|
PAK5
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK5'' gene. The PAK5 enzyme is one of three members of Group II PAK family of serine/threonine kinases, and evolutionary conserved across species. Discovery The PAK5 was initially cloned as a brain-specific kinase with a predominant expression in brain with a suggested role in neurite growth in neuronal cells. Selectivity of PAK5 signaling was recognized by its ability to stimulate the JNK kinase but not p38 or ERK kinases. Gene and spliced variants The PAK5 gene, the longest among the PAK family, contains a total of 12 exons of which four exons are for 5’-UTR and remaining 8 exons for protein coding(Gene from review). Alternative exon splicing of the PAK5 gene generates three transcripts, and one of the transcript encodes a 719 amino acids long protein(Gene from review). The exon splicing of the murine PAK5 gene generates three transcripts, two of which code an identical 719 amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAK4
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK4'' gene. PAK4 is one of six members of the PAK family of serine/threonine kinases which are divided into group I (PAK1, PAK2 and PAK3) and group II (PAK4, PAK6 and PAK5/7). PAK4 localizes in sub-cellular domains of the cytoplasm and nucleus. PAK4 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling, phenotypic signaling and gene expression, and affects directional motility, invasion, metastasis, and growth. Similar to PAK1, PAK4-signaling-dependent cellular functions also regulate both physiologic and disease processes such as cancer, as PAK4 is overexpressed and/or hyperstimulated in human cancer, at-large. Discovery PAK4, the founding member of Group II PAK member, was cloned and identified by Minden A. and colleagues in 1998 using a PCR-based strategy from a cDNA library prepared from Jurkett cells. Gene and spliced variants The group II PAKs have less coding exons compared with group I PAKs, highlights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior that is inappropriate for a given situation. There may also be sleep problems, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, and difficulties carrying out daily activities. Psychosis can have serious adverse outcomes. As with many psychiatric phenomena, psychosis has several different causes. These include mental illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, sensory deprivation and in rare cases, major depression (psychotic depression). Other causes include: trauma, sleep deprivation, some medical conditions, certain medications, and drugs such as cannabis, hallucinogens, and stimulants. One type, known as postpartum psychosis, can occur after giving birth. The neurotransmitter dopamine is believed to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DISC1
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DISC1'' gene. In coordination with a wide array of interacting partners, DISC1 has been shown to participate in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, neuronal axon and dendrite outgrowth, mitochondrial transport, fission and/or fusion, and cell-to-cell adhesion. Several studies have shown that unregulated expression or altered protein structure of DISC1 may predispose individuals to the development of schizophrenia, clinical depression, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. The cellular functions that are disrupted by permutations in DISC1, which lead to the development of these disorders, have yet to be clearly defined and are the subject of current ongoing research. Although, recent genetic studies of large schizophrenia cohorts have failed to implicate DISC1 as a risk gene at the gene level, the DISC1 interactome gene set was associated with schizophrenia, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machine learning, machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a Heat, hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before in terms of an embryo's need for both interaction with, and freedom within its environment within the womb.) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory processor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Locomotion
Animal locomotion, in ethology, is any of a variety of methods that animal (biology), animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding. There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called Passive locomotion in animals, passive locomotion, e.g., sailing (some jellyfish), Ballooning (spider), kiting (spiders), rolling (some beetles and spiders) or riding other animals (phoresis (biology), phoresis). Animals move for a variety of reasons, such as to find Foraging, food, a Mating system, mate, a suitable microhabitat, or to Escape response, escape predators. For many animals, the ability to move is essential for survival and, as a result, natural selection has shaped the locomotion methods and mechanisms used by moving organisms. For example, Animal migration, migratory animals that travel vast dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
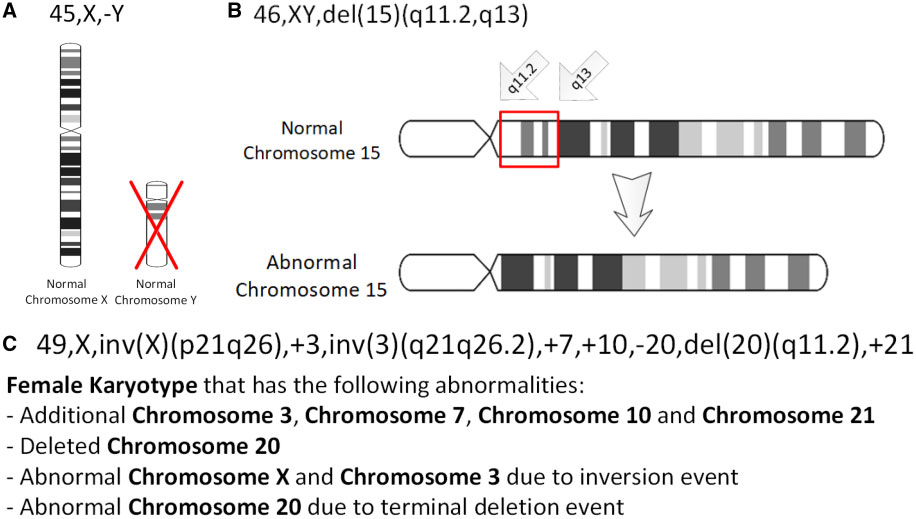
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, organell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Survival
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |