|
PDCD1LG2
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (also known as PD-L2, B7-DC) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PDCD1LG2'' gene. PDCD1LG2 has also been designated as CD273 (cluster of differentiation 273). PDCD1LG2 is an immune checkpoint receptor ligand which plays a role in negative regulation of the adaptive immune response. PD-L2 is one of two known ligands for Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). Structure PD-L2 is a cell surface receptor belonging to the B7 protein family. It consists of both an immunoglobulin-like variable domain and an immunoglobulin-like constant domain in the extracellular region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. PD-L2 shares considerable sequence homology with other B7 proteins, but it does not contain the putative binding sequence for CD28/CTLA4, namely SQDXXXELY or XXXYXXRT. The crystal structure of murine PD-L2 bound to murine PD-1 has been determined. as well as the structure of the hPD-L2/mutant hPD-1 complex. Expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
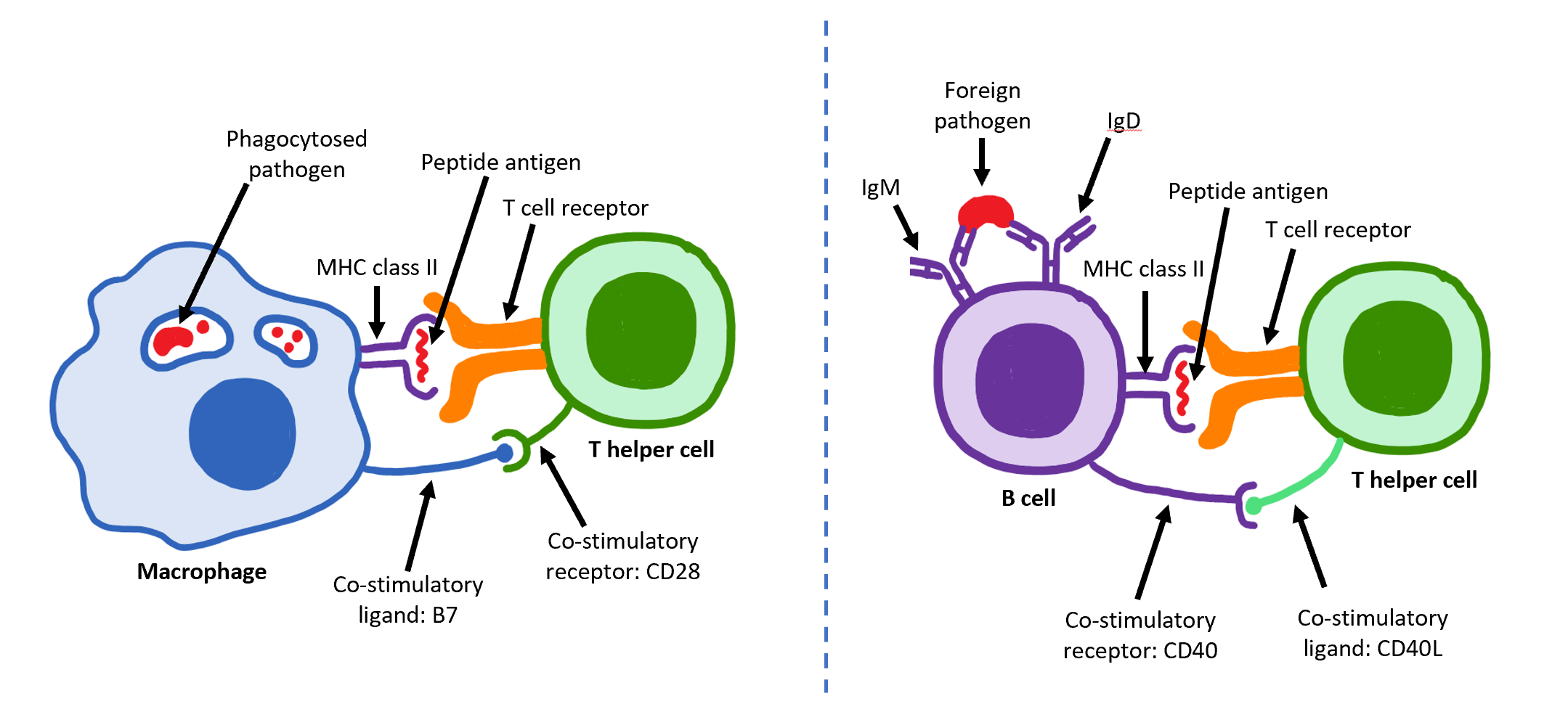
B7 (protein)
B7 is a type of integral membrane protein found on activated antigen-presenting cells (APC) that, when paired with either a CD28 or CD152 (CTLA-4) surface protein on a T cell, can produce a costimulatory signal or a coinhibitory signal to enhance or decrease the activity of a major histocompatibility complex, MHC-T cell receptor, TCR signal between the APC and the T cell, respectively. Binding of the B7 of APC to CTLA-4 of T-cells causes inhibition of the activity of T-cells. There are two major types of B7 proteins: B7-1 or CD80, and B7-2 or CD86. It is not known if they differ significantly from each other. So far CD80 is found on dendritic cells, macrophages, and activated B cells, CD86 (B7-2) on B cells. The proteins CD28 and CTLA-4 (CD152) each interact with both B7-1 and B7-2. Costimulation There are several steps to activation of the immune system against a pathogen. The T-cell receptor must first interact with the Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) surface protein. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein secreted by macrophages, T cells, mast cells, natural killer cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts that functions as a cytokine. The pharmaceutical analogs of naturally occurring GM-CSF are called sargramostim and molgramostim. Unlike granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which specifically promotes neutrophil proliferation and maturation, GM-CSF affects more cell types, especially macrophages and eosinophils. Function GM-CSF is a monomeric glycoprotein that functions as a cytokine—it is a white blood cell growth factor. GM-CSF stimulates stem cells to produce granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and monocytes. Monocytes exit the circulation and migrate into tissue, whereupon they mature into macrophages and dendritic cells. Thus, it is part of the immune/ inflammatory cascade, by which activation of a small number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 4
The interleukin 4 (IL4, IL-4) is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells ( Th0 cells) to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4 in a positive feedback loop. IL-4 is produced primarily by mast cells, Th2 cells, eosinophils and basophils. It is closely related and has functions similar to IL-13. Function Interleukin 4 has many biological roles, including the stimulation of activated B cell and T cell proliferation, and the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. It is a key regulator in humoral and adaptive immunity. IL-4 induces B cell class switching to IgE, and up-regulates MHC class II production. IL-4 decreases the production of Th1 cells, macrophages, IFNγ, and dendritic cells IL-12. Overproduction of IL-4 is associated with allergies. * Inflammation and wound repair Tissue macrophages play an important role in chronic inflammation and wound repair. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, genetic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. RCC occurrence shows a male predominance over women with a ratio of 1.5:1. RCC most commonly occurs between 6th and 7th decade of life. Initial treatment is most commonly either partial or complete removal of the affected kidney(s). Where the cancer has not metastasised (spread to other organs) or burrowed deeper into the tissues of the kidney, the five-year survival rate is 65–90%, but this is lowered considerably when the cancer has spread. The body is remarkably good at hiding the symptoms and as a result people with RCC often have advanced disease by the time it is discovered. The initial symptoms of RCC often include blood in the urine (occurring in 40% of affected persons at the time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is any breast cancer that lacks or show low levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification (i.e. the tumor is negative on all three tests giving the name ''triple-negative''). Triple-negative is sometimes used as a surrogate term for basal-like. Triple-negative breast cancer comprises 15–20% of all breast cancer cases and affects more young women or women with a mutation in the BRCA1 gene than other breast cancers. Triple-negative breast cancers comprise a very heterogeneous group of cancers. TNBC is the most challenging breast cancer type to treat. Hormone therapy that is used for other breast cancers does not work for TNBC. In its early stages, the cancer is typically treated through surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. In later stages where surgery is not possible or the cancer has spread from the initial localised area, treatment i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Nephrectomy.jpg)

