wrote about "small lyres" brought by the Slavs who settled the Balkans; some researchers believe that this might have been the gusle. Others, such as F. Sachs, believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igil
The ''igil'' ( Tuvan: игил) is a two- stringed Tuvan musical instrument, played by bowing the strings. (It is called "ikili" in Western Mongolia.) The neck and lute-shaped sound box are usually made of a solid piece of pine or larch. The top of the sound box may be covered with skin or a thin wooden plate. The strings, and those of the bow, are traditionally made of hair from a horse's tail (strung parallel), but may also be made of nylon. Like the morin khuur of Mongolia, the igil typically features a carved horse's head at the top of the neck above the tuning pegs, and both instruments are known as the horsehead fiddle. The igil is held nearly upright when played, with the sound box of the instrument in the performer's lap, or braced against the top of the performer's boot. Playing technique involves touching the strings with the nails or fingertips, but without pressing them to the neck. The igil has no frets. The bow is held with an underhand grip. The igil formerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krar
Krar (Amharic: ክራር) is a five-or-six stringed bowl-shaped lyre from Ethiopia and Eritrea. It is tuned to a pentatonic scale. A modern ''Krar'' may be amplified, much in the same way as an electric guitar or violin. The ''Krar'', along with ''Masenqo'' and the ''Washint'', is one of the most widespread musical instruments of the Amhara ethnic group. Role in Amhara society Historical In Amhara society the ''krar'' was viewed as an instrument inspired by the Devil and was therefore inferior, whereas the '' Begena'' was for praising God and seen as sacred. The ''krar'' was used to adulate feminine beauty, to create sexual arousal and to eulogize carnal love. The instrument has been associated with brigands, outlaws and wanderers. Wanderers played the ''krar'' to solicit food, and outlaws played it to sing an Amhara war song called ''Fano''. Contemporary Today, the ''krar'' which used to be the plaything of the Amharas, has become one of the most popular Ethiopian stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ( United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at about million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent. Early history in West Africa included a number of prominent regional powers that dominated different parts of both the coastal and internal trade networks, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West African Musical Instruments
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |