|
P50 (neuroscience)
In electroencephalography, the P50 is an event related potential occurring approximately 50 ms after the presentation of a stimulus, usually an auditory click. The P50 response is used to measure sensory gating, or the reduced neurophysiological response to redundant stimuli. Research has found an abnormal P50 suppression in people with schizophrenia, making it an example of a biological marker for the disorder. Besides schizophrenia, abnormal P50 suppression has been found in patients with traumatic brain injury, recreational drug use, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Paired click test In a paired click test, one auditory click sound will be presented, followed by a second click approximately 500 ms after the first one. The second sound is considered redundant, and so a typical control showing normal sensory gating will produce a reduced response (in wave amplitude) to the second click. The suppression is measured as the percentage of amplitude decrease in response to the seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10-20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called " intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention
Attention is the behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a discrete aspect of information, whether considered subjective or objective, while ignoring other perceivable information. William James (1890) wrote that "Attention is the taking possession by the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought. Focalization, concentration, of consciousness are of its essence." Attention has also been described as the allocation of limited cognitive processing resources. Attention is manifested by an attentional bottleneck, in terms of the amount of data the brain can process each second; for example, in human vision, only less than 1% of the visual input data (at around one megabyte per second) can enter the bottleneck, leading to inattentional blindness. Attention remains a crucial area of investigation within education, psychology, neuroscience, cognitive neuroscience, and neuropsychology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10-20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called " intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P300 (neuroscience)
The P300 (P3) wave is an event-related potential (ERP) component elicited in the process of decision making. It is considered to be an endogenous potential, as its occurrence links not to the physical attributes of a stimulus, but to a person's reaction to it. More specifically, the P300 is thought to reflect processes involved in stimulus evaluation or categorization. It is usually elicited using the oddball paradigm, in which low-probability target items are mixed with high-probability non-target (or "standard") items. When recorded by electroencephalography (EEG), it surfaces as a positive deflection in voltage with a latency (delay between stimulus and response) of roughly 250 to 500 ms. In the scientific literature a differentiation is often made in the P3, which is divided according to time: Early P3 window (300-400 ms) and Late P3 window (380-440 ms). The signal is typically measured most strongly by the electrodes covering the parietal lobe. The presence, magnitude, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Startle Response
In animals, including humans, the startle response is a largely unconscious defensive response to sudden or threatening stimuli, such as sudden noise or sharp movement, and is associated with negative Affect (psychology), affect.Rammirez-Moreno, David. "A computational model for the modulation of the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex". ''Biological Cybernetics'', 2012, p. 169 Usually the onset of the startle response is a startle reflex reaction. The startle reflex is a brainstem reflectory reaction (reflex) that serves to protect vulnerable parts, such as the back of the neck (whole-body startle) and the eyes (eyeblink) and Fight-or-flight response, facilitates escape from sudden stimuli. It is found across many different species, throughout all stages of life. A variety of responses may occur depending on the affected individual's emotional state, body posture, preparation for execution of a motor task, or other activities. The startle response is implicated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
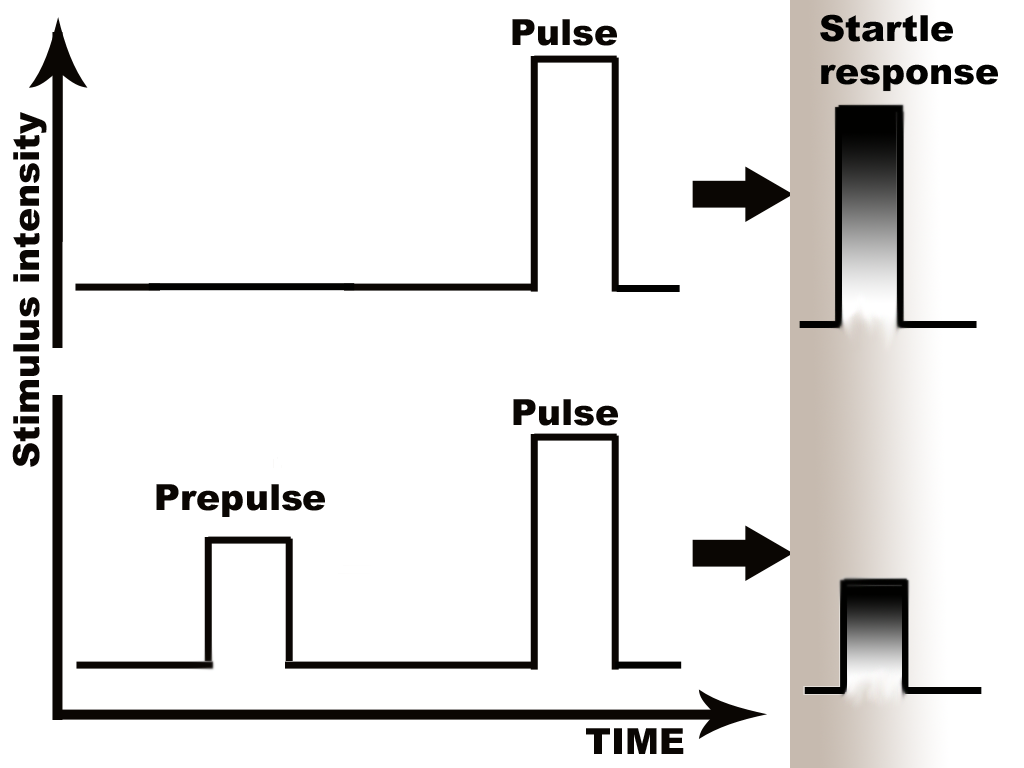
Prepulse Inhibition
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) is a neurological phenomenon in which a weaker prestimulus (prepulse) inhibits the reaction of an organism to a subsequent strong reflex-eliciting stimulus (pulse), often using the startle reflex. The stimuli are usually acoustic, but tactile stimuli (e.g. via air puffs onto the skin) and light stimuli are also used. When prepulse inhibition is high, the corresponding one-time startle response is reduced. The reduction of the amplitude of startle reflects the ability of the nervous system to temporarily adapt to a strong sensory stimulus when a preceding weaker signal is given to warn the organism. PPI is detected in numerous species including mice and humans. Although the extent of the adaptation affects numerous systems, the most comfortable to measure are the muscular reactions, which are normally diminished as a result of the nervous inhibition. Deficits of prepulse inhibition manifest in the inability to filter out the unnecessary information; they h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophenotype
In genetic epidemiology, endophenotype (or intermediate phenotype) is a term used to separate behavioral symptoms into more stable phenotypes with a clear genetic connection. The concept was coined by Bernard John and Kenneth R. Lewis in a 1966 paper attempting to explain the geographic distribution of grasshoppers. They claimed that the particular geographic distribution could not be explained by the obvious and external "exophenotype" of the grasshoppers, but instead must be explained by their microscopic and internal "endophenotype". The next major use of the term was in psychiatric genetics, to bridge the gap between high-level symptom presentation and low-level genetic variability, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms. It is therefore more applicable to more heritable disorders, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Since then, the concept has expanded to many other fields, such as the study of ADHD, addiction, Alzheimer's disease, obesity and cystic fibrosis. Some ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
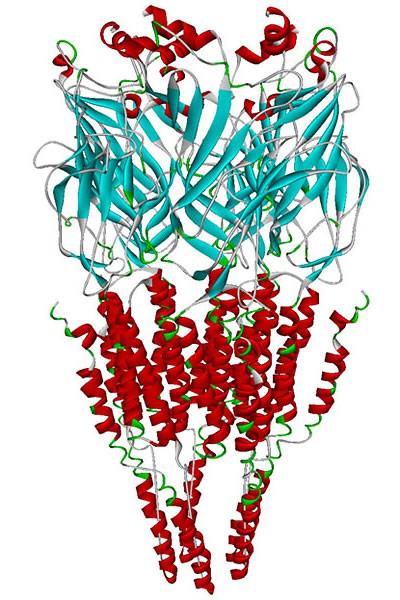
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric .e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability. Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Medical relevance Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude & semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves, square waves or triangle waves ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value (DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Related Potential
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to a stimulus. The study of the brain in this way provides a noninvasive means of evaluating brain functioning. ERPs are measured by means of electroencephalography (EEG). The magnetoencephalography (MEG) equivalent of ERP is the ERF, or event-related field. Evoked potentials and induced potentials are subtypes of ERPs. History With the discovery of the electroencephalogram (EEG) in 1924, Hans Berger revealed that one could measure the electrical activity of the human brain by placing electrodes on the scalp and amplifying the signal. Changes in voltage can then be plotted over a period of time. He observed that the voltages could be influenced by external events that stimulated the senses. The EEG proved to be a useful source in recording brain activity over the ensuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event. Young children are less likely to show distress but instead may express their memories through play. A person with PTSD is at a higher risk of suicide and intentional self-harm. Most people who experience traumatic events do not develop PTSD. People who experience interpersonal violence such as rape, other sexual assaults, being kidnapped, stalking, physical abuse by an intimate partner, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recreational Drug Use
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an intoxicating effect. Generally, recreational drugs are divided into three categories: depressants (drugs that induce a feeling of relaxation and calmness); stimulants (drugs that induce a sense of energy and alertness); and hallucinogens (drugs that induce perceptual distortions such as hallucination). In popular practice, recreational drug use generally is a tolerated social behaviour, rather than perceived as the medical condition of self-medication. However, heavy use of some drugs is socially stigmatized. Many people also use prescribed and controlled depressants such as opioids, as well as opiates and benzodiazepines. Common recreational drugs include caffeine, commonly foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
